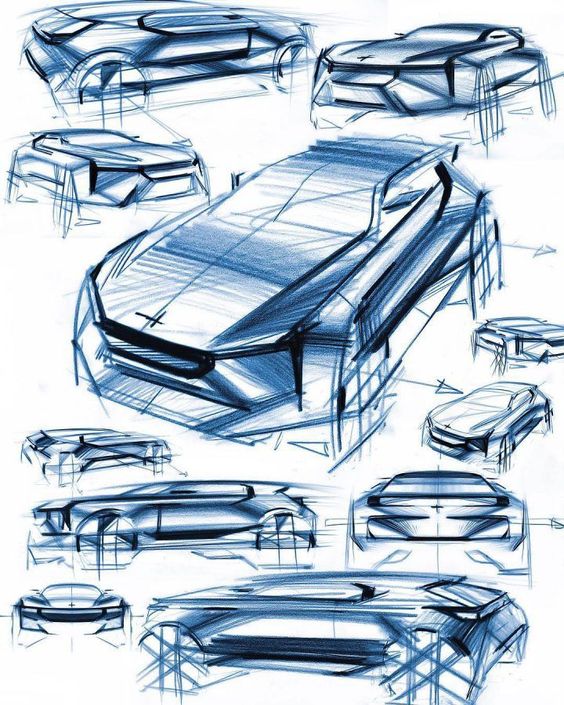

Car sketches serve as the foundation of automotive design, allowing designers to visualize concepts before they become tangible. These preliminary drawings play a critical role in shaping the final vehicle and communicate ideas efficiently. Understanding the techniques and tools used in car sketching can inspire both aspiring designers and enthusiasts alike.
Many industry professionals began their journeys with simple sketches that evolved into complex designs. The history of car sketching reflects ongoing innovations and trends, revealing how artists adapt to new technologies and methodologies. By exploring these concepts, readers can grasp the significance of sketching in the car design process.
As the automotive industry evolves, the importance of proficiency in sketching remains paramount. Designers must balance traditional techniques with digital tools to create compelling visuals. Through this exploration, car enthusiasts and future designers can appreciate the art and science behind every vehicle they admire on the road.
Key Takeaways
- Car sketches are essential in the car design process.
- Understanding sketching techniques and tools is vital for aspiring designers.
- The evolution of car sketching reflects changes in technology and design trends.
History of Car Sketching
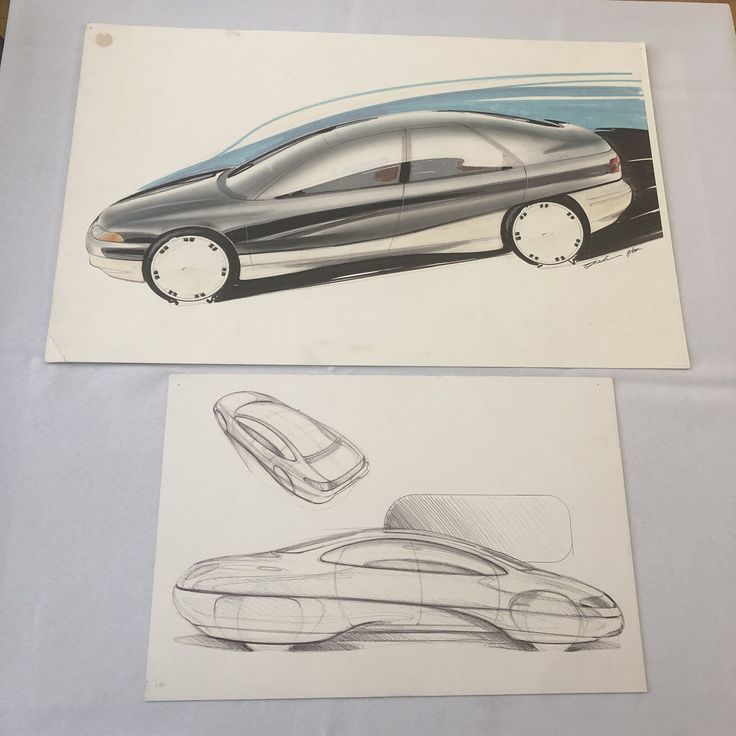

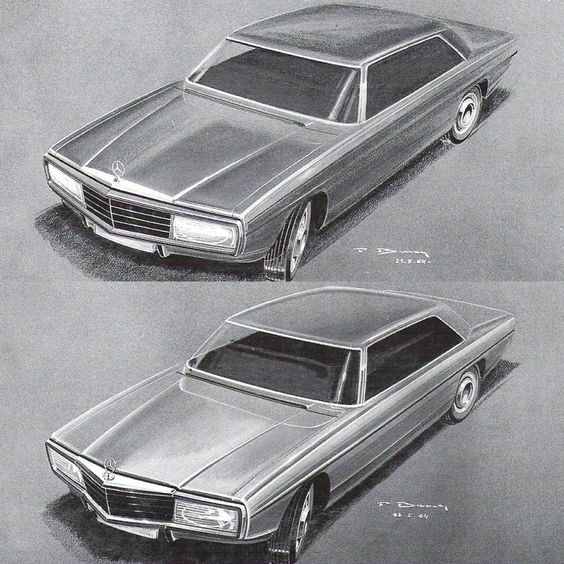
Car sketching has a rich history that reflects the evolution of automotive design. The methods and styles have changed significantly, influenced by technology and the creative visions of notable designers. This section explores the development of design techniques and highlights influential designers known for their impactful sketches.
