Design Thinking is a dynamic and creative problem-solving methodology that has gained traction in recent years. It encourages innovative solutions by focusing on understanding the user’s needs, redefining problems, and brainstorming ideas. At its core, Design Thinking is about putting people first and crafting user-centric solutions.
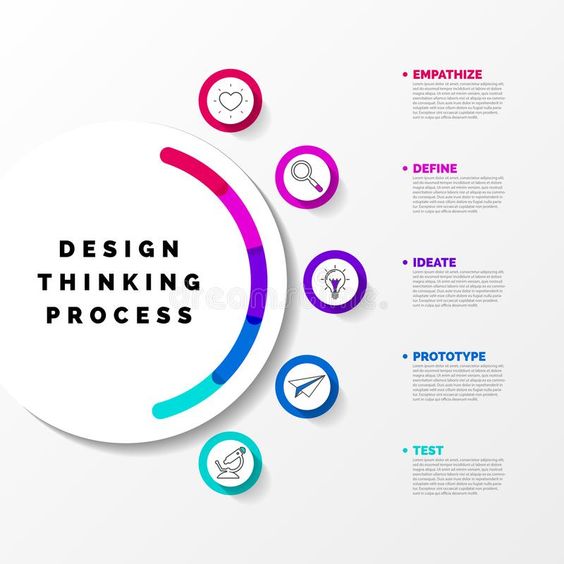
The process is typically broken down into five phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product or solution is effective and meets the user’s expectations. This structured yet flexible approach allows for continuous iteration and improvement, making it highly adaptable to various fields.
Companies and individuals alike have embraced Design Thinking for its practical applications and ability to foster creativity. By leveraging tools and techniques specific to this methodology, they can navigate complex challenges with agility and innovation. Whether in education, product development, or service design, Design Thinking proves to be a versatile and powerful tool.
Key Takeaways
- Design Thinking focuses on user-centric problem-solving.
- The process includes five essential phases for structured innovation.
- It is adaptable for various fields and promotes creative solutions.
Fundamentals of Design Thinking

Design thinking centers on creative problem solving, with a strong emphasis on empathy, innovation, and an iterative process. It involves understanding user needs deeply and provides a holistic approach to design.
What Is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a methodology focused on solving complex problems by prioritizing the user’s needs. It involves a hands-on approach where ideas are rapidly prototyped and tested. Design thinking is used by companies like IDEO to drive innovation and create user-centered designs. The five stages of this process include empathizing with users, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing.
Historical Context and Evolution
Design thinking has its roots in the field of industrial design, growing in popularity in the late 20th century. Its evolution was influenced by the work of designers and engineers who sought to integrate user experience into product development. IDEO played a significant role in popularizing the mindset through its consultancy work. Today, design thinking is applied across various industries, from software development to healthcare, emphasizing human-centered design principles. For example, in healthcare, elements like the best custom scrub caps for healthcare professionals can be designed to meet both functionality and individual preferences, enhancing both comfort and personal expression.
Key Principles of Design Thinking
Several key principles define design thinking. Empathy is crucial, as it involves understanding the user’s experience and needs. An iterative process ensures continuous improvement through repeated cycles of prototyping and testing. Collaboration across disciplines fosters diverse ideas and solutions. Experimentation and prototyping are essential, encouraging creative and practical solutions. This mindset, adopted by many innovators, allows for flexible and effective problem-solving in various contexts.
