Automotive design shapes the cars we drive today. This creative process involves both appearance and function, making sure that vehicles are not only beautiful but also practical to use. The outer look of a car can attract buyers, but the inside design ensures comfort and usability.

Over the years, car design has changed a lot. From classic models of the early 20th century to the sleek, tech-savvy vehicles of today, automotive design adapts to new tech and market trends. Automotive designers work hard to blend style with performance, considering things like safety and efficiency.
Different types of vehicles require different design approaches. A sports car and an SUV will have unique features to meet their specific needs. This variety keeps the field of automotive design exciting and always evolving.
Key Takeaways
- Automotive design combines beauty and function in cars
- Changes in design reflect tech progress and market needs
- Different vehicles need unique design approaches
History and Evolution of Automotive Design

Automotive design has transformed significantly through the years, influenced by technological advancements and visionary designers. From early innovations of metal structures to the modern use of plastic and new materials, the journey of automotive design is fascinating.
Early Innovations and Iconic Designs
In the early 20th century, car designs were simple. Henry Ford’s Model T, introduced in 1908, marked a significant milestone. Cars were boxy and built with metal. This era saw the rise of designers like Bruno Sacco, who shaped many Mercedes-Benz models. The focus was on functionality over style, but it laid the groundwork for future innovations.


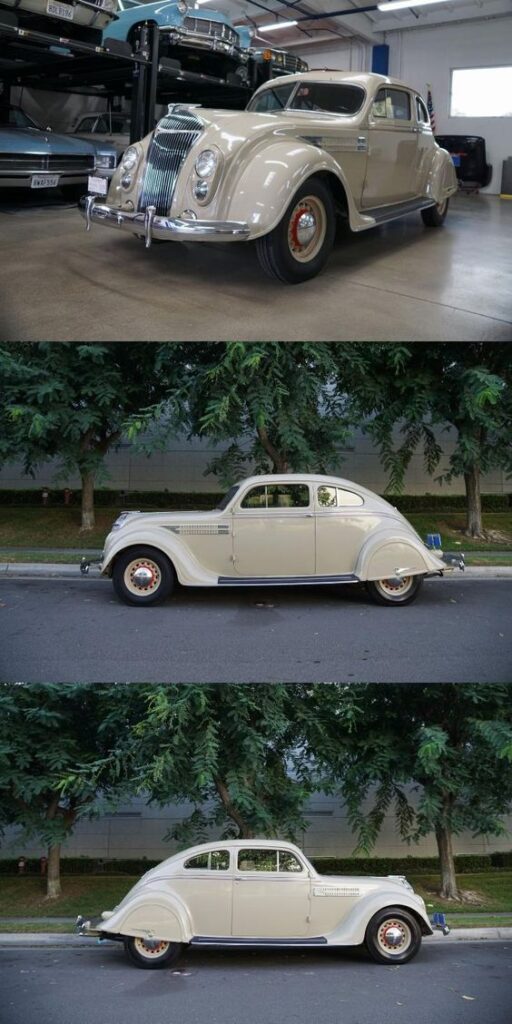
Industrial design began to play a role in the 1930s. The Chrysler Airflow, designed by Carl Breer, introduced aerodynamic principles. The post-World War II period saw a shift towards more stylish and sleek designs. Many of these cars are now considered classics, cherished for their elegant looks.