Evolution of Design Techniques
In the early days of automotive design, sketches served as the primary means for designers to communicate ideas. Initial methods involved basic hand-drawn illustrations that focused on functionality and aerodynamics.
As technology advanced, the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) transformed the sketching process. Designers could create more precise and complex shapes, integrating 3D modeling into their workflow.
Digital tools also allowed for rapid iterations and modifications, enabling designers to visualize concepts more effectively. The shift from physical media to digital platforms has streamlined the workflow and expanded creative possibilities.
Influential Car Designers and Their Sketches
Several car designers have made significant contributions to the art of car sketching. Figures such as Pininfarina, Giugiaro, and Ferdinand Porsche are known for their iconic designs and distinctive sketches.
Pininfarina, for instance, produced numerous sketches that captured the essence of elegance combined with performance. His work influenced the styling of many luxury vehicles.
Similarly, Giorgetto Giugiaro introduced groundbreaking design principles through his sketches, impacting the direction of automotive aesthetics in the 20th century. Each designer’s unique approach has shaped modern automotive design, leaving a lasting legacy in the industry.
These designers continue to inspire new generations, demonstrating the vital role that car sketches play in the creative process of automotive engineering.
Fundamentals of Car Sketching
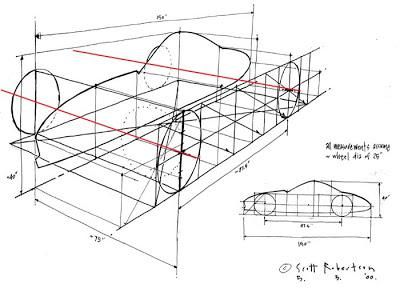
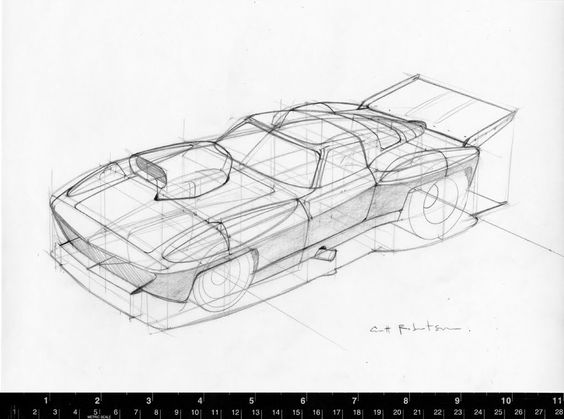
Car sketching requires a solid understanding of key elements such as anatomy, techniques, and perspective. Mastery of these fundamentals helps in creating accurate and aesthetically pleasing drawings. Attention to detail plays a crucial role in bringing automotive designs to life.
Understanding Car Anatomy
Anatomy refers to the structure and components of a car, which sketch artists must grasp to create realistic representations. Key parts include:
- Chassis: The frame structure supporting the body.
- Body: The external shell that defines the car’s shape.
- Wheels and Tires: Crucial for stability and aesthetics.
- Windows and Lights: Essential features that add character.