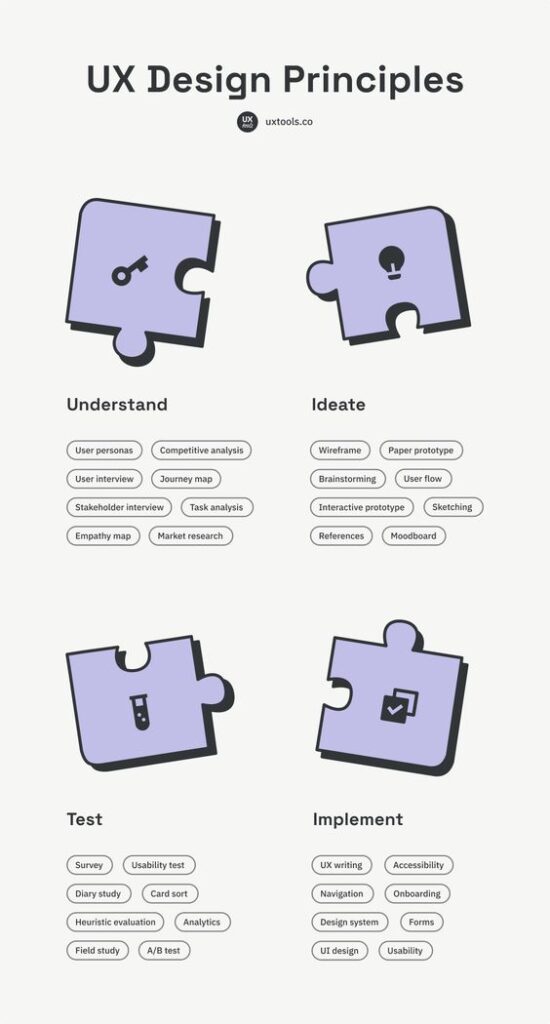
The Five Phases of Design Thinking

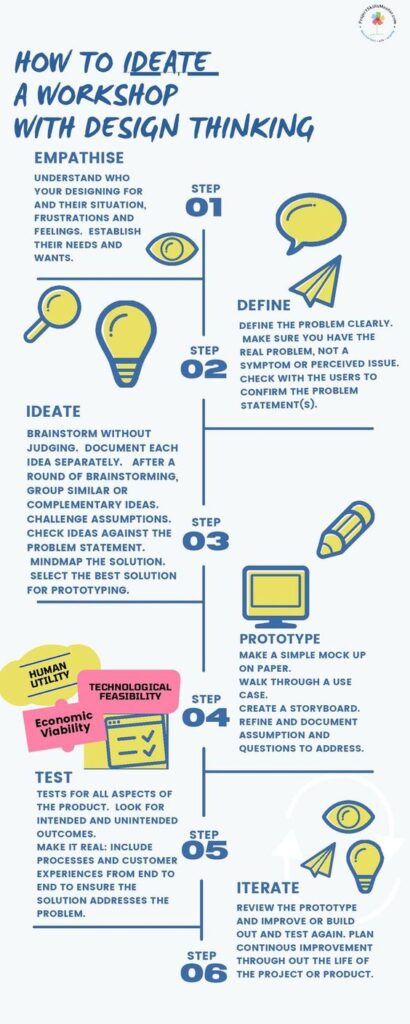
Design Thinking is divided into five phases which help guide teams through solving problems and creating innovative solutions. These phases are designed to foster empathy, creativity, detailed planning, and iterative testing.
Empathize
The Empathize phase centers on understanding the users’ needs and experiences. This involves observing, engaging with, and empathizing with people to gain deep insights into their world. Techniques such as interviews, surveys, and direct observation are essential during this phase. By connecting with the users, designers can gather rich, qualitative data which forms the foundation for the rest of the process.
A key aspect of this phase is stepping into the users’ shoes to understand their motivations and pain points. Designers must remain open-minded and avoid jumping to conclusions. They gather stories and anecdotes which highlight the core issues faced by the users.
Define
In the Define phase, designers synthesize the information collected during the Empathize phase. This step involves organizing and analyzing the gathered data to identify the main problems and opportunities. Designers create a clear problem statement that focuses on the users’ needs and pain points.
This phase is crucial as it sets the direction for the project. Using tools like personas and user journey maps helps to visualize the users’ experiences and highlight the most critical issues. A well-defined problem statement ensures that the team remains focused on solving the right problems.
Ideate
During the Ideate phase, team members brainstorm and generate a wide array of ideas and solutions. This is the phase where creativity is unleashed, and all potential solutions are considered. Techniques such as brainstorming sessions, mind mapping, and sketching help to surface innovative ideas.