The Impact of Technology and Engineering on Design
Technological advancements have greatly impacted automotive design. The introduction of plastic in the 1950s allowed for more complex shapes and lighter vehicles. Engineering breakthroughs, such as unibody construction, improved vehicle safety and performance. Designers had more freedom to experiment and innovate.
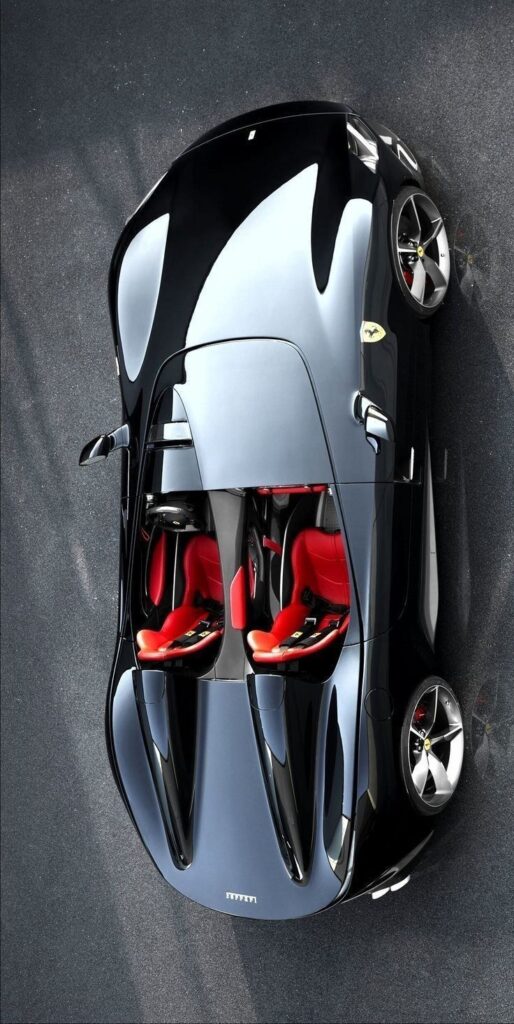


Advancements in automotive engineering continued to shape car design. The 1980s and 1990s saw the integration of computers in design processes. Concepts like computer-aided design (CAD) became standard. This allowed for precise and intricate designs, opening new possibilities in aerodynamics and styling.
Influential Automotive Designers
Several designers have left a lasting impact on the industry. Marcello Gandini, known for his work with Lamborghini, designed iconic models like the Miura and Countach. His bold and futuristic designs have influenced many.


Bruno Sacco shaped the elegant lines of Mercedes-Benz cars in the late 20th century. Ian Callum, with his work at Jaguar, brought a modern take on classic British sports cars. These designers combined artistic vision with engineering excellence, pushing the boundaries of what cars could look like.
Throughout history, automotive design has continuously evolved. It reflects changes in technology, materials, and artistic trends, guided by visionary designers who shape the future.
The Design Process

The design process in automotive design involves several key stages, each integral to creating a successful vehicle. These stages include sketching concepts, modeling both in clay and digitally, and thorough testing.
Concept Development and Sketching
Designers start by developing concepts through sketches. This stage is where creative ideas take form. Sketches may begin as rough outlines but advance to detailed drawings showing different angles of the car.


Artists often use tape drawings on large boards to experiment with proportions. It’s common to use tools like pencils, markers, and digital software like Autodesk Alias. These sketches help visualize the design before more complex steps begin.


Modeling Techniques: From Clay to Digital
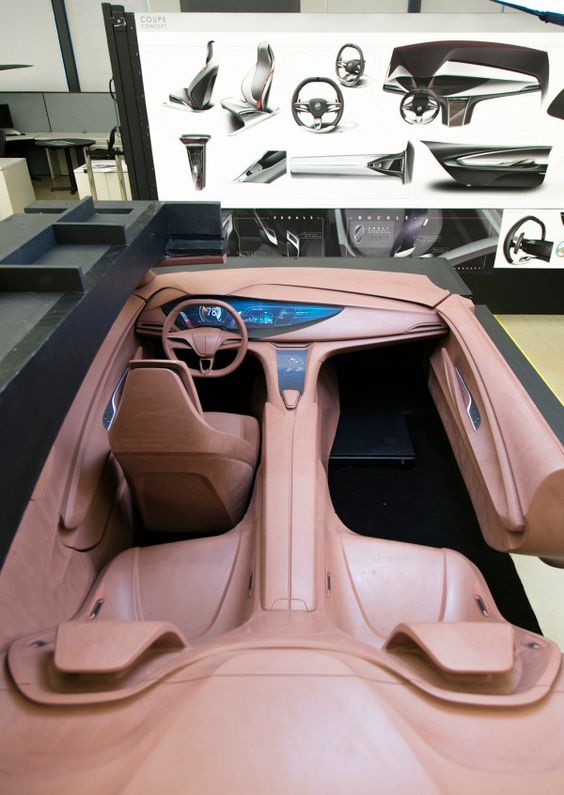


Once sketches are refined, they move to modeling. The first models are often crafted in clay. Clay models allow designers to explore shapes and surfaces in real life. These models are usually built at a scale of 1:4 or full size.


