Car design enhancement represents a pivotal area in automotive engineering, marrying aesthetics with functionality to deliver vehicles that not only capture the eye but also provide improved performance and user experience. Over the years, the evolution of car design has been shaped by a host of factors including advancing technology, consumer preferences, and an increasing focus on sustainability.

The role that technology plays in car design today is transformative. Innovations in materials science, aerodynamics, and automotive software development contribute to cars that are safer, more efficient, and more pleasurable to drive. These design enhancements also reflect a relentless pursuit of sustainability, with manufacturers striving to reduce emissions and fuel consumption through smarter design choices.


Collaboration across disciplines is key to today’s car design enhancements. Designers, engineers, marketers, and customers are contributing to a feedback loop that propels the continuous improvement of automotive design. From initial sketches to sophisticated 3D models, and from conceptual designs to road-ready vehicles, the journey of car design is an iterative process that seeks to balance creativity with practicality.
Key Takeaways
- Car design enhancement is driven by the integration of aesthetic appeal with advanced functionality.
- Technological advancement and sustainable practices are central to the modern car design process.
- Ongoing collaboration and iteration in design development play crucial roles in delivering enhanced vehicles to the market.
Evolution of Car Design

Throughout the history of automobiles, the design has constantly evolved, reflecting technological advancements and consumer preferences. This evolution has been marked by significant milestones and continues today with modern design trends that leverage the latest innovations.
Historical Milestones


The car design landscape was first transformed with the introduction of the Model T by Ford in 1908, which established the moving assembly line as a standard for mass production, shaping the industry’s approach to car manufacturing. In the decades that followed, key innovations such as the use of aerodynamics in the 1930s by brands such as Bugatti and the introduction of monocoque chassis in the 1960s by Lotus transformed car design by enhancing performance and safety.
| Decade | Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1900s | Assembly Line | Standardized mass production |
| 1930s | Aerodynamics | Increased performance |
| 1960s | Monocoque Chassis | Enhanced safety and rigidity |

Modern Automotive Design Trends
In recent years, car design has focused on sustainability and technology. Electric vehicles (EVs), led by companies like Tesla, have seen significant advancements, with design elements such as battery placement lowering the car’s center of gravity and improving handling.


The integration of autonomous technology has also dictated changes in car interiors, optimizing space for new experiences as drivers become passengers.
- Sustainability Focus: Materials derived from renewable sources are being used to reduce environmental impact.
- Technology Integration: Dashboard designs incorporate touchscreens and digital interfaces for enhanced connectivity and control.
The Role of Technology in Car Design

Advancements in technology have revolutionized car design, enhancing functionality and safety through tools like virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and predictive modeling. These innovations directly impact the efficiency of prototyping, the capabilities of predictive analytics, and the sophistication of driver assistance systems.
Virtual Reality in Prototyping


Virtual reality (VR) transforms the prototyping process by allowing designers and engineers to create and interact with 3D models before any physical prototype is built. This method streamlines the development stage, reducing time and cost. For example, BMW utilizes VR to simulate vehicle interiors, enabling a rapid iteration of design options and ergonomics assessment. With VR headsets such as the Oculus Rift, designers can inspect aspects of car designs in a fully immersive environment, enhancing decision-making accuracy and speed.


AI and Predictive Modeling
Artificial Intelligence (AI), when paired with predictive modeling, enables designers to anticipate and respond to potential design impacts before they arise. Automotive companies employ machine learning algorithms to optimize vehicle aerodynamics and fuel efficiency. By inputting various design parameters into AI systems, they can simulate and analyze countless scenarios in a fraction of the time it would take humans. Ford, for example, uses AI to assess and predict the outcomes of different engineering choices, leading to more efficient designs and better performance vehicles.
Driver Assistance Systems


Driver assistance systems have greatly improved in accuracy and capability through the integration of advanced sensors and intelligent software. These systems, which include features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automated emergency braking, rely heavily on the precise functioning of AI. Tesla’s Autopilot and General Motors’ Super Cruise are instances where AI processes data from various in-vehicle sensors to help ensure safety and support drivers. As technology evolves, these systems are constantly refined to reduce human error and enhance road safety.
Enhancing User Experience