The goal is to think outside the box and explore different approaches without judgment or constraints. Quantity over quality is the mantra here; the more ideas generated, the better the chance of finding a truly innovative solution. Once a pool of ideas is created, the team can start narrowing them down to the most viable options.
Prototype
The Prototype phase involves turning ideas into tangible products. Prototypes can be simple and low-cost models that showcase key features and functionalities. They enable designers to explore different solutions and refine them through hands-on experimentation.
It is important to create multiple prototypes to test various aspects of the solution. By building quick and inexpensive versions, designers can identify what works and what doesn’t. This phase encourages a cycle of creation and evaluation, allowing the team to learn and improve the designs rapidly.
Test
In the Test phase, prototypes are tested with actual users to gather feedback. The primary goal is to validate the solutions and understand their effectiveness in real-world scenarios. Feedback from users is invaluable as it highlights strengths and areas needing improvement.
Testing often reveals insights that weren’t apparent during earlier phases. Designers should conduct multiple rounds of testing and iterating, refining the prototypes based on feedback. This iterative approach ensures that the final solution is both user-centered and effective in addressing the identified problems.
Applying Design Thinking
Applying design thinking involves understanding user needs, generating ideas, and refining solutions through feedback. Key steps include user research, developing a clear problem statement, creating prototypes, and iterative improvements.
Gathering and Analyzing User Research
Understanding users is at the heart of design thinking. The aim is to gather deep insights into their needs, behaviors, and challenges. Methods such as interviews, surveys, and observations are commonly used.
Data collected during this phase helps to uncover patterns and pain points. It’s important to approach this with an open mind, avoiding any assumptions. Organizing findings can be done using tools like empathy maps and personas, providing a clear picture of user-centric needs.
Developing a Problem Statement
A well-defined problem statement guides the entire design process. This statement should be user-centered, clearly articulating the specific needs identified during research.
Crafting the problem statement involves synthesizing insights and focusing on key issues. This clarity directs brainstorming sessions and keeps the team aligned. A good problem statement is concise and actionable, making it easier to generate innovative solutions.
From Ideas to Prototypes
Brainstorming sessions generate a wide range of ideas, with the goal of addressing the problem statement. Quantity over quality is encouraged initially to foster creativity.
Prototypes bring ideas to life and make them tangible. These can range from simple sketches to more detailed models. The purpose is to implement quickly and learn from user interactions.
Iterative Improvement and Feedback Loops
Iterative improvement is critical in refining solutions. Prototypes are tested with users, and their feedback is collected and analyzed. This feedback loop ensures that the design evolves based on real user experiences and needs.
Adjustments are made based on feedback, and new versions of the prototype are tested. This cycle of continuous improvement leads to more user-centric and effective solutions.
Design Thinking in Practice

Design Thinking is a versatile method that has transformed many organizations. This section highlights how companies have successfully implemented it, the cultural shift needed, its applications across industries, and the hurdles encountered.
Case Studies of Successful Design Thinking
Companies like Airbnb and Apple have excelled by integrating Design Thinking. Airbnb was struggling to grow until they reimagined their user experience from the ground up, a move inspired by Design Thinking principles. They focused on understanding and solving user pain points, which resulted in a user-friendly platform and substantial business growth.
IDEO, a pioneer in Design Thinking, has numerous examples of turning around projects by emphasizing empathy and iterative prototyping. Tim Brown of IDEO often cites the transformation of healthcare services as a significant success, showcasing how Design Thinking can lead to innovative and effective solutions.
Building a Culture of Design Thinking
Creating a culture of Design Thinking within an organization requires commitment from the top management to encourage creativity and risk-taking. The Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford advocates for a mindset shift towards prioritizing human-centered design.
Companies can foster such a culture by training employees in Design Thinking methods and creating collaborative spaces where ideas can be freely exchanged. Encouraging iterative learning and celebrating small successes helps embed this methodology into the daily workflows and decision-making processes.
Design Thinking for Various Industries
Design Thinking is adaptable to various sectors, from technology to healthcare. In the technology industry, companies like Apple have utilized this approach to create user-centric products like the iPhone, revolutionizing the way people interact with technology.
