3D modeling is a fascinating process that allows creators to develop three-dimensional objects on computers. It is used in various fields, including film, gaming, architecture, and virtual reality. Understanding this skill opens up many opportunities for those interested in design and technology.
As technology advances, 3D modeling continues to evolve. New software and techniques make it easier to create detailed and realistic models. Knowing the core principles and applications of this art form is essential for anyone wanting to work in these creative areas.
Learning 3D modeling can be a rewarding journey. With dedication, anyone can learn to bring their ideas to life and make an impact in many industries.
Key Takeaways
- 3D modeling is essential for various creative industries.
- New software simplifies the modeling process.
- Anyone can learn 3D modeling with practice and dedication.
History of 3D Modeling
Three-dimensional modeling has a rich and varied history. It shows how technology has changed over time, from simple shapes to complex digital worlds. Key developments in this field have shaped many industries, including gaming, film, and architecture.
Early Developments
The roots of 3D modeling go back to the 1960s. Early pioneers like Ivan Sutherland created simple wireframe models using computers. These models were foundational for understanding how to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional screen.
In 1972, Sutherland introduced “Sketchpad,” which allowed users to interact with graphical images. This program let users create shapes and manipulate them. It set the stage for future graphical user interfaces.
Evolution of 3D Graphics
The 1980s brought significant changes with the rise of computer graphics software. Programs like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) made 3D modeling more accessible to engineers and architects. They used these tools to visualize designs and create accurate blueprints.
Around the same time, traditional animation studios began exploring 3D animation. The film “Tron” (1982) featured groundbreaking graphics. This sparked interest in 3D in entertainment. The introduction of Pixar’s “Toy Story” in 1995 further pushed the boundaries of what could be done with 3D modeling.
Modern Advances
Today, 3D modeling has expanded even more with advanced software like Blender and Autodesk Maya. These tools come with features that allow for photorealistic rendering and complex simulations.
Moreover, the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) has added new dimensions to 3D modeling. Models can now interact with real-world elements, enhancing user experiences.
3D printing is another major development. It enables physical objects to be created from digital files. This has applications in manufacturing, medicine, and art.
The history of 3D modeling highlights its growth and importance in various fields. Each stage has built upon the last, creating rich opportunities for creativity and innovation.
Core Principles of 3D Modeling


3D modeling involves several key elements that define how objects are created and represented in three dimensions. Understanding geometry, textures, lighting, and animation principles is crucial for effective modeling.
Geometry and Topology
Geometry refers to the shapes and forms in 3D models. It includes points, lines, and surfaces that create an object. Topology is how these elements connect. It affects how models deform and move.
- Polygons are the building blocks, often using triangles or quadrilaterals.
- The mesh is a collection of polygons that form the surface.
- Vertices are points where polygons meet. Their arrangement influences the model’s quality.
Good topology ensures models are made with efficiency. Proper edge flow helps in animation and deformation. Poor geometry can lead to problems in rendering or animating, making understanding these concepts essential.
Textures and Materials
Textures add detail and realism to 3D models. They are images applied to the surface of a model. Materials define how the surface interacts with light.
- Diffuse maps show the base color of a surface.
- Normal maps create the illusion of depth without changing the model’s geometry.
- Specular maps control shiny spots where light reflects.
Using high-quality textures increases realism. It is important to create a seamless look across different surfaces. This helps maintain consistency in the visual appearance of the model, enhancing the overall quality.
Lighting and Rendering