Improved car design directly contributes to a user’s comfort, ease of use, and overall satisfaction. Manufacturers focus on ergonomics and personal touches to elevate the driving experience.
Ergonomics and Functionality
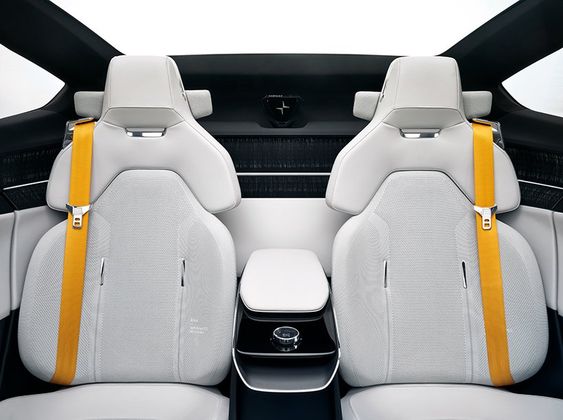


Manufacturers strategically design car interiors to enhance the functionality for the user. They consider the placement and operation of knobs, buttons, and levers to ensure they are intuitive and within easy reach for drivers of all sizes. The use of adjustable seats and steering wheels allows for a more comfortable driving position, reducing fatigue on long journeys.
- Steering Wheel: Telescoping design for optimal driver reach and comfort.
- Pedals: Adjustable for users with varying leg lengths.
- Seats: Contoured with lumbar support to minimize back strain.
- Controls: Strategically placed to minimize driver distraction.
Customization and Personalization
Car manufacturers offer a suite of options that allow users to personalize their vehicles, making each car unique to its owner. Technology integration is a key aspect, with infotainment systems that support customization from wallpaper to widget arrangement.
- Interior Themes: Users can choose from various colors and materials.
- Ambient Lighting: Adjustable lighting colors and intensities to suit personal preference.
- Infotainment Settings: Personal profiles for seat adjustments, climate control, and entertainment preferences.
Sustainability and Efficiency

Sustainable car design focuses on minimizing environmental impact while enhancing vehicle efficiency. It involves the use of eco-friendly materials and the development of advanced propulsion systems that reduce fuel consumption or eliminate it altogether.
Eco-Friendly Materials
The automotive industry increasingly employs materials that have a reduced carbon footprint. Bioplastics, for instance, are derived from renewable sources like sugarcane or corn starch and are used in car interiors to replace conventional plastics. The lightweight nature of these materials also contributes to overall vehicle efficiency by reducing weight, which in turn decreases fuel consumption.


Another sustainable choice are recycled materials. They come from post-consumer products or industrial scrap and are repurposed for use in vehicles. Recycled steel, aluminum, and rubber are regularly integrated into new car designs. For example:
- Steel: Parts of the chassis and body panels
- Aluminum: Engine components and wheels
- Rubber: Tires and sealing
Fuel Efficiency and Electric Vehicles
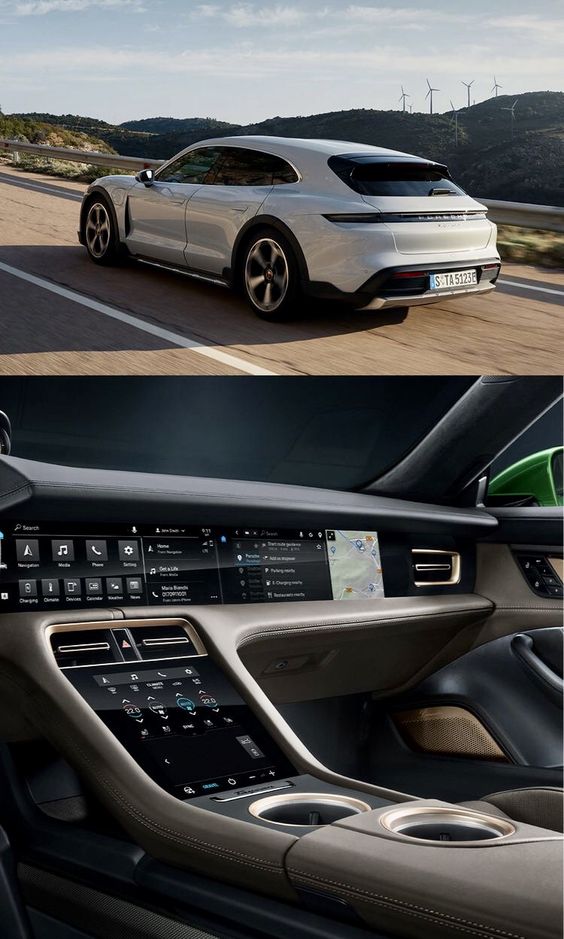


