I spent months filling sketchbooks with fashion designs that looked amazing on paper—flowing dresses, structured jackets, pieces I was genuinely proud of. Then I tried to actually make one. The proportions were wrong for real bodies. The fabric I chose wouldn’t drape the way I’d drawn it. The construction I’d imagined was physically impossible without industrial equipment.
The gap between “fashion drawing” and “fashion design” hit me hard. Drawing pretty clothes isn’t designing—it’s illustration. Real fashion design means understanding how garments work: how fabric behaves, how bodies move, how pieces get constructed. Without that knowledge, you’re just making art that can’t exist off the page.
Here’s what separates hobbyist sketchers from actual fashion designers: technical knowledge layered under creative vision. You need both. The creativity gets you excited; the technical skills make your ideas wearable.
This guide covers the complete process—from understanding design principles through fabric selection to final construction. Whether you want to create one custom piece for yourself or launch a fashion career, you’ll learn how to turn ideas into clothes that actually exist in three dimensions.
Understanding Fashion Design Principles
Fashion design relies on specific ideas that help create clothes that look good and work well. These ideas include the parts that make up a design, the shapes that clothes take, and the ways color can affect style and mood.
Elements of Design


The basic parts of any fashion design are called elements. They include line, shape, texture, color, and space.
- Line guides the eye and can make designs look long, short, soft, or sharp.
- Shape is the form of the garment, such as square, round, or angular.
- Texture refers to how fabric feels or looks, like smooth silk or rough denim.
- Color adds mood and style.
- Space is the area around and inside the design that helps balance the look.
A designer uses these elements to create clothes that catch attention and feel balanced.
Understanding Silhouettes
Silhouettes are the overall outlines or shapes of garments. They help define a person’s style by emphasizing certain body parts. Common silhouette types include:
- A-line: Fits at the top and flares out, like the letter A.
- Sheath: Follows the body shape closely.
- Ball gown: Puffed out and wide, often for formal wear.
Silhouettes influence how clothing fits and moves. Knowing how silhouettes affect the body helps designers create flattering and functional clothes.
Color Theory in Fashion


Color plays a big role in fashion by setting mood and style. Designers use color theory to mix and match colors effectively.
- Warm colors (red, orange, yellow) create energy and attention.
- Cool colors (blue, green, purple) feel calm and relaxed.
- Neutral colors (black, white, gray) offer balance and go with everything.
Designer tools like color wheels help choose combinations, such as complementary (opposite colors) or analogous (colors next to each other). Using color wisely can make designs stand out or blend smoothly.
Researching Fashion Trends
Research helps designers understand what people want to wear and what styles will work well. It involves looking at what’s popular now, learning from famous designers, and noticing cultural changes that affect fashion choices.
Analyzing Current Market Trends
Designers watch what’s selling well in stores and online to see which styles, colors, and fabrics are popular. They use sales data, social media, and fashion shows to spot trends early.
Paying attention to consumer feedback helps designers know what customers like and dislike. For example, if eco-friendly fabrics are in demand, designers might include sustainable materials to meet that need.
Trends can change fast, so continual research helps keep designs fresh and relevant. This means staying updated with new looks and adjusting ideas to match what people want to wear next season.
Studying Iconic Designers


Learning from well-known designers gives insight into successful styles and design methods. Designers study their collections, techniques, and how they mix innovation with tradition.
This includes looking at how iconic designers balance creativity with wearability. Understanding their problem-solving skills and use of colors, shapes, and fabrics helps shape new ideas.
Studying past and present designers also shows how fashion evolves over time. This helps designers predict what might come next and inspire their own unique work.
Incorporating Cultural Influences



Culture shapes what people wear and how fashion develops. Designers observe art, music, lifestyle, and social changes to create clothes that reflect current cultural moments.
Paying attention to different cultures adds variety and richness to designs. For example, patterns or colors inspired by a specific region can make a collection more interesting and meaningful.
Trends often come from cultural events or movements, so designers look for these signals when researching. This keeps their work relatable and connected to the world around them.
Another crucial aspect of fashion design is pure functionality and the environment where the garment will be worn. Great design isn’t just about visual aesthetics; it’s about solving specific problems for the wearer.
A perfect example of balancing style with high-level ergonomics is professional workwear. For instance, when designing performance chef jackets for demanding kitchens, creators must carefully select durable, breathable fabrics and engineer a fit that protects against high temperatures without restricting movement. Always apply this functional mindset to your collections—let the real-world needs of your end-user guide your design choices.
Developing Fashion Sketches
Designing fashion clothes starts with clear ideas and good visual planning. This involves gathering inspiration, mastering sketching skills, and using the right tools. These steps help bring clothing concepts to life on paper or screen, showing how a design should look and feel.
Creating Mood Boards