In healthcare, Design Thinking has been applied to improve patient experiences, redesign hospital environments, and enhance medical products. The focus is on empathy and understanding the needs of patients and healthcare providers, leading to more effective and compassionate care solutions.
Challenges and Limitations of Design Thinking
Despite its versatility, Design Thinking is not without challenges. One key difficulty is addressing Wicked Problems—complex issues with no clear solution. The process may also demand more time and resources than traditional methods, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
Resistance to change is another significant hurdle. Employees accustomed to conventional methods might find it challenging to adopt a new mindset. Moreover, without proper implementation, Design Thinking could lead to superficial solutions rather than meaningful innovation. Organizations must therefore ensure thorough training and support to overcome these challenges.
Innovative and Agile Methodologies
Innovative and agile methodologies are essential for developing flexible and creative solutions. These methods help businesses maintain a competitive advantage and adapt to fast-changing markets.
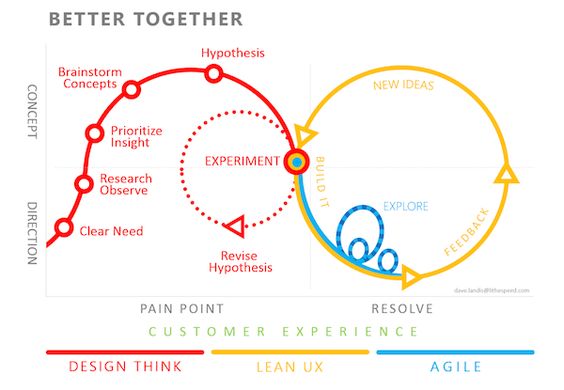
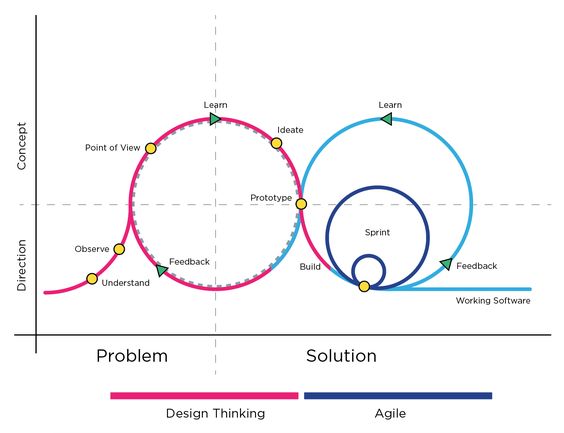
Relation Between Design Thinking and Agile
Design Thinking and Agile methodologies are both focused on creating solutions that meet user needs effectively. Design Thinking is a user-centered approach that emphasizes understanding users’ problems through empathy and creativity. Agile, on the other hand, is a project management approach that prioritizes iterative development, allowing teams to adjust plans based on real-time feedback.
The integration of Design Thinking and Agile can lead to significant innovation. For example, using Design Thinking to define user problems can inform Agile sprints, ensuring that development efforts are focused on the most critical features first. This combination accelerates growth and improves product-market fit.
Agile methodologies complement Design Thinking by encouraging regular iterations and short feedback loops. This ensures that the creative solutions generated during Design Thinking phases are continuously tested and refined. Both methods together support dynamic and responsive business models, fostering an environment where continuous improvement is standard practice.
Design Thinking for Business Strategy
Design Thinking can play a crucial role in shaping business strategies by focusing on user-centered innovation. By deeply understanding customer needs and behaviors, businesses can develop strategies that are both innovative and closely aligned with market demands. This can lead to a sustainable competitive advantage.
Incorporating Design Thinking into business strategy involves using its principles at every level of decision making. For instance, during strategy sessions, teams can use Design Thinking techniques like brainstorming and prototyping to explore new business models or product ideas. This iterative approach to strategy development ensures that business plans remain flexible and adaptable to changes.