Digital modeling also plays a crucial role. Software such as Autodesk Alias is used to create 3D models. These virtual models offer precise details and modifications are quicker compared to clay. Rendering tools then provide realistic images of the car for review.
Prototyping and Testing
Prototyping is the stage where models become functional vehicles. Engineers build prototypes using parts that match the design to test various functions. This includes assessing performance, safety, and efficiency.
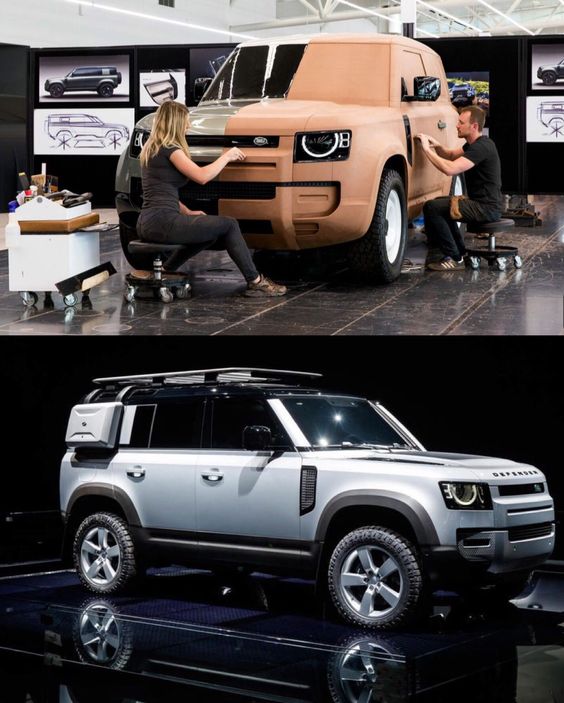


Tests are rigorous and conducted in different environments. Wind tunnels test aerodynamics whereas tracks test handling and speed. These prototypes are crucial for identifying issues and making necessary design adjustments.
Exterior Design Elements

Exterior design is critical in crafting vehicles that not only function well but also captivate. Key aspects include optimizing for speed with aerodynamics, choosing the right materials, considering brand identity through styling, and selecting appropriate wheels and tires.
Aerodynamics and Performance


Aerodynamics is about how air flows over the car. Efficient designs can reduce drag, leading to better fuel efficiency and higher performance.
Examples:
- BMW uses sleek lines and vents to cut through air effortlessly.
- Ferrari incorporates spoilers and diffusers to enhance stability at high speeds.
Improving aerodynamics doesn’t just make cars faster. It helps with fuel economy by reducing wind resistance. The design has to balance aesthetics and functionality, creating a vehicle that looks good and performs well.
Materials and Manufacturing


The choice of materials impacts a car’s weight, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Aluminum, carbon fiber, and high-strength steel are common.
Examples:
- BMW often uses lightweight aluminum for parts like hoods and doors.
- Ferrari uses carbon fiber for its strength-to-weight ratio.
Manufacturing processes are also key. Advanced techniques such as 3D printing and robotics ensure precision and quality in every vehicle. These methods help in producing complex shapes that are both strong and light, contributing to the car’s overall performance and efficiency.
Styling and Brand Identity
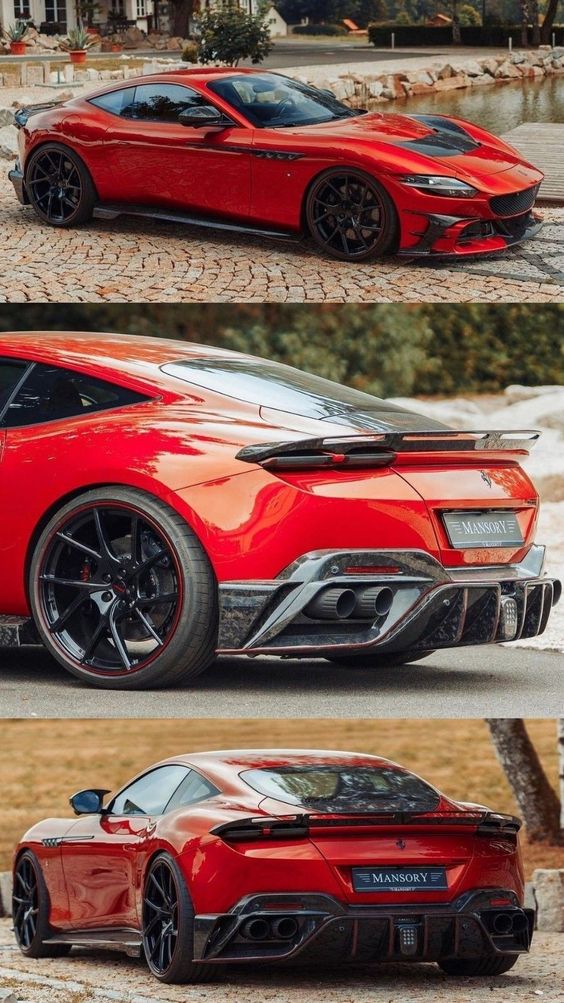