A mood board gathers images, colors, fabrics, and other elements that inspire a designer. It helps focus the theme and style for a collection or individual pieces. Designers often include photos from magazines, color swatches, textures, and sketches.
Mood boards organize ideas visually, making it easier to see how colors and styles work together. This step saves time during sketching because it sets a clear direction. Many designers use digital tools like Pinterest or Adobe to create mood boards, but physical boards with printed materials also work well.
Mood boards can be flexible. They evolve as the designer refines the concept. This early planning guides fabric choice, colors, and details in sketches.
Hand Sketching Techniques
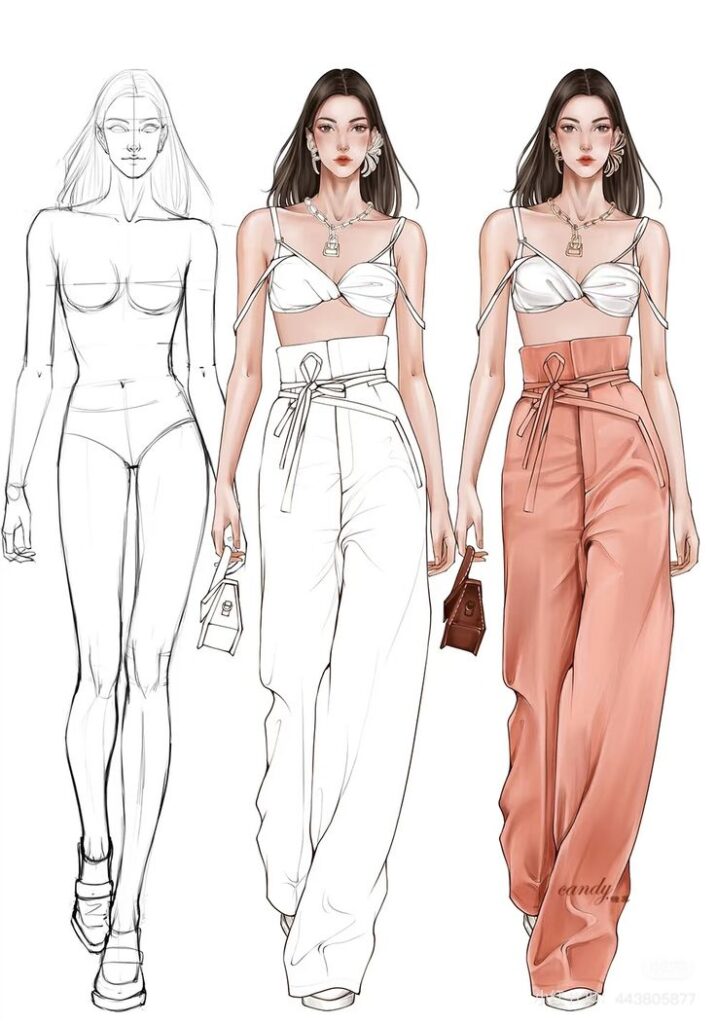