Understanding these components enables an artist to depict a car’s design accurately, ensuring that features are proportionate and logical. Recognizing the flow and connection between parts also helps in achieving dynamic sketches.
Basic Sketching Techniques
Effective sketching techniques form the backbone of strong car illustrations. Practitioners should focus on several critical methods:
- Gesture Drawing: This technique helps capture the car’s essence quickly. It involves making rapid sketches to convey movement and dynamic angles.
- Line Work: Clean, confident lines define edges and shapes. Artists should refine their lines to ensure clarity and precision.
- Shading: Proper shading techniques add depth and dimension. Using light and dark areas helps to create the illusion of volume on a flat surface.
Regular practice of these techniques enhances precision and increases the artist’s ability to convey their vision effectively.
Perspective and Proportions
Understanding perspective and proportions is vital for creating believable car sketches. Artists should consider different viewpoints, such as:
- Eye Level: This standard viewpoint helps maintain proportions.
- Bird’s Eye View: Useful for emphasizing overall shape.
- Worm’s Eye View: Adds drama and grandeur to the design.
Maintaining accurate proportions is essential. The average car is about 1.5 times longer than its height. Ensuring that all elements are in scale fosters realism. Using grid systems can help maintain correct proportions and placement in the sketch.
Tools and Materials
Artists utilize various tools and materials to enhance their car sketches, both in traditional and digital formats. Each method offers unique advantages that cater to different preferences and styles.
Traditional Sketching Tools
Traditional sketching requires specific tools that enable artists to express their creativity effectively. Essential items include:
- Pencils: Graphite pencils ranging from H (hard) to B (soft) allow for varied line quality. Artists often use different grades to achieve specific shading or detail levels.
- Markers and Inks: Permanent markers or pens, such as fine-tipped and brush markers, provide bold lines and precision, making them suitable for finalizing sketches.
- Sketch Pads: High-quality sketch paper is critical. It needs to support pencil, ink, and marker without bleeding or tearing.
- Erasers: Kneaded or vinyl erasers assist in correcting mistakes without damaging the paper.
These tools help create detailed and dynamic representations of automotive designs.
Digital Design Software
Digital platforms have revolutionized car sketching, offering advanced features and flexibility. Popular software includes:
- Adobe Photoshop: A versatile choice for digital artists, it allows for detailed painting, layering, and editing.
- Autodesk Sketchbook: Known for its intuitive interface, this software caters specifically to sketch artists, featuring multiple brushes and tools.
- Corel Painter: This program simulates traditional tools, offering various brushes that recreate the look of pencils, inks, and paints.
- Procreate: Targeted at iPad users, it boasts a user-friendly design and countless customization options, making it ideal for on-the-go sketching.
These tools support a wide range of styles, from quick concepts to polished illustrations.
The Design Process

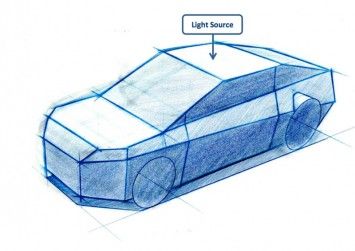
The design process for car sketches involves multiple stages that contribute to crafting a cohesive and functional design. Key areas include initial concept development, ideation through thumbnails, and the refinement of sketches with detailed elements. Each step is crucial in achieving an effective design.
Conceptualization and Research
Conceptualization marks the beginning of the car design process. Designers must gather information about market trends, target audiences, and existing automotive designs.
Key tasks include:
- Market analysis: Understanding customer preferences.
- Competitor research: Evaluating similar car models and their features.
This research helps define the design philosophy that will guide the sketching process. Visual references from art, architecture, and nature can provide inspiration. These ideas serve as a foundation for the sketching phase, ensuring the design is innovative and relevant.
Thumbnail Sketches and Ideation
Once the concept is clear, designers create thumbnail sketches to manifest their ideas quickly. These sketches are small, rough drafts that capture different angles, forms, and proportions of the car.
Key aspects include:
- Rapid exploration: Quick iterations allow for creativity.
- Variations: Offering different interpretations of a single concept.
Reviewing these thumbnails helps designers select promising concepts for further development. Feedback from peers can refine directions taken, ensuring the initial concepts resonate with the intended audience.