Lighting is crucial in 3D modeling. It affects how models are seen and perceived. Different lighting setups create various moods and highlights.
- Key light is the main light source that defines shadows.
- Fill light softens shadows created by the key light.
- Backlight can create depth by illuminating the back of the object.
Rendering is the process of producing an image from a 3D model. High-quality rendering takes into account light, textures, and details. This creates a final product that looks realistic and polished. The choice of rendering technique can also impact the time taken and resources used.
Rigging and Animation
Rigging is preparing a model for animation by adding a skeleton. This skeleton allows for movement, making models come to life.
- Bones and joints create a structure for motion.
- Skinning binds the model’s surface to the skeleton.
Animation is the process of making a model move. Techniques include keyframing, where positions are set at specific times, and using physics for more natural movement. Proper rigging and animation techniques ensure that movements look smooth and lifelike.
These core principles provide the foundation for effective 3D modeling. Each element plays a crucial role in creating dynamic and realistic models.
Popular 3D Modeling Software
Several software options are popular for 3D modeling. Each has unique features that cater to different needs in creative fields like animation, game design, and product visualization.
Blender
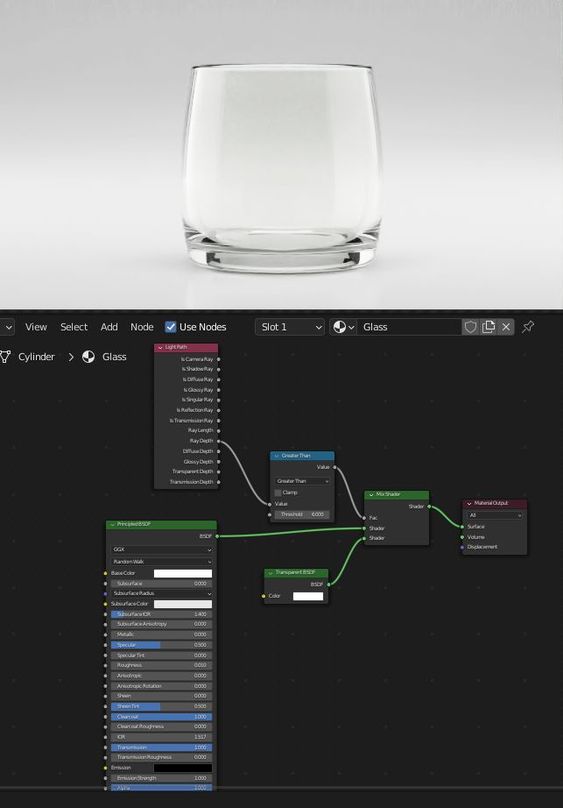
Blender is a free, open-source software widely used in the 3D community. It offers a comprehensive range of tools for modeling, sculpting, and animation.
Users appreciate its flexibility and capability to handle complex projects. The interface provides various layouts, making it adaptable for beginners and advanced users alike.
Blender supports add-ons, allowing for further customization of tools. The strong online community also provides resources, tutorials, and forums for support. This vibrant ecosystem helps users enhance their skills.
Autodesk Maya