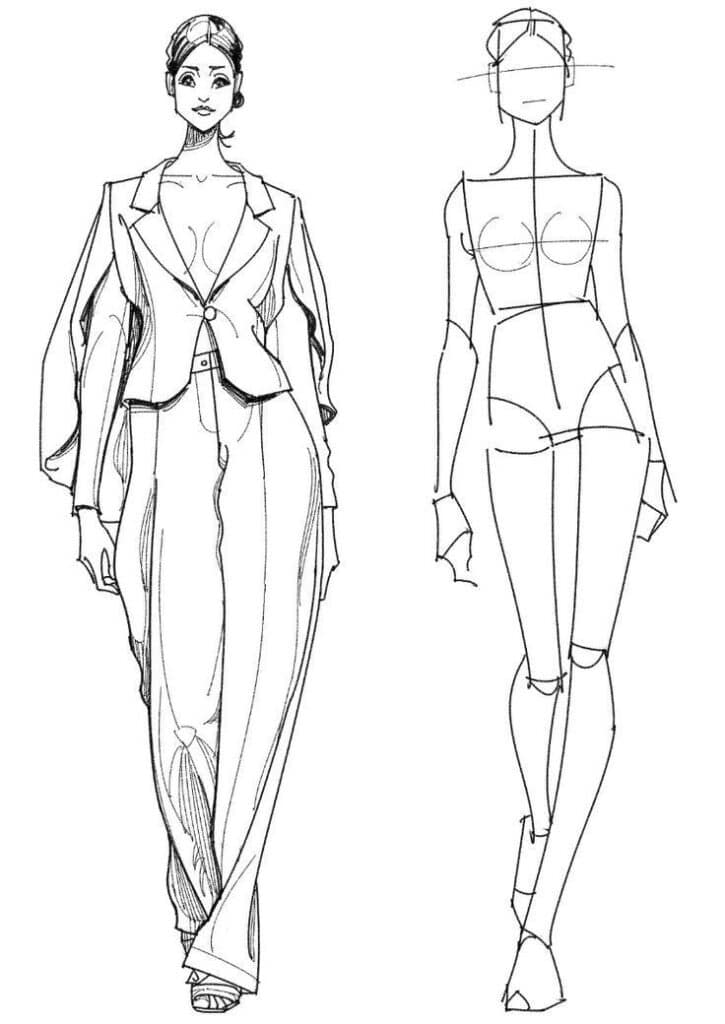
Hand sketching is a basic skill in fashion design. It starts with drawing a croquis—a simple figure showing body proportions. The croquis acts as a base to add clothing details.
Designers focus on balance lines, the torso, arms, legs, and the model’s center of gravity. This ensures the figure and clothes look natural. Using pencils with different hardness helps create clear lines and shading.
Quick, loose sketches capture the idea fast. More detailed drawings show seams, textures, buttons, and folds. Using ink or markers can add color and emphasis. Keeping proportions correct is important to make clothes look realistic on the body.
Using Digital Design Tools
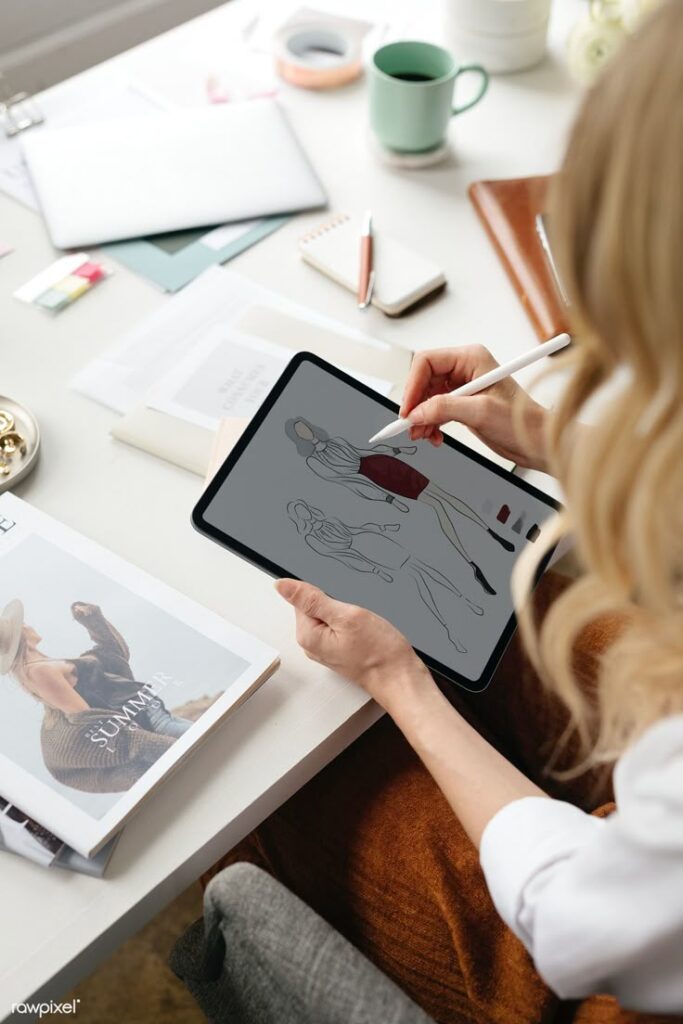