Styling helps distinguish one brand from another and creates emotional connections with customers. Design elements such as grille shape, logo placement, and body lines all contribute.
Examples:
- BMW‘s kidney grille is iconic and instantly recognizable.
- Ferrari uses sleek, aggressive lines that convey speed and luxury.
Brand identity is critical in exterior design. Designers must ensure that each model reflects the company’s ethos and appeals to its target audience. This balance of tradition and innovation is crucial in maintaining a strong brand presence.
Wheels and Tires


Wheels and tires are crucial for aesthetics and performance. They affect handling, ride comfort, and the vehicle’s overall look.
Examples:
- BMW often chooses alloy wheels for a blend of strength and style.
- Ferrari uses specialized tires that can handle high speeds and provide excellent grip.
Tire selection is vital. Performance tires can handle greater speeds and provide better handling, while all-season tires offer versatility. The choice of rims, whether they are polished, painted, or chromed, also adds to the visual appeal and can reflect the overall design philosophy of the vehicle.
Interior Design Considerations

Interior design in automobiles focuses on ergonomics, comfort, materials, technology, and environmental controls. Each aspect plays a crucial role in the experience of the driver and passengers.
Ergonomics and Comfort


Ergonomics ensure that the vehicle is easy to use and comfortable for all occupants. Interior designers carefully position seats, controls, and displays. Adjustable seats, steering wheels, and mirrors are standard. Designers also focus on lumbar support and cushioning. Good ergonomics reduce fatigue and improve safety. Comfort is enhanced by proper insulation, preventing road noise, and vibrations.
Materials and Textiles
The choice of materials and textiles impacts aesthetics and functionality. High-quality fabrics, leathers, and synthetic materials are used for seats and panels. These materials need to be durable, easy to clean, and pleasant to touch. Additionally, they must meet safety standards, such as being flame retardant. The selection of colors and textures also plays a key role in the overall atmosphere of the interior.
Technology Integration
Technology integration is a major focus for interior designers. Infotainment systems, touchscreens, and voice controls are common features. Designers ensure that these technologies are easily accessible and user-friendly. Navigation systems, audio controls, and connectivity options like Bluetooth are standard. Seamless integration of these technologies enhances the driving experience.
Environmental Controls and Lighting


Environmental controls and lighting contribute to the comfort and functionality of the vehicle’s interior. Climate control systems provide cooling and heating. Designers work on efficient air circulation and filtering systems. Proper lighting, including ambient lights and reading lamps, is essential. Adjustable brightness and color options can create a pleasant atmosphere and aid in visibility.
The Role of Automotive Designers