Moreover, integrating Design Thinking into business strategy encourages a culture of experimentation and openness to new ideas, essential for long-term growth. By prioritizing empathy and creativity, companies can consistently develop innovative solutions that meet real customer needs, driving business growth and success.
For further information on combining these methodologies, you can explore more details in the related studies on agile development with design thinking and innovative IT projects.
Tools and Techniques

Effective design thinking involves using specific tools and techniques to foster creativity and solve problem statements. Key techniques include prototyping tools and brainstorming methods, which aid in ideation and refining ideas.
Prototyping Tools
Prototyping is essential in the design thinking process. It involves creating wireframes, mock-ups, or models to test ideas. These tools help turn abstract concepts into tangible forms, allowing teams to explore and iterate on designs quickly.
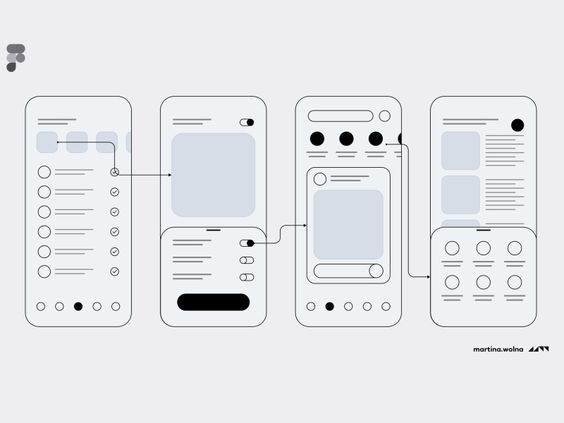
Wireframes are basic visual guides that outline the structure of a design. They show the placement of elements without detailed styling. Wireframes make it easier to focus on functionality over aesthetics.
Mock-ups provide more detail and realism than wireframes. They include colors, graphics, and typography. Mock-ups help stakeholders visualize the end product more effectively.
3D models and interactive prototypes add another layer of realism. They can simulate the user experience and show how the product will function in real life. Tools like Sketch, Figma, and InVision are commonly used.
Ideation and Brainstorming Methods
Brainstorming is a powerful method for generating a wide range of ideas. During brainstorming sessions, participants are encouraged to think freely and share ideas without judgment. This fosters creativity and helps in addressing problem statements.
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps organize thoughts and ideas. It involves writing down a central concept and branching out into related ideas. This method helps in exploring different aspects of a problem.
SCAMPER (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Rearrange) is another effective technique. It prompts creative thinking by asking specific questions about existing ideas/products to spark innovation.


Role-playing involves participants acting out different personas to understand various perspectives. This technique can uncover unique insights and solutions.
Crazy 8s is a fast sketching exercise. Participants fold a sheet of paper into eight sections and draw a different idea in each section within eight minutes. This method encourages rapid ideation and creativity.
Using these techniques can help teams come up with a diverse array of innovative solutions.
Design Thinking and Education
Design thinking has become a significant approach in education, impacting how teachers instruct and how students learn. It encourages problem-solving, creativity, and hands-on learning.
Teaching Design Thinking
Teaching design thinking focuses on integrating this methodology into the curriculum. At Stanford University, the d.school has been a pioneer in implementing design thinking in education. This approach involves defining problems, brainstorming, prototyping, and testing solutions.
Teachers are trained to guide students through these steps, allowing them to explore real-world problems. They use design thinking projects that align with existing subjects such as science and mathematics. By embedding these practices, educators make learning more interactive and engaging.
Design thinking also promotes collaboration among students. Teachers emphasize teamwork and communication, which are essential skills in today’s world. Schools adopting this method report increased student interest and participation in their subjects.
Design Thinking for Students and Educators
Design thinking empowers both students and educators. For students, it encourages a mindset of exploration and innovation. According to a review, students engaged in design thinking show improved problem-solving skills and creativity.
For educators, it provides tools to create dynamic and flexible lesson plans. Teachers can adapt their teaching styles and habits to better suit student needs. The process builds confidence in students as they realize their ability to develop solutions.