Modern vehicles have made significant strides in fuel efficiency by utilizing advanced technologies. Automobiles now often feature direct fuel injection, turbocharging, and advanced aerodynamic designs that reduce drag. These improvements help cars burn fuel more completely and move through the air with less resistance, thereby enhancing fuel economy.
Electric vehicles (EVs) take the concept of efficiency to the next level by foregoing fuel altogether. Here’s a comparative look at electric vs. traditional propulsion systems:
| Aspect | Electric Vehicles | Traditional Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High (electric motors convert more than 60% of electrical energy into wheel power) | Lower (internal combustion engines convert only about 20% of fuel energy into wheel power) |
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe emissions | Greenhouse gases and pollutants emitted |
| Fuel | Electricity (often sourced from renewable energy) | Gasoline or Diesel (fossil fuels) |
Manufacturers are optimizing the efficiency of EVs by improving battery technology and making advancements in power electronics, which manage the flow of electrical energy in the vehicle. The goal for EVs is not just zero emissions, but also maximized range and efficiency.
Collaborative Efforts in Car Design

Collaborative efforts are reshaping the landscape of car design, with industry partnerships and community-based initiatives playing pivotal roles.
Industry Partnerships
Industry collaborations often result in a fusion of expertise from various automotive sectors, which is imperative for innovation. General Motors (GM), as a case in point, has formed alliances with technology companies to introduce features like advanced infotainment systems and autonomous driving. These partnerships leverage GM’s manufacturing prowess with cutting-edge tech from industry specialists.
- Cross-Industry Alliances:
- Technology Providers: Integration of new software and user interface designs.
- Supply Chain Contributors: Co-development of unique materials for enhanced performance.
Such strategic partnerships accelerate development and refine vehicle design, while sharing costs and risks among entities.
Community-Based Design Initiatives
Community engagement initiatives are becoming a cornerstone in car design, allowing manufacturers to gain insight directly from end users. GM has sought to involve customers through social media platforms and design contests to gather feedback and ideas on vehicle aesthetics and functionality.
- Community Feedback Channels:
- Social Media Polls & Surveys: Direct input on design elements.
- Design Contests: Innovation through crowdsourcing and rewarding community input.
These initiatives lead to cars that reflect consumer preferences and address real-world usability, aligning product design with market expectations.
From the Garage to the Road

Before a vehicle makes its journey from the concept to the consumer, it goes through a rigorous design and development process. Each phase of this transformation involves extensive planning and revision to ensure the final product meets market demands and safety standards.
The Tuning Culture


Car enthusiasts often begin the customization of vehicles in their own garages. This tuning culture focuses on enhancing a car’s performance and aesthetic qualities to reflect the individuality of the owner. Many innovations in car design originate from this grassroots level, with modifications including:
- Engine Tuning: Adjustments to the engine control unit (ECU) to improve efficiency and power.
- Suspension Modifications: Upgrades to the suspension system for better handling and stability.
- Aesthetics: Custom paint jobs, body kits, and interior modifications to create a unique look.
Product Development Cycle
The transformation from an abstract design in a garage to a mass-produced model on the road involves a complex product development cycle. This cycle consists of a series of detailed and iterative stages:
- Conceptualization: Ideas are generated and an initial design is established.
- Design Refinement: Engineers use computer-aided design (CAD) tools to refine the vehicle’s specifications.
- Prototyping: Functional prototypes are created for real-world testing.
- Testing and Validation: Prototypes undergo various tests to ensure safety, reliability, and performance.
- Production Planning: A strategy is developed for mass production, considering costs and logistics.
- Manufacturing: The vehicle is finally assembled using efficient production lines.
- Quality Control: Rigorous inspections are performed to assure the vehicle meets all standards and regulations.
Throughout this process, feedback loops and adjustments ensure the final product is optimized for consumer satisfaction before hitting the road.
Marketing and Selling Enhanced Designs