Automotive designers play a key role in shaping the look and functionality of vehicles. They use their skills to craft cars that are both visually appealing and functional for consumers.
Education and Career Paths
To become an automotive designer, one typically needs a degree in industrial design or transportation design. Renowned institutions like the ArtCenter College of Design in Pasadena, California, are highly regarded in the field. Many designers start as interns or junior designers, gradually advancing to roles like chief designer.
Education Requirements:
- Degree in Industrial Design or Transportation Design
- Courses in Engineering and Art
- Proficiency in CAD software
Career Progression:
- Internships
- Junior Designer
- Senior Designer
- Chief Designer
Key Responsibilities and Challenges
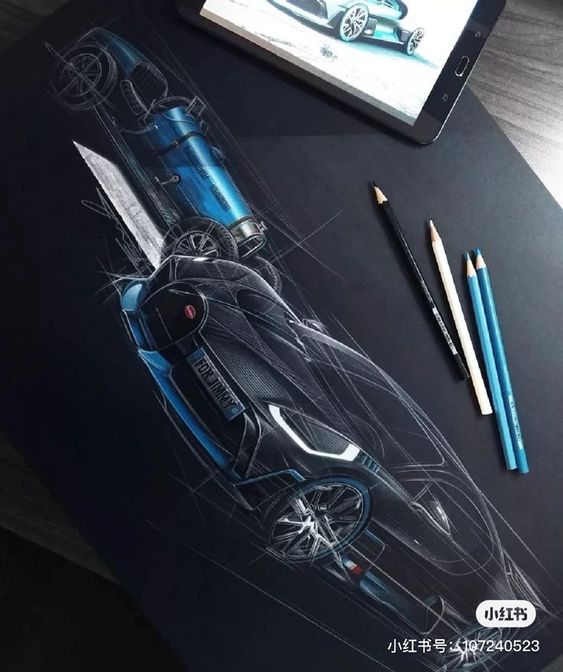
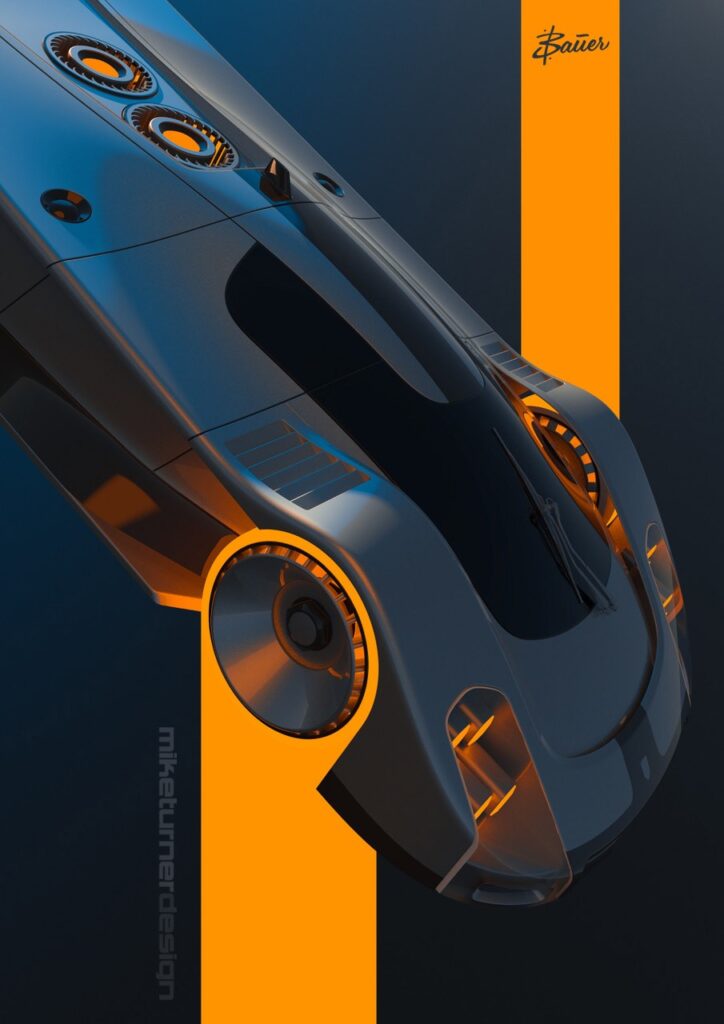


Automotive designers are responsible for drawing and modeling new car designs. They need to balance aesthetics with practical aspects like aerodynamics and safety. One of the main challenges they face is integrating new technologies without compromising the car’s overall look.
Responsibilities:
- Sketching car designs
- Creating 3D models
- Working on both interior and exterior aesthetics
Challenges Include:
- Balancing form and function
- Complying with safety regulations
- Keeping up with technological advances
Collaboration with Engineers and Manufacturers
Designers often work closely with engineers and manufacturers to bring their concepts to life. They ensure that their designs can be feasibly manufactured without sacrificing quality or design integrity. This collaboration is crucial for the successful roll-out of new vehicles.
Collaboration Tasks:
- Regular meetings with engineers
- Adjusting designs based on manufacturing feedback
- Prototype testing and refinement
Key Players:
- Design Teams
- Engineers
- Manufacturing Departments
Effective communication and mutual respect between these teams are essential for delivering vehicles that meet consumer expectations and company standards.
Global Influence and Market Trends