Educational institutions like Stanford University have shown how impactful these methods can be. Teachers who implement design thinking can transform their classrooms into spaces of discovery and collaboration, leading to more effective learning outcomes.
Expanding Beyond Products

Design Thinking can be used outside of products to improve services and enhance digital experiences. This approach places the user at the center, ensuring solutions cater to their needs.
Service Design and Experience
Service design uses Design Thinking to streamline and improve how services are delivered. It focuses on how each touchpoint affects the customer experience. By mapping the customer journey, companies can spot pain points and opportunities.
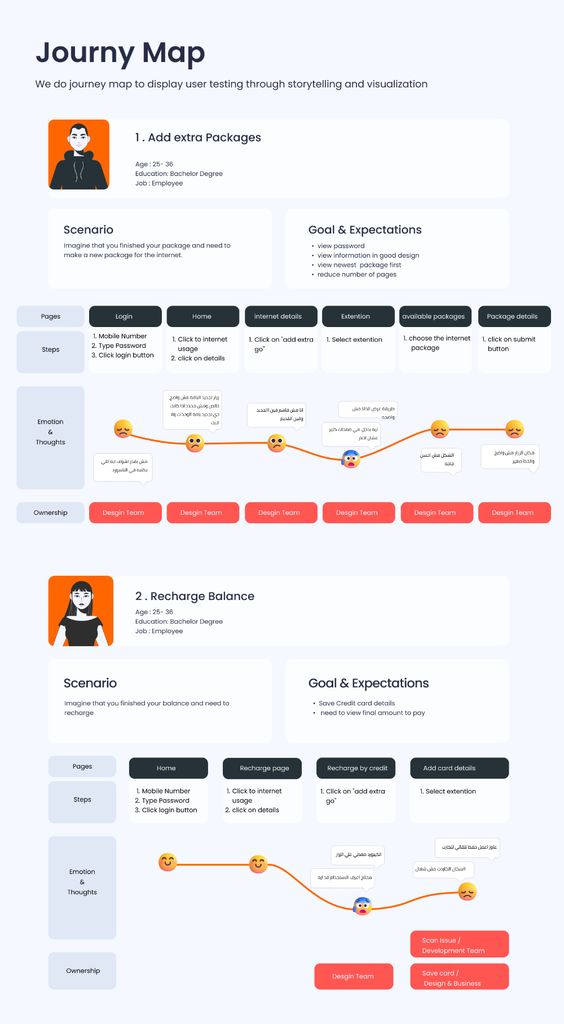
Human-centered design ensures services are tailored to customers, making processes smoother and more enjoyable. For example, hospitals use service design to optimize patient flow and interaction. This approach results in satisfied customers and better outcomes.
In retail, service design can restructure the checkout process, making it faster and more efficient. Improving these touchpoints leads to a better overall customer experience.
Design Thinking in Technology and Digital Spaces
In technology, Design Thinking transforms digital products and services. It simplifies complex systems and enhances user engagement. This method is critical for app development, ensuring that end-users find the software intuitive and enjoyable.
Human-centered design emphasizes empathy, understanding user problems to create relevant solutions. For instance, a banking app might use this approach to make transactions easier and more secure.
Design Thinking drives innovation in digital platforms. Companies focus on what users need in their digital interactions. Whether it’s a website or an interactive kiosk, the goal is to be user-friendly and efficient. This results in higher customer satisfaction and retention.
The Future of Design Thinking

Design thinking continues to evolve, tapping into emerging trends, scaling processes, and extending into diverse disciplines. These advancements show promise for significant innovation and wider application.
Emerging Trends in Design Thinking
Emerging trends focus on embracing technology and enhancing user experiences. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are playing crucial roles in shaping new design thinking frameworks. These technologies allow designers to analyze vast amounts of data, improve user insights, and create more personalized solutions.

Sustainability is another important trend. Designers are increasingly considering environmental impacts in their projects. This shift encourages the creation of products that are not only user-friendly but also eco-friendly.
Moreover, greater emphasis on inclusive design is becoming prevalent. This approach ensures that products and services are accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities. These trends reflect a broader commitment to responsible and forward-thinking design practices.