Digital tools have changed how fashion sketches are made. Programs like Adobe Illustrator, Clo3D, and Procreate allow designers to draw, color, and edit quickly.
Digital sketches can be resized and changed easily without redrawing everything. Layers help separate the body, clothing, and details for better control. Some tools include fabric simulation to see how materials hang or stretch.
Using a tablet and stylus mimics hand drawing but adds precision. Designers can add textures, lighting, and even 3D views. These tools also speed up the process of making variations of a design to explore colors or styles before finalizing.
Selecting Fabrics and Materials
Choosing the right fabric involves balancing how a garment looks and feels with how it performs. It means thinking about comfort, durability, texture, and the impact on the environment. These factors help bring a designer’s vision to life.
Choosing Fabrics for Function and Style


Designers start by matching fabric types to what the garment needs to do. For example, cotton is great for casual wear because it’s soft and breathable. Wool works well for warm coats since it holds heat.
They also consider the weight of the fabric. Lightweight fabrics like chiffon drape nicely for flowy dresses, while heavier fabrics like denim add structure to jackets.
Key points to check include:
- Material type (natural or synthetic)
- Fabric weight and thickness
- Stretch and recovery for fit
- Color and print choices
Understanding Textures
Texture affects both how a garment looks and how it feels on the skin. Smooth fabrics like silk give a polished, elegant look. Rougher textures, such as tweed, add visual interest and warmth.
Textures can also change how light interacts with the fabric, making some garments shiny and others matte. Designers often mix textures to create contrast or highlight parts of an outfit.
Texture guides comfort too. Breathable fabrics with a soft texture increase wearability. Stiff or scratchy textures might limit comfort or suitability for certain clothing items.
Exploring Sustainable Materials
More designers choose eco-friendly fabrics to reduce environmental impact. Sustainable fabrics use fewer chemicals and less water in production. Examples include organic cotton, bamboo, and hemp.
Recycled materials like polyester from plastic bottles are also popular. They help lower waste and use resources wisely.
Using sustainable materials means checking for certifications like GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) or OEKO-TEX. These labels show fabrics meet strict environmental and health guidelines.
Choosing eco-friendly fabrics supports both fashion and the planet.
Transforming Designs Into Finished Garments
Turning a fashion design into a real piece of clothing takes careful planning and skill. This process involves creating patterns, sewing the fabric together, and making sure the garment fits well. Each step is important to create a polished, wearable item.
Pattern Making Basics


Pattern making is like creating a blueprint for clothes. It starts with taking accurate body measurements. These measurements help draft pieces of paper or digital patterns that match the shape and size needed.
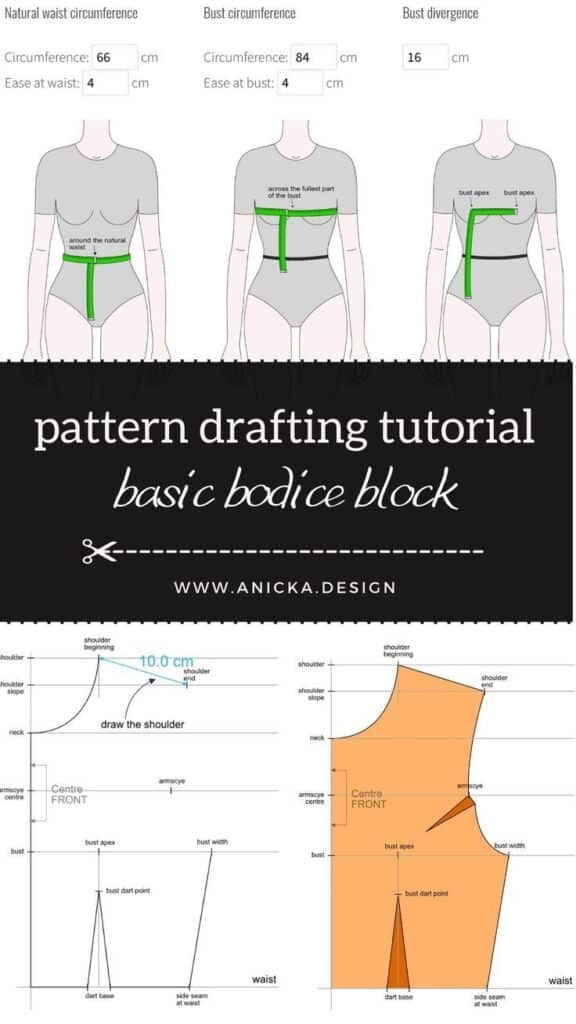