Automotive design is shaped by regional hubs, evolves with consumer preferences, and increasingly focuses on sustainability.
Major Automotive Design Hubs
United States: Detroit is a leading center for automotive engineering and design. Companies like General Motors, Ford, and Stellantis have their headquarters here. The focus is often on large vehicles like trucks and SUVs, reflecting American consumer preferences.
Europe: Home to luxury brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi. European design emphasizes performance and elegance. Cities like Stuttgart and Munich are significant hubs.
Asia: Japan and South Korea lead in this region. Companies like Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda focus on reliability and innovation. Cities like Tokyo and Seoul are central to automotive and transportation design.
Adapting to Consumer Preferences and Market Demands
United States Preferences: Consumers often favor large, powerful vehicles. Manufacturers prioritize comfort and advanced technology.


European Preferences: Demand tends toward smaller, fuel-efficient cars. There is a strong interest in premium and luxury vehicles with high performance.
Asian Preferences: In markets like Japan, there is a demand for compact and efficient cars due to limited space and urban environments. South Korea sees a rise in electronic and smart features.
Global Trends: Increasing interest in electric and hybrid vehicles. Consumers value technology integration, such as connectivity and autonomous features.
Sustainability and Future Directions


Focus Areas: Manufacturers are investing in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid technology to reduce emissions. Sustainable materials are being used in automotive design, such as recycled plastics and eco-friendly fabrics.
Legislation: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions regulations, pushing companies to innovate in cleaner technologies.
Future Insights: The industry is moving towards autonomous driving, smart infrastructure, and shared transportation solutions. Companies are also exploring the use of AI in design and production processes.
Economic Impact: Shifts in consumer demands and regulatory pressures are influencing market dynamics and investment priorities in the automotive sector.
Design in Different Vehicle Categories

Automotive design varies significantly across different types of vehicles, such as passenger cars, sports cars, motorcycles, and trucks. Each category addresses specific needs and aesthetics, from comfort and style to performance and functionality.
Passenger Cars and Luxury Vehicles
Design in passenger cars emphasizes comfort, safety, and fuel efficiency. Passenger cars often feature spacious interiors, intuitive driver interfaces, and modern entertainment systems. They prioritize comfort and functionality to suit family use or daily commuting.
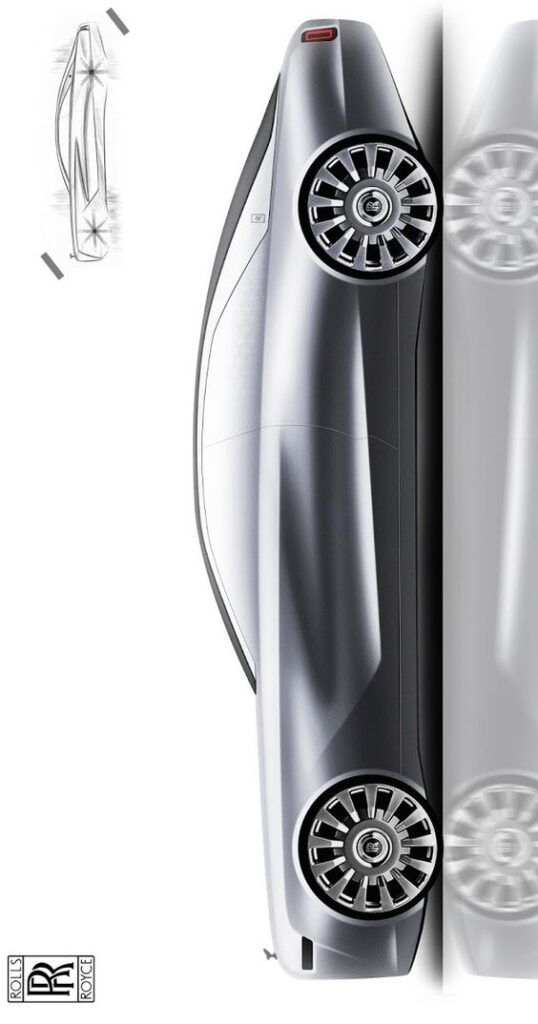
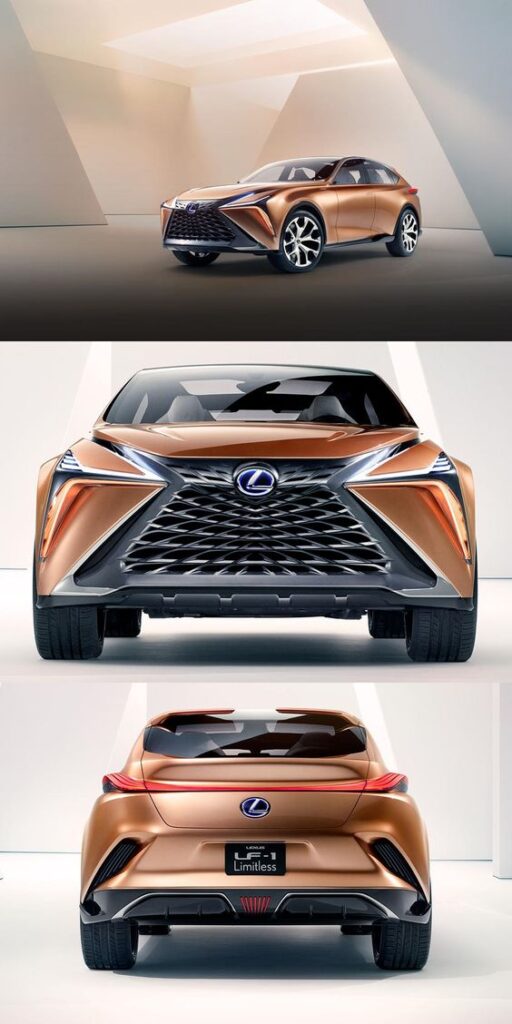