The Scaling of Design Thinking
Scaling design thinking across organizations involves embedding its principles into company culture. Leaders must champion this mindset, and everyone from executives to frontline employees should understand its value. According to Harvard Business Review, companies that scale design thinking effectively often see higher innovation rates and greater alignment across teams.
Training programs and workshops are critical in this scaling process. They help employees develop necessary skills and foster a collaborative spirit. Regular practice and reinforcement of design thinking methods ensure that they become second nature.
Additionally, digital platforms and tools are making it easier to share knowledge and collaborate on a larger scale. These technologies support remote and cross-functional teams, enabling them to work seamlessly together despite geographical barriers.
Interdisciplinary Application of Design Thinking
Design thinking is increasingly applied across various disciplines, breaking down traditional silos. In healthcare, it is used to improve patient experiences and streamline healthcare processes. In education, it enhances learning environments and teaching methods.
Cross-functional teams benefit immensely from design thinking. These teams bring together diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to more innovative and effective solutions. The collaborative nature of design thinking fosters creative problem-solving and promotes a holistic approach to challenges.
The interdisciplinary application extends to public services and social enterprises as well. Policymakers and civic planners utilize design thinking to create more user-centered public services and policies, aiming to address societal issues more effectively. This broad application demonstrates the versatility and impact of design thinking on solving complex problems in various fields.
Frequently Asked Questions
The design thinking process involves several key steps that help in problem-solving and innovation. It is widely used in various fields, including business, to create better solutions.
What are the key steps involved in the design thinking process?
The design thinking process usually includes five main steps: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. These steps help designers understand the user’s needs, define the problem, generate ideas, create prototypes, and test the solutions.
Can you provide an example of the design thinking process in action?
Consider a company that wants to improve its customer service. They would start by empathizing with customers to understand their needs and problems. Next, the company would define the main issues, brainstorm ideas, create a prototype of a new service solution, and then test it with real customers.
How can I find a comprehensive PDF guide on design thinking?
A detailed PDF guide on design thinking can be found in various online resources. One example is the PDF on design thinking which provides a thorough overview of the process and its applications.
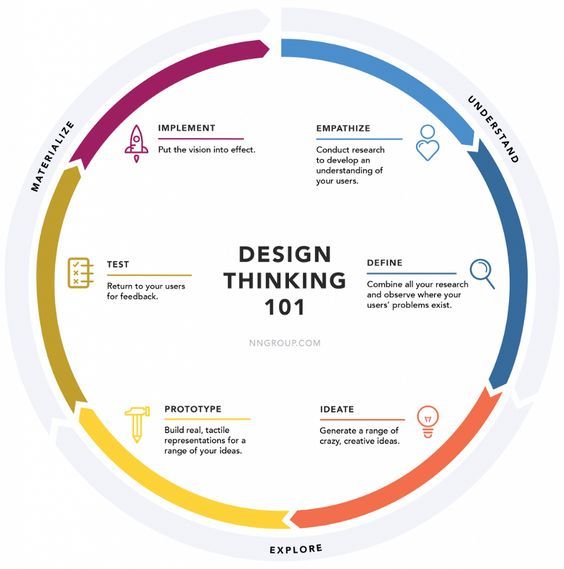
Could you explain how a design thinking process diagram visually represents the stages?
A design thinking process diagram typically shows the five key stages: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. Each stage is interconnected, often represented in a circular or iterative format, emphasizing that the process is non-linear and cyclical.
In what ways does the design thinking process apply to business innovation?
In business, design thinking helps to create innovative products and services by focusing on the end-user. It encourages companies to address real customer needs, which leads to more effective and market-friendly solutions. This approach helps businesses remain competitive and responsive to change.
What sets apart the fifth stage of the design thinking process from the others?
The fifth stage, “test,” is crucial because it provides feedback on how well the prototypes meet user needs. Unlike other stages focused on generating ideas or understanding problems, testing is about validating the practical effectiveness of the proposed solutions and making necessary adjustments.
- 886shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest886
- Twitter0