Refining Sketches and Detailing
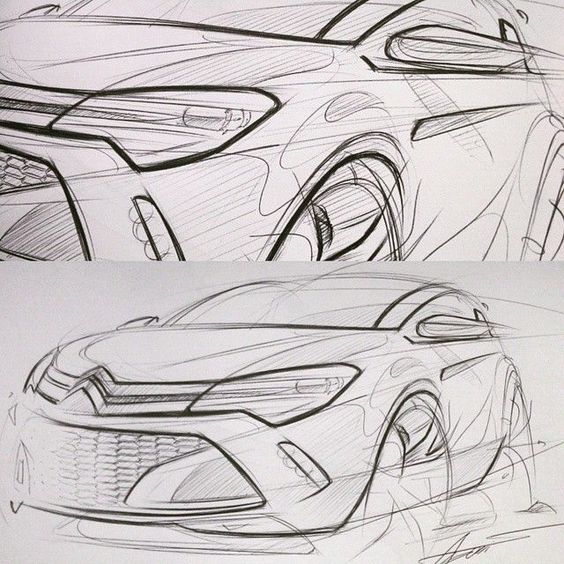

After selecting the most compelling thumbnails, designers refine their sketches into more detailed renderings. This stage emphasizes the physical attributes of the vehicle, such as:
- Proportional accuracy: Ensuring dimensions are correct.
- Material consideration: Thinking about textures and finishes.
Further detailing may include the integration of functional elements like lighting and aerodynamics. Digital tools can aid in this phase, allowing for precise adjustments. The goal is to produce sketches that are both aesthetically pleasing and practical, ready for presentation to stakeholders or clients.
3D Modeling and Rendering
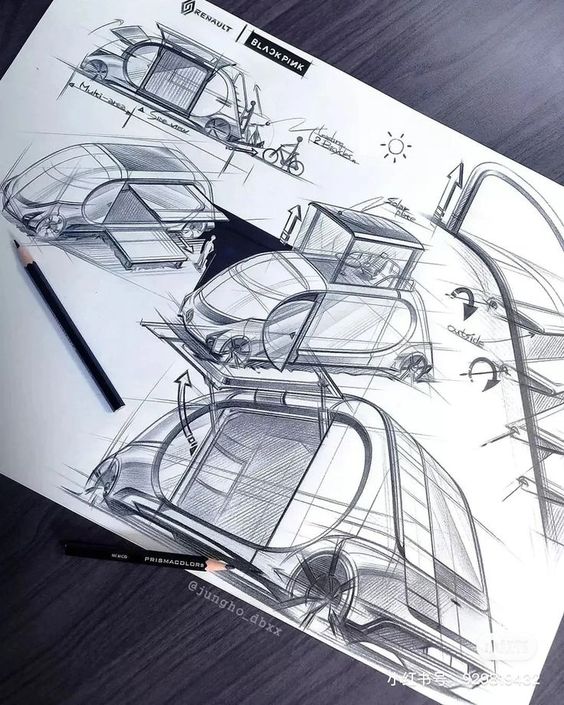


3D modeling and rendering are essential processes in converting car sketches into lifelike representations. These techniques allow designers to visualize concepts in three dimensions, enabling finer details and realistic depictions.
Transition from 2D to 3D
Transitioning from 2D sketches to 3D models involves several steps. Initially, designers use software like AutoCAD or CAD applications to trace the sketches. This process ensures that proportions and dimensions are accurately represented.
Once traced, the designer begins to extrude shapes to create a base model. At this stage, adding details like curves and indentations is crucial. Software tools allow for modifications, enabling designers to refine their models iteratively.
The use of references from real vehicles enhances accuracy. This transition not only improves visualization but also aids in making design decisions early in development. As a result, the final model is more aligned with functional and aesthetic goals.
Rendering Techniques for Realism
Rendering is the process that creates the final visuals from 3D models. Techniques used include ray tracing and rasterization. Ray tracing simulates light more realistically, capturing reflections and shadows for greater depth.
Texturing plays a significant role in realism. Designers apply various materials to surfaces, such as metals, fabrics, and plastics. These textures are often sourced from libraries or created from photographs, mimicking real-world characteristics.
Lighting setups also contribute heavily to visual impact. By adjusting light positions and intensities, designers can create different times of day or atmospheric conditions. This attention to detail elevates the presentation of the car model significantly, making it appealing for stakeholders or marketing purposes.