Patterns are typically made for each garment part, like the front, back, sleeves, and collars. These pieces guide where the fabric should be cut. It’s important to add seam allowances to allow space for sewing.
Adjusting patterns is common to change fit or style. Sometimes designers make a toile, which is a test garment from cheap fabric, to check the pattern before cutting final materials.
Sewing and Construction Techniques


Sewing is the process of joining fabric pieces using stitches. Different stitch types and sewing machines are used depending on the fabric and garment design. Basic stitches include straight, zigzag, and overlock.
Key construction techniques include hemming edges, adding darts or pleats for shaping, and attaching fasteners like zippers or buttons. Precision is important to keep seams clean and strong.
Layers and lining might be added for comfort or structure. Quality control during sewing helps avoid weak spots in the garment that could wear out quickly.
Fitting and Adjustments
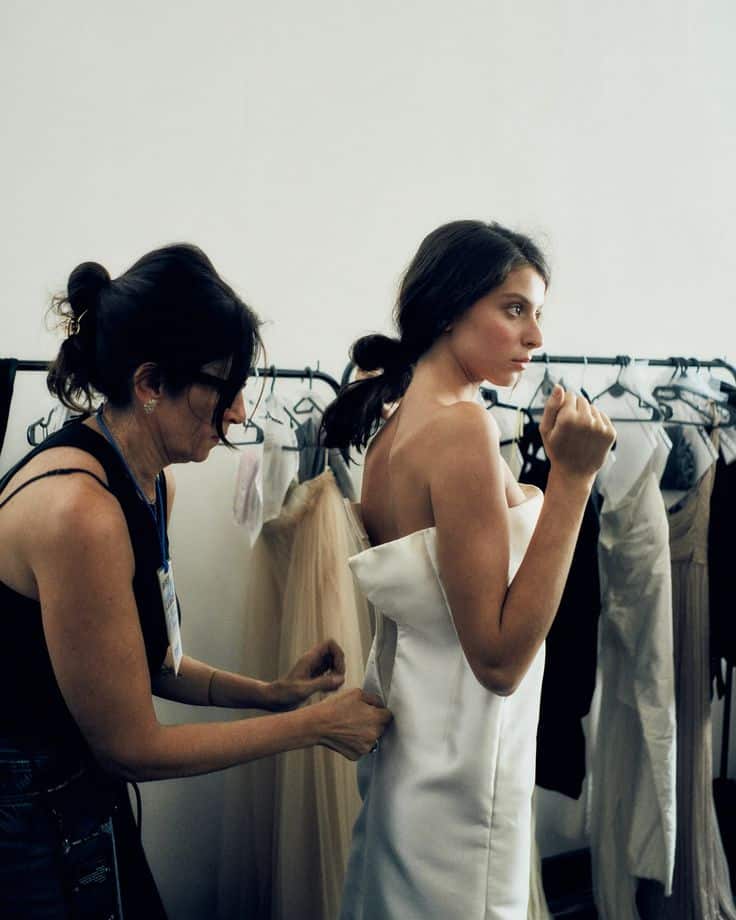


Fitting tests how well the garment matches the wearer’s body. Designers or tailors check the garment on a model or fitting form, looking for tight spots, loose areas, or uneven hems.
Adjustments often involve pinching fabric to remove excess or letting out seams to add room. It’s common to reshape elements like sleeves or necklines for better comfort.
Multiple fittings may be needed to perfect the fit. Accurate alterations ensure the finished clothing looks intentional and feels comfortable to wear.
Showcasing and Marketing Your Fashion Designs
To get noticed, designers need to organize their work well, present it effectively at events, and use social media smartly. These steps help build a strong brand and connect with buyers, clients, and collaborators.
Creating a Fashion Portfolio