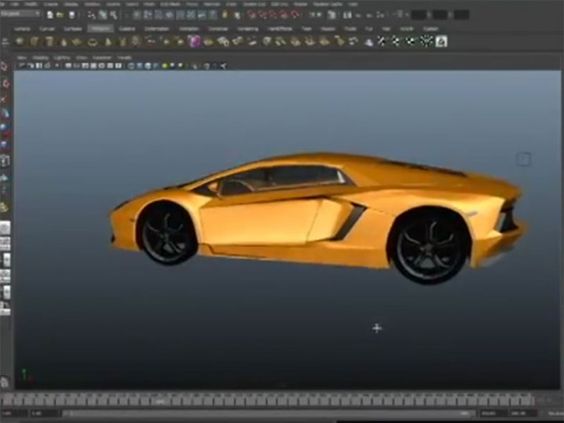
Autodesk Maya is a powerful software known for its robust modeling and animation tools. It is favored in industries such as film, gaming, and visual effects.
Maya excels in character rigging and animation, making it a top choice for animators. The software features a time slider and graph editor, which help control animation timing efficiently.
Many professionals use Maya for complex simulations and effects. The ability to create high-quality models and animations makes it a valuable asset for studios.
3ds Max
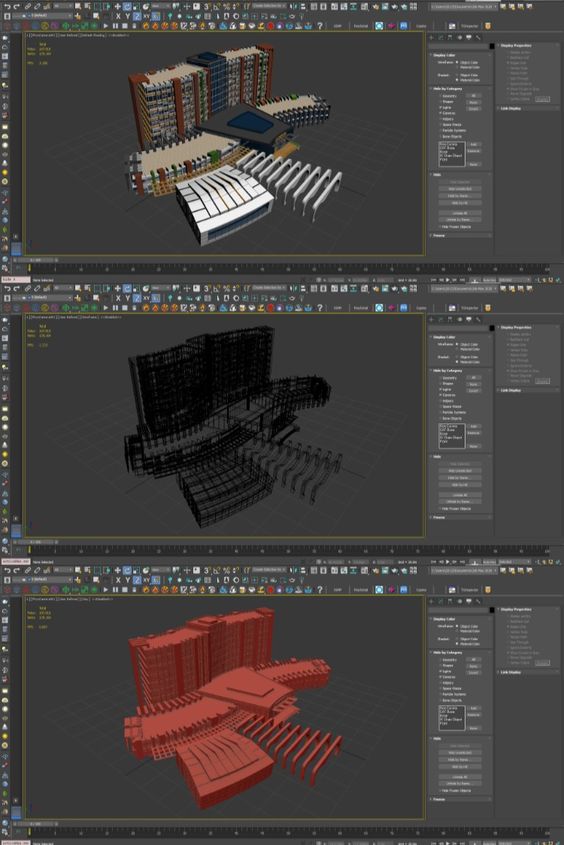

3ds Max is another product by Autodesk that focuses on 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. It is particularly popular among game developers and architectural visualization experts.
The software offers a user-friendly interface with powerful modeling tools. Features like the “Modifier Stack” allow users to apply effects non-destructively, which enhances workflow.
3ds Max is known for its rendering capabilities, providing high-quality visual outputs. The extensive library of textures and materials supports realistic scene creation.
Cinema 4D


Cinema 4D is a professional 3D software known for its ease of use and powerful features. It is popular among motion graphics artists and designers.
The intuitive interface simplifies the modeling process, making it approachable for newcomers. Users often highlight its fast rendering times and integration with Adobe products.
Cinema 4D includes features like the MoGraph toolset, which allows for creating stunning motion graphics. The active user community shares many resources and tutorials, supporting skill development.
3D Modeling Techniques
There are several key techniques used in 3D modeling. Each method offers unique advantages and is suited for different types of projects. The following techniques include box modeling, sculpting, NURBS and curves, and procedural modeling.
Box Modeling
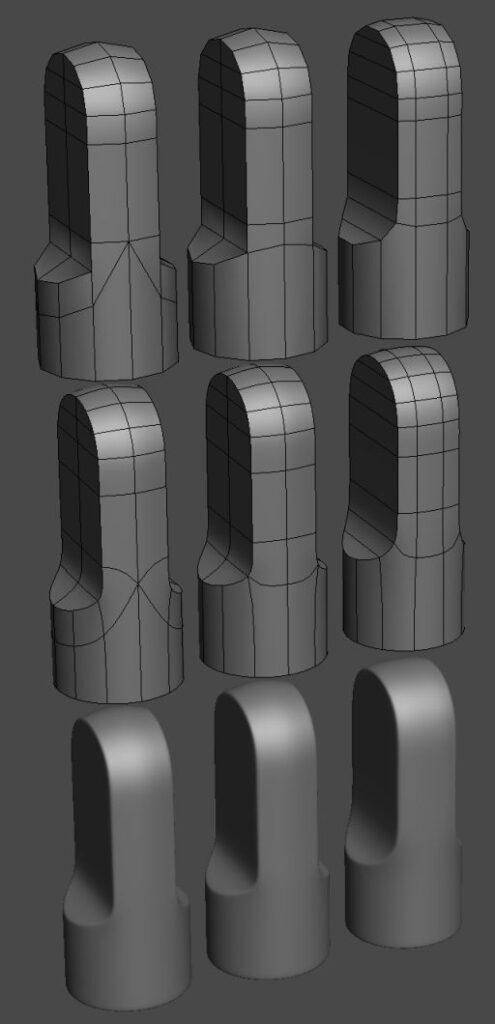