Incorporating these elements produces a striking representation that resonates with viewers’ expectations.
Presentation and Critique


Effective presentation and critique are essential components of showcasing car sketches. Designers must compile a polished portfolio and hone their presentation skills to effectively communicate their concepts.
Compiling a Portfolio
A well-structured portfolio is vital for any designer. It should include a diverse selection of car sketches that demonstrate proficiency in various styles and techniques.
Key elements to consider:
- Variety: Include sketches of different car types, from concept models to more refined designs.
- Process: Showcase the development stages, displaying initial concepts alongside final sketches.
- Quality: Ensure high-resolution images and clean presentation, as clarity impacts perception.
- Personal Branding: Incorporate a consistent style that reflects the designer’s identity.
This combination enhances the portfolio’s effectiveness in capturing attention and conveying a designer’s capabilities.
Presentation Skills for Designers
Presentation skills play a crucial role in delivering ideas effectively. Designers must engage their audience and articulate their vision clearly.
Essential skills include:
- Storytelling: Narrate the design journey, explaining inspirations, challenges, and solutions.
- Visual Aids: Use slides, boards, or digital tools to enhance the presentation and support verbal communication.
- Body Language: Maintain an open posture and eye contact to establish connection and confidence.
- Question Handling: Prepare for inquiries and critiques with thoughtful responses, demonstrating openness to feedback.
Mastering these skills leads to impactful presentations that resonate with clients and stakeholders.
Trends and Future of Car Sketching
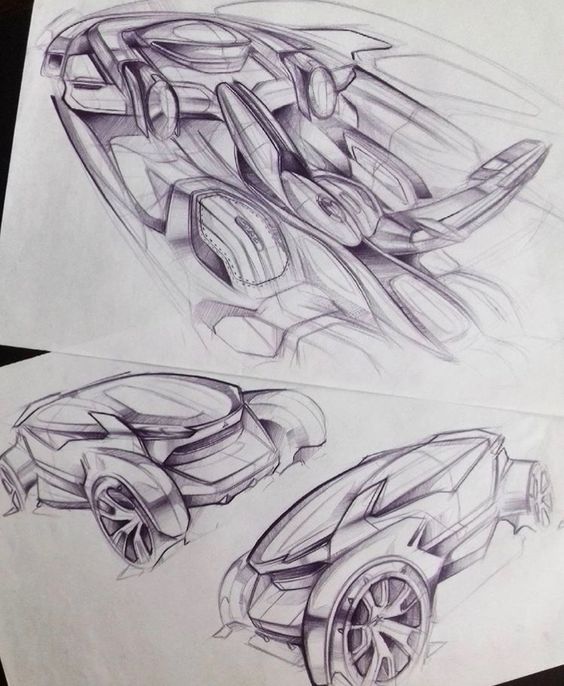
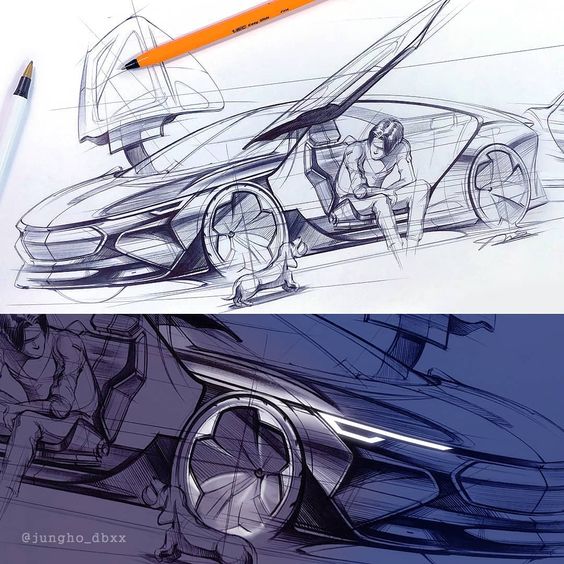

Car sketching is evolving with technology and societal changes. Innovations in design tools and a focus on sustainability are shaping the future of automotive illustration.
Innovations in Automotive Design
Recent advancements in digital tools have transformed car sketching. Software like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and 3D modeling are now essential. These tools allow designers to produce precise sketches quickly.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) offer new dimensions for visualizing designs. Designers can create immersive experiences, enabling stakeholders to explore concepts in real-time. This immediacy streamlines the feedback process and enhances collaboration.