In the competitive automotive industry, effectively marketing and selling enhanced car designs is crucial. It is essential for manufacturers to convey the value of their innovations and implement strategic pricing.
Building a Brand Around Innovation
Manufacturers must highlight their advances in technology and design to build a brand associated with innovation. They should create compelling narratives around their enhanced designs to engage potential buyers. Advertising campaigns can utilize various media platforms with targeted messaging to showcase unique features. For example, they may post videos demonstrating new car functionalities on social media to generate buzz and encourage viewers to subscribe to their updates.
Pricing Strategies for Enhanced Vehicles
The price of an enhanced vehicle must reflect its value while remaining competitive. To determine optimal pricing, companies should conduct thorough market research to understand consumer willingness to pay for new features. Here’s a simplified approach to pricing strategy in table format:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost-Plus Pricing | Set a price based on production costs plus a fair profit margin. |
| Value-Based Pricing | Price vehicles according to the perceived value to the consumer. |
| Competitive Pricing | Align prices with those of competitors offering similar features. |
| Dynamic Pricing | Adjust prices based on demand, seasonality, and market trends. |
By aligning the price with the perceived benefits of the enhanced design, manufacturers can position their vehicles appealingly while justifying the cost to consumers.
Design Iteration and Improvement

The process of enhancing car design revolves around a cycle of gathering user feedback and implementing design changes iteratively. This continual refinement ensures the vehicle meets consumer needs and stays competitive.
Gathering User Feedback
Manufacturers solicit feedback through surveys, focus groups, and real-world testing. This feedback is then analyzed, often using quantitative methods such as satisfaction rates, and qualitative insights like user experience narratives. They highlight what users enjoy and what could be improved.
- Surveys: Rate features from 1-5; list common complaints.
- Focus Groups: Collect diverse opinions; observe reactions to design elements.
- Testing: Record performance data; gather user interactions.
Implementing Iterative Design Changes


Once feedback is gathered, manufacturers apply it to produce iterative design enhancements. They prioritize changes based on feedback urgency and feasibility, resulting in prototypes that undergo rigorous testing.
Prioritization:
- High Priority: Safety concerns, widespread criticism.
- Medium Priority: Ergonomics, fuel efficiency.
- Low Priority: Aesthetic preferences.
Prototyping and Testing:
- First Iteration: Address urgent issues, test internally.
- Subsequent Iterations: Refine aesthetics, test user experience.
Through iteration, the car design evolves to better meet user requirements and adapt to new market trends. This process remains central to car design enhancement.
Frequently Asked Questions

This section addresses common queries regarding the tools and strategies involved in car design improvements, costs, trends, and terminology within the industry.
What software is most effective for enhancing the look of a car’s exterior and interior?
When improving a vehicle’s design, software like Autodesk Alias, Rhino3D, and Adobe Photoshop are industry standards. These programs offer a range of tools for detailed modeling and rendering of car exteriors and interiors.
How can I ensure the best outcome when enhancing my car’s design?
To ensure high-quality results, one should focus on coherence between form and function, adhere to ergonomic principles, and use high-quality materials. Collaborating with experienced design professionals is also recommended to bring refined improvements to fruition.
What factors influence the cost of implementing a new design on a vehicle?
The cost factors include complexity of the design, selection of materials, labor required, and the reputation of the design studio or professional engaged. Customizations that require extensive manual labor or high-end materials typically incur higher costs.
How can interior aesthetics be improved in a functional yet stylish manner?
Interior aesthetics can be improved by using materials that blend luxury and practicality, such as high-grade leather or advanced synthetic fabrics. Ergonomic upgrades, ambient lighting, and integrating user-friendly technology can also elevate the vehicle’s interior functionally and visually.
What are the latest trends in car design modifications?
Current trends in car design modifications include minimalist interiors, incorporation of digital interfaces, sustainable materials, and aerodynamic exteriors that enhance performance. Electrification has also spurred innovative battery placements that affect overall vehicle design.
What is the commonly used terminology for professional car customization?
Common terms include ‘aftermarket parts’, which refer to any part added after the vehicle leaves the factory; ‘OEM’, standing for Original Equipment Manufacturer parts; ‘tuning’, relating to adjustments made for improved performance; and ‘restyling’, which pertains to significant aesthetic changes made to a vehicle’s appearance.
- 2.3Kshares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest2.3K
- Twitter0