Luxury vehicles elevate these aspects further with high-end materials, advanced technology, and superior craftsmanship. They often include plush seating, enhanced sound systems, and cutting-edge safety features. The exterior design is typically sleek and elegant, reflecting the vehicle’s premium status. Aesthetics play a key role, making the car a symbol of status.
Sports Cars and Performance-Focused Design
Sports cars focus on performance and speed. Their design prioritizes aerodynamics, lightweight materials, and powerful engines. Features like low ground clearance, streamlined shapes, and aggressive lines are common. These elements enhance the car’s agility and performance on the road.
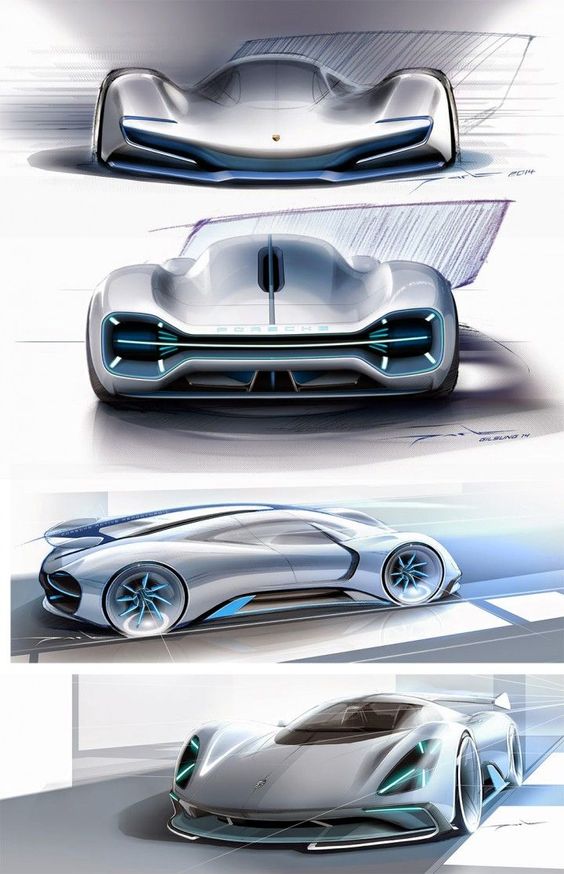


Interior design in sports cars is often minimalistic, concentrating on essential controls and a driver-centric layout. Emphasis on materials like carbon fiber and aluminum helps reduce weight. The aesthetics are bold and striking, aligning with the car’s high-performance nature. Every aspect is engineered to deliver an exhilarating driving experience.
Motorcycles, Trucks, and Alternative Transport