Moreover, generative design algorithms harness machine learning to propose creative solutions. This allows designers to experiment with forms that might not be feasible through traditional methods.
Sustainability in Car Design
Sustainability is a crucial consideration in modern car sketching. Designers increasingly focus on materials and processes that minimize environmental impact. This includes the use of recycled materials and innovations like biomimicry.
The shift towards electric vehicles drives new design requirements. Car sketches now incorporate efficient aerodynamics and lightweight structures to enhance performance.
There is also a growing emphasis on holistic design approaches. This includes considering a vehicle’s lifecycle, from production to recycling. Designers aim to create cars that are not only appealing but also sustainable, reflecting consumer demand for responsible choices.
Case Studies
Case studies of car sketches highlight the evolution of iconic designs and the impact of redesigns on brand identity. These explorations provide insights into how successful automotive designs are conceived and adapted over time.
Iconic Car Designs
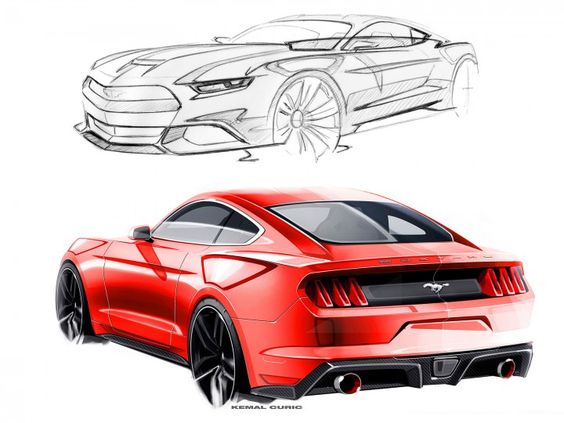


Iconic car designs often emerge from initial sketches that capture the essence of innovation and aesthetics. For instance, the Ford Mustang, first sketched in the early 1960s, revolutionized the American muscle car market. The original sketches showcased a blend of aggressive lines and sporty stance, appealing to a youthful demographic.
Another notable example is the Porsche 911. Its distinct silhouette and design elements have remained largely unchanged since the 1960s. The sketches emphasized functionality and aerodynamics while maintaining a timeless appeal, solidifying its status in automotive history.
These designs illustrate how initial concepts can lead to enduring models that symbolize a brand’s legacy.
Redesigns and Rebranding


Redesigns often play a crucial role in refreshing a brand’s image while retaining its heritage. The Volkswagen Beetle, originally designed in the 1930s, underwent several transformations. The more modern renditions retained the recognizable round shape but incorporated contemporary technology and design elements.
Similarly, the Mini Cooper saw significant redesigns since its launch in the 1960s. The sketches aimed at modernizing the classic appeal while introducing enhanced features for today’s consumers.
These case studies demonstrate the balance between innovation and the preservation of iconic attributes, essential for successful rebranding efforts.
Career Pathways in Car Design
A career in car design involves a distinct combination of education and practical experience. Understanding the necessary qualifications and pathways to enter the industry is crucial for aspiring auto designers.
Education and Skill Development
To succeed in car design, formal education is often essential. Many professionals hold degrees in industrial design, automotive engineering, or fine arts. Programs that focus on transportation design can be particularly beneficial.
Critical skills include:
- 3D modeling: Proficiency in software like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) or Rhino is vital.
- Sketching and rendering: Ability to create compelling designs through sketches that capture vision.
- Understanding materials: Knowledge of different materials used in car manufacturing helps designers select appropriate options.
Internships and hands-on projects during studies can provide practical experience and enhance portfolios, making candidates more appealing to employers.
Breaking into the Industry
Entering the car design industry can be competitive. Building a strong portfolio that highlights unique concepts and technical skills is necessary.
Many start as design interns or junior designers within automotive firms. Networking opportunities, such as attending industry conferences or joining design organizations, can facilitate connections with professionals.
Consider exploring:
- Automaker internships: These provide on-the-job training and insight into company operations.
- Design competitions: Participating in competitions can showcase talent and gain visibility among industry leaders.
Persistence and adaptability are key traits for those looking to carve out a successful career in car design.
- 132shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest132
- Twitter0