Box modeling focuses on creating shapes from simple geometric forms. It begins with a basic cube, which is gradually refined by adding and manipulating more detail.
- Easy to Learn: This method is user-friendly, making it accessible for beginners.
- Controlled Shapes: It allows artists to create precise and controlled surfaces.
- Edge Loop Optimization: Artists can easily manage edge flow for animation.
Box modeling is popular in character design and hard surface modeling. It is effective for both organic and mechanical shapes, allowing for flexibility in the design process.
Sculpting

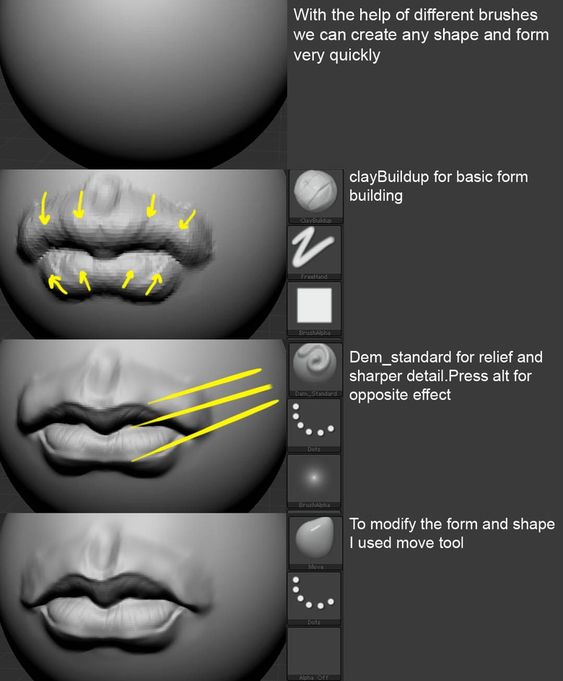
Sculpting mimics traditional clay sculpting in the digital space. Artists can manipulate a base mesh using tools that push, pull, pinch, or smooth surfaces.
- Natural Look: This method achieves a more organic appearance, ideal for characters and creatures.
- Detailing: It allows for high levels of detail, enabling fine features like wrinkles or textures.
- Dynamic Tools: Many software options provide various brushes and tools for customization.
Sculpting is often used in film and game development. It is suitable for creating models that require intricate details, making it a favored technique among professional artists.
NURBS and Curves

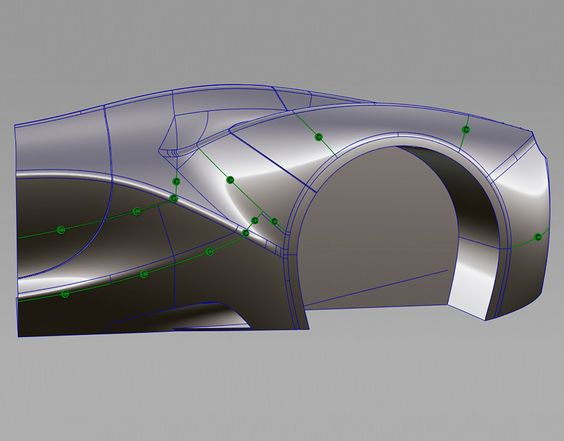
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) modeling uses curves to create smooth and complex shapes. This technique is especially useful in industries like automotive design.
- Precision: NURBS provides high accuracy, making it ideal for technical and industrial designs.
- Smooth Surfaces: It excels in creating smooth, continuous surfaces without visible facets.
- Flexibility: Artists can easily adjust curves and manipulate them to change the shape.
This method is best for projects requiring clean, refined designs such as product models or architectural objects.
Procedural Modeling