Motorcycles offer unique design challenges and opportunities. They require a balance of performance, safety, and maneuverability. Key features include exposed frames, ergonomic seating, and powerful engines. Motorcycles often emphasize a raw, mechanical aesthetic that appeals to riders.
Trucks are designed for durability and functionality. This includes robust frames, high torque engines, and large cargo spaces. Trucks often incorporate rugged styling to reflect their utility purpose. Interior designs prioritize practicality with features like spacious cabins and multiple storage options.
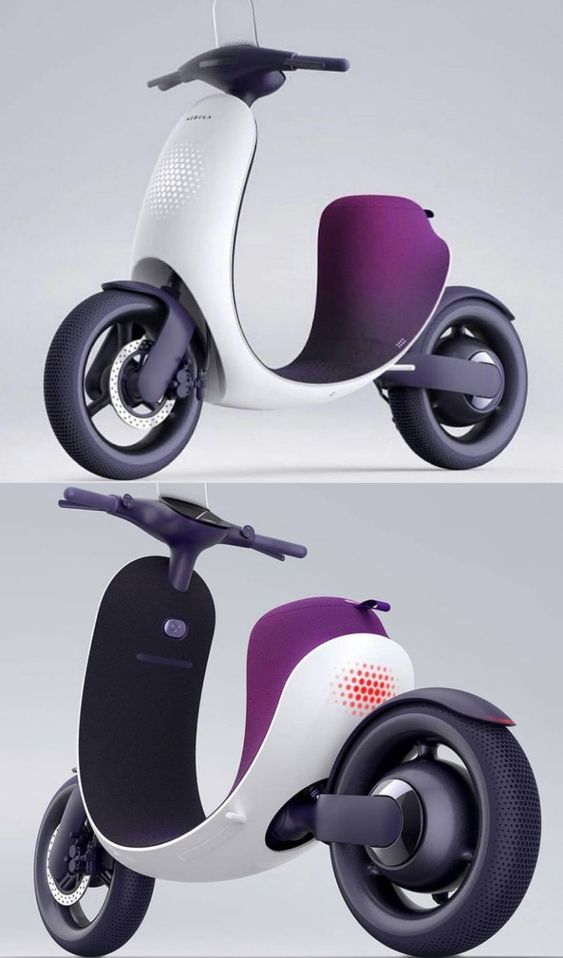
Alternative transport methods, such as electric scooters and hybrids, focus on eco-friendly design. These vehicles prioritize efficiency and sustainability. Sleek, modern designs with lightweight materials are common. Emphasis on battery life and energy efficiency is essential. Their aesthetics often reflect an innovative and futuristic appeal.
Frequently Asked Questions

Automotive design is a complex field, involving qualifications, tools, education, career paths, salaries, and trends. Each aspect contributes significantly to the expertise required in this industry.
What qualifications are required to become an automotive designer?
To become an automotive designer, individuals typically need a bachelor’s degree in industrial design, automotive design, or mechanical engineering. Additionally, creativity, a strong portfolio, and an understanding of design principles are essential. Internships and work experience can also be very helpful.
Which software tools are commonly used in the automotive design industry?
Common software tools include Autodesk Alias for 3D modeling, Adobe Photoshop for rendering and sketches, and CATIA for engineering design. Rhino, SolidWorks, and Blender are also popular for various stages of the design process.
Are there specific schools or programs renowned for automotive design?
Some renowned schools for automotive design are the College for Creative Studies in Detroit, ArtCenter College of Design in California, and the Royal College of Art in London. These programs are well-respected for their comprehensive courses and industry connections.
How does one pursue a career in automotive design?
Starting with a degree in a relevant field, building a strong portfolio, and gaining experience through internships are key steps. Networking and staying updated on industry trends are also important. Many automotive designers begin their careers in related fields, such as industrial design.
What is the typical salary range for an automotive design engineer?
The typical salary range for an automotive design engineer varies by experience and location, but generally falls between $60,000 and $100,000 annually. Top designers at major companies can earn significantly more.
What are the latest trends influencing automotive design?
Current trends include the move towards electric vehicles, incorporating advanced technology like AI and autonomous driving, and a focus on sustainability. Designers are also exploring new materials and innovative manufacturing processes to create lighter, more efficient vehicles.
- 973shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest973
- Twitter0