A fashion portfolio is a must-have for any designer. It shows the best pieces and highlights their skills and style. The portfolio should include high-quality photos of finished garments, sketches, and mood boards.
Designers should keep it clear and easy to navigate. Grouping pieces by collection or theme helps tell a story. Adding short descriptions with details about materials and techniques used adds value.
A digital version is important now. It can be emailed or shared on websites and social media. Using platforms like Behance or a personal website makes the work easy to find and professional.
Presentation for Fashion Shows
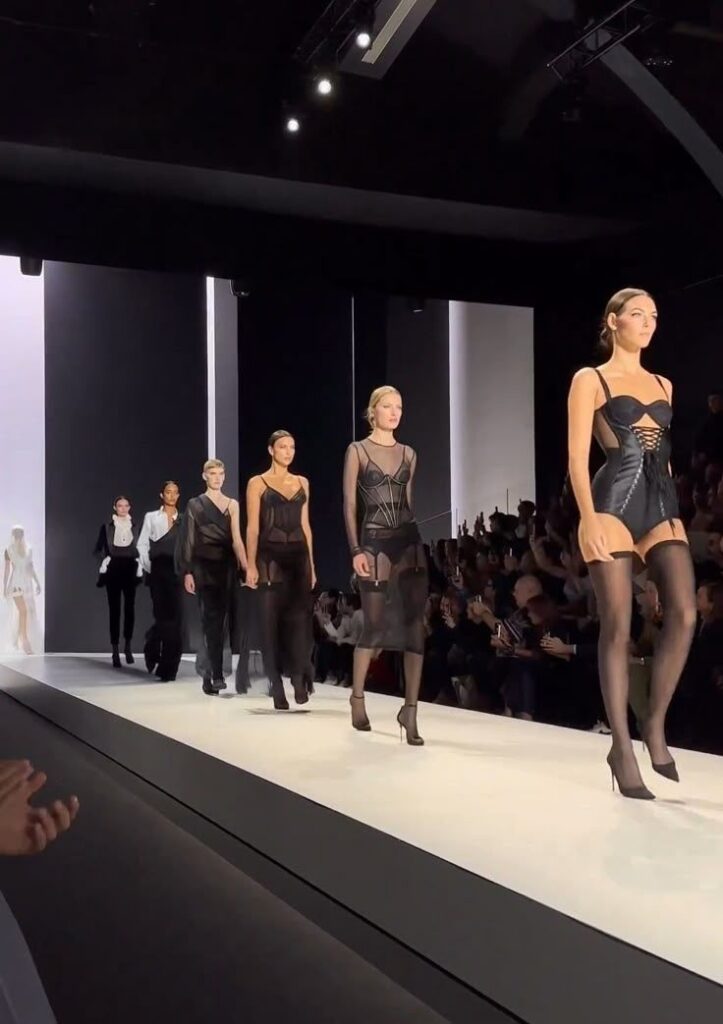


Fashion shows are a key way to show designs in action. Designers should focus on selecting pieces that represent their brand clearly. It’s important to plan the order and style of outfits for a strong flow.
Lighting, music, and model choices also affect how the clothes are seen. Creating an atmosphere that matches the collection’s mood helps leave a lasting impression.
Networking is another benefit of shows. Designers can meet buyers, press, and other industry people. Being prepared with business cards and a clear message helps make these connections count.
Leveraging Social Media
Social media lets designers reach a wide audience quickly. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Pinterest are perfect for sharing photos, videos, and behind-the-scenes content.
Posting regularly keeps followers interested. Using hashtags and tagging relevant accounts can increase exposure. Collaborating with influencers can also help reach new clients.
Designers should interact with followers by replying to comments and messages. This builds a loyal audience who feel connected to the brand.
Tracking which posts get the most attention helps adjust the strategy for better results. Being active and genuine on social media is key to growing a fashion brand today.
Conclusion
Fashion design looks glamorous from the outside—sketches, mood boards, runway shows. But the actual skill is more practical than artistic. It’s understanding that certain fabrics won’t hold the shape you drew. It’s knowing that a seam placed wrong will pull uncomfortably across the shoulder. It’s accepting that your gorgeous sketch needs to be completely reimagined to work on a real body.
The designers who succeed aren’t necessarily the most creative—they’re the ones who bridge imagination and construction. They sketch knowing how the garment will be built. They choose fabrics understanding how they’ll behave. They adjust patterns knowing how bodies actually move.
This week: Create a mood board for one simple garment—a basic skirt or top. Include fabric swatches, not just images. Touch the materials. Think about how they’d feel against skin, how they’d drape, whether they’d wrinkle.
Next month: Make that garment. Use a commercial pattern if you’re new to sewing. The goal isn’t perfection—it’s understanding the gap between your design vision and construction reality. That gap is where real fashion design knowledge lives.
Ongoing: Build your fabric vocabulary. Every time you encounter a new material, note how it behaves: stretch, drape, weight, texture. This knowledge will inform every design decision you make. A designer who understands materials designs differently than one who only understands aesthetics.
Fashion design is learnable. Not easy, but learnable. Start with the fundamentals covered here, accept that your first constructions won’t match your sketches, and keep closing the gap between vision and reality. That’s the work.
- 4shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest0
- Twitter4
- Reddit0