Procedural modeling relies on algorithms to generate shapes and forms based on defined rules. This technique is excellent for creating complex environments.
- Efficiency: It can produce large amounts of geometry without manual intervention.
- Variation: Artists can easily create variations of a model using parameters, which saves time.
- Dynamic Changes: Changes can be made without starting over, which increases workflow efficiency.
Procedural modeling is widely used in video games and visual effects, allowing for the rapid creation of detailed landscapes and assets.
Applications of 3D Modeling
3D modeling has many important uses across different fields. It enhances creativity and boosts efficiency in projects. Below are some key applications of 3D modeling.
Entertainment and Film


In entertainment and film, 3D modeling creates realistic characters and environments. Artists use software to design animated characters that look lifelike. They build detailed worlds that captivate audiences. Movies often use 3D models for special effects. For instance, creatures in sci-fi or fantasy films rely on 3D models for visual storytelling.
The process includes sculpting, texturing, and rigging. Tools like Autodesk Maya and Blender are common choices. These applications allow for high-quality rendering. Many animated films, like Pixar’s productions, depend heavily on this technique. It helps to produce rich visuals that pull viewers into the story.
Video Game Development

Video game development uses 3D modeling for character design and environment creation. Game designers create objects, landscapes, and avatars. These models are essential for gameplay and player interaction. High-quality visuals enhance the gaming experience.
Developers use software such as Unity or Unreal Engine. These programs allow them to integrate models into the game. Creating models involves multiple steps, including modeling, texturing, and animation. The better the models, the more immersive the game becomes. Popular franchises like Call of Duty showcase advanced 3D modeling skills.
Industrial Design


In industrial design, 3D modeling helps in product development. Designers create accurate representations of new products. This process reduces the need for physical prototypes. They can easily adjust shapes, sizes, and colors within the model.
Software like SolidWorks and AutoCAD is standard for industrial designers. These tools aid in creating functional and aesthetic designs. The models can also be tested for usability and ergonomics. This approach leads to more efficient and effective product design.
Architecture and Visualization
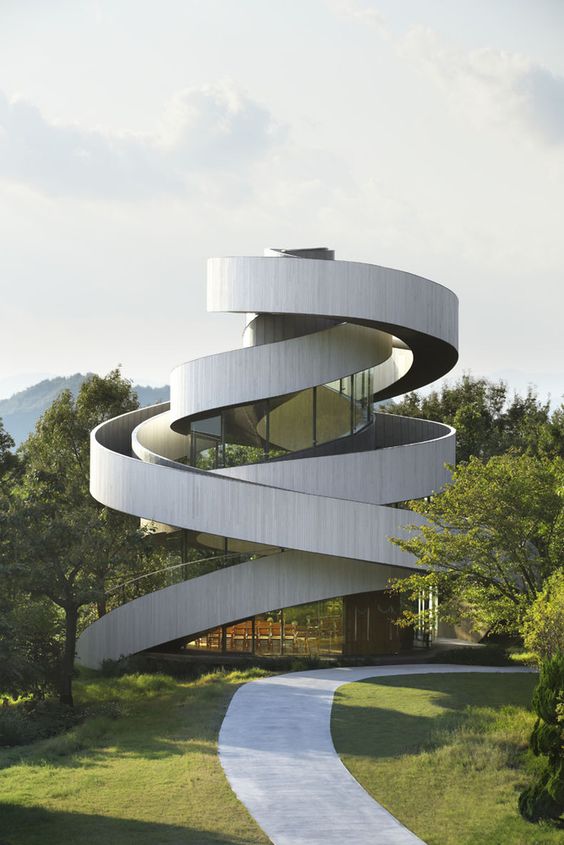


For architecture, 3D modeling plays a crucial role in design and presentation. Architects create detailed building models to visualize spaces. This practice helps clients understand the project before construction begins.
Architects use programs like SketchUp or Revit to design structures. They can present realistic images and animations to stakeholders. These models help in making decisions about materials and layout. Visualizing the final outcome improves communication and reduces changes during the build.
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality relies on 3D modeling to create immersive experiences. It allows users to explore spaces and objects in a simulated environment. This application is popular in gaming and training.
Developers create 3D environments that users can navigate. Software like Oculus Medium enables artists to design for VR. The detailed models provide a sense of presence in the virtual world. This technology is also used in fields like education and healthcare for simulations.
3D Printing and Model Preparation


Preparing a 3D model for printing includes several key tasks to ensure high-quality results. Important steps include optimizing the mesh, using slicing software, and choosing the right materials. Each of these areas affects the final printed object.
Mesh Optimization
Mesh optimization is crucial for successful 3D printing. A model must have a clean and efficient mesh to prevent printing errors. This involves checking for non-manifold edges and ensuring all faces are closed.
Common issues to fix include:
- Duplicate vertices: These can confuse the printer.
- Holes in the mesh: These lead to gaps in the printed object.
- Excessive polygons: Reducing complexity helps speed up slicing.
Using software tools, she can analyze and repair these issues. Tools like Blender or Meshmixer are popular choices for mesh repair.
Slicing Software
Slicing software converts a 3D model into instructions that a printer understands. It calculates the layers that will be printed and the necessary paths.
Key features to consider are:
- Layer height: This affects print quality and time.
- Infill density: Higher infill makes a model stronger but takes longer.
- Supports: These are necessary for complex shapes.
Popular slicing software includes Cura and PrusaSlicer. Each tool has settings that can be customized based on the specific model and desired outcome.
Material Considerations
Choosing the right material is vital for 3D printing success. Different materials offer unique properties, impacting the strength, flexibility, and finish of the final product.
Common 3D printing materials:
- PLA: Easy to print, biodegradable, and good for beginners.
- ABS: Stronger than PLA, but might warp and needs careful handling.
- PETG: Combines strength with flexibility, resistant to impact and moisture.
Consider the desired use of the printed object when selecting a material. Each option has its advantages and limitations affecting cost and durability.
Challenges in 3D Modeling
3D modeling involves several challenges that can affect the final output. Key issues include managing complexity, balancing realism with style, and navigating ethical concerns.
Complexity and Resource Management
Creating detailed 3D models often requires significant computational power and memory. High-resolution textures and complex geometry increase the demand for resources.
This can lead to slow rendering times and crashes if the hardware is not sufficient. Modelers must find a balance between detail and performance.
Strategies for Managing Resources:
- Optimization: Reduce polygon count where possible without losing quality.
- LOD (Level of Detail): Use different model versions for varying distances in a scene.
- Texture Management: Use lower resolution textures when high detail is unnecessary.
Effective resource management is crucial for producing efficient and functional models.
Realism vs. Stylistic Choice
Another challenge is deciding between realism and stylized representation. Realistic models cling closely to real-life references, while stylized models allow for more creativity.
Choosing a direction impacts the modeling process, textures, and shading. Models must fit the desired aesthetic of the project, whether it’s a realistic game or a cartoon.
Factors to Consider:
- Audience: Know what appeals to the target audience.
- Project Goals: Align the model style with the project’s vision.
- Technical Requirements: Some styles may require less detail and thus be more efficient.
Designers must be skilled in adapting their approach based on these factors to meet project needs.
Ethics and Copyright
Ethical issues in 3D modeling often arise around copyright and ownership. It is important to respect existing works and avoid plagiarism.
Using copyrighted models or textures without permission can lead to legal trouble. Modelers should seek original sources or properly license assets.
Best Practices:
- Create Original Content: Always aim to produce unique designs.
- Use Proper Licensing: Get permissions for any third-party assets.
- Credit Sources: Always acknowledge collaborators and creators of shared resources.
Understanding these ethical guidelines protects both the modeler and the integrity of the industry.
Future of 3D Modeling
The future of 3D modeling promises exciting changes. Key developments include the integration of AI, enhancements in rendering techniques, and the introduction of haptic feedback systems. These advancements will shape how designers and users interact with 3D models.
Integration with AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionize 3D modeling. AI tools can automate tedious tasks, such as generating textures or optimizing models. This helps designers focus on creativity and innovation.
AI-driven software can analyze a designer’s style and suggest improvements. These tools can even predict project outcomes. As these technologies evolve, 3D modeling workflows will become faster and more efficient.
AI can also play a role in creating realistic animations. With machine learning, programs can simulate human movement and reactions. This feature allows for more lifelike character designs and environments.
Advancements in Rendering Techniques

Rendering is crucial in 3D modeling. New techniques will produce faster and higher-quality images. Ray tracing, for example, simulates light more accurately. This results in stunning visuals that look almost real.
Cloud rendering is another promising advancement. It allows users to take advantage of powerful servers without needing high-end hardware. This flexibility opens doors for more people to create detailed visuals.
Emerging technologies like real-time rendering will change how designers work. They can see changes immediately, making the design process more interactive. This also encourages collaboration among teams.
Haptic and Tactile Feedback Systems
Haptic technology adds a new dimension to 3D modeling. It allows users to feel textures and shapes through touch. By using special devices, designers can manipulate models as if they were real objects.
These systems enhance user experience in virtual reality (VR) environments. Users can “feel” their designs, leading to better understanding and refinement. This feedback helps identify issues early in the design process.
As haptic technology improves, it will become more affordable and accessible. This shift will likely see wider adoption in various fields, including gaming, education, and healthcare. Enhancing the 3D modeling experience will pave the way for innovative applications in the future.
Learning 3D Modeling
To learn 3D modeling, individuals can explore various educational resources, engage with communities, and focus on building a portfolio. These steps can help them gain confidence and skills as they navigate the 3D modeling landscape.
Educational Resources
There are many educational resources available for new learners. Online platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy offer structured courses. These courses often range from beginner to advanced levels, allowing learners to progress at their own pace.
YouTube is also a valuable resource. Many channels provide free tutorials on specific software like Blender, Maya, or 3ds Max. These tutorials cover specific techniques and tools.
Books on 3D modeling can give deeper insights into theory and principles. Recommended titles include “Blender for Dummies” and “Digital Modeling”. These resources cover both practical skills and foundational knowledge, helping learners to understand the field.
Community and Collaboration
Joining online forums and communities can greatly enhance the learning experience. Sites like Reddit, Discord, and 3D modeling forums offer platforms for discussion and feedback. Members can share tips, ask questions, and showcase their work.
Collaboration projects can also be beneficial. Participating in game jams or collaborative art projects lets learners work with others. This exposes them to different styles and techniques.
Attending local meetups or workshops helps learners connect with professionals in the field. Networking opens opportunities for mentorship or collaboration. Engaging with a community makes the learning process more enjoyable and less isolating.
Building a Portfolio
Creating a portfolio is essential for showcasing skills. A strong portfolio should include a variety of work, such as models, animations, and textures. This diversity demonstrates adaptability and creativity.
Online platforms like ArtStation and Behance allow artists to display their work. These sites also offer exposure to potential employers or clients. Regular updates to the portfolio are important as skills improve.
Including personal projects shows passion and dedication. It’s helpful to document the process, such as sketches or concept art, to give viewers insight into thought processes. A well-organized portfolio can lead to job opportunities in 3D modeling.
- 661shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest661
- Twitter0
- Reddit0


