My first butterfly drawing looked like a squashed avocado with antennae. I’d copied what I thought a butterfly looked like from memory — and completely missed the most useful trick: butterflies are basically two mirror-image triangles attached to a sausage. That’s it.
Once I figured that out, everything clicked. And that’s exactly what I’m going to show you here.
- 1. Understanding Butterfly Anatomy (So Your Drawing Doesn't Look Like Guesswork)
- 2. The 3 Easiest Butterfly Species to Draw (and Why)
- 3. Materials That Make a Real Difference (Without Breaking the Bank)
- 4. Drawing a Butterfly Step by Step: The 5-Step Method
- 5. Coloring Techniques That Make Wings Look Real
- FAQ: Butterfly Drawing Questions People Actually Ask
- Q: How do I draw a butterfly that looks symmetrical?
- Q: What's the easiest butterfly to draw for beginners?
- Q: How do you make butterfly wings look realistic?
- Q: Do I need expensive colored pencils for butterfly drawing?
- Q: How long does it take to draw a butterfly?
- Q: Can kids learn to draw butterflies easily?
- Your First Butterfly is 5 Steps Away
This guide walks you through butterfly drawing in 5 concrete steps — from the initial gesture to adding color that actually pops. You’ll also learn which species are easiest to start with, what materials make the biggest difference, and the one anatomy detail most tutorials skip that changes everything.
No prior experience needed. Grab a pencil.
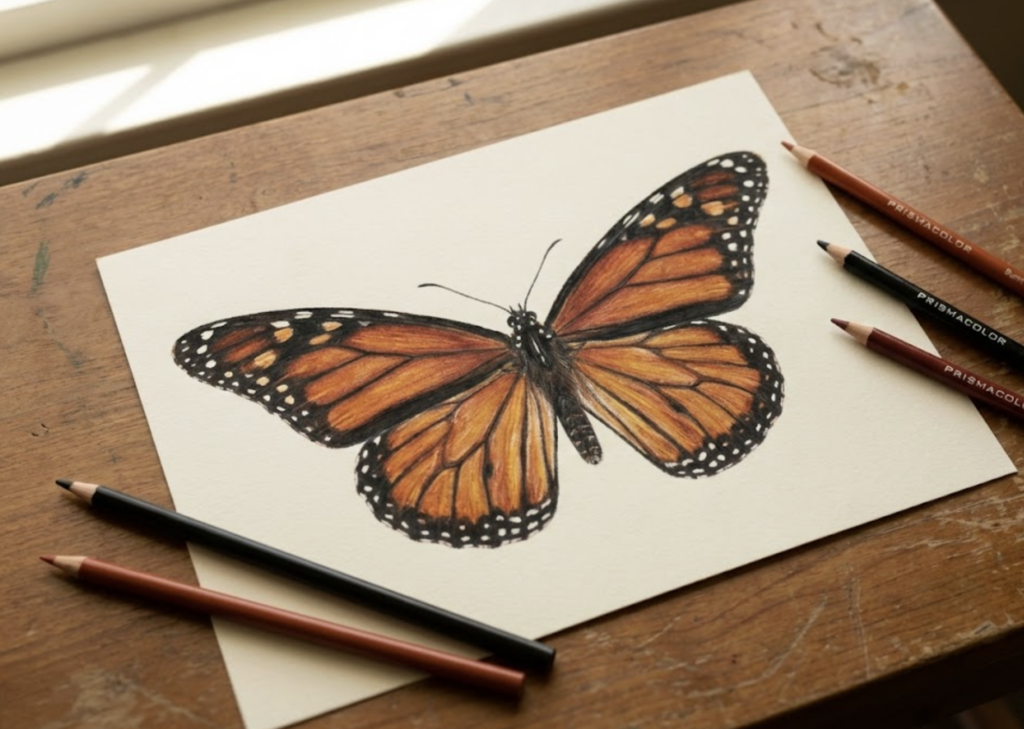

1. Understanding Butterfly Anatomy (So Your Drawing Doesn’t Look Like Guesswork)
Here’s the shortcut nobody tells beginners: butterflies are symmetrical. Draw one half well, mirror it, and you’ve got a butterfly. That’s the whole secret. But first, you need to understand the four main parts you’re actually drawing.
The Body: Think ‘Pill Capsule’
The body isn’t just a line — it has three distinct sections: a small, round head, a wider thorax (where the wings attach), and a longer, tapered abdomen. When drawing, make the thorax about as wide as two pencil tips. The whole body should be roughly 1/3 the total wingspan — not half, not a quarter.

I’ve noticed beginners almost always draw the body too thin and too long. If your butterfly looks like a stick insect in disguise, the body proportions are probably off.
Wings: Forewings vs. Hindwings
Forewings (the top pair) are roughly triangular — wider at the top, narrowing toward the body. Hindwings (bottom pair) are rounder and smaller, often scalloped at the edges. In a resting butterfly with wings spread flat, the hindwings slightly overlap the forewings near the body.


Antennae: The Detail Everyone Forgets
Real butterfly antennae end in a club — a small, rounded knob. Moth antennae taper to a point or look feathery. If your drawing has plain, straight lines for antennae, that’s a moth. Add the small club at the tip, and suddenly your butterfly looks like the real thing.
✦ Quick anatomy check: head tiny, thorax wider, abdomen longest. Hindwings are rounder than forewings. Clubs on antennae, not points.
2. The 3 Easiest Butterfly Species to Draw (and Why)
Not all butterflies are equal when it comes to drawing them. Some have complex eyespots and gradient patterns that’ll frustrate a beginner in minutes. These three have clear, simple markings that are actually forgiving to replicate.

Monarch: The Best Beginner Choice
Orange wings with bold black veins and a white-spotted black border. That’s the whole pattern. The Monarch’s markings follow the wing veins, which gives you a built-in grid to work with. Start here if you’re drawing for the first time.

- Wing color: burnt orange (Copic YR07 or Prismacolor Dark Umber + Yellowed Orange)
- Key detail: thick black border along outer wing edges with small white dots
- Body: entirely black with white dots — easy to replicate
Cabbage White: For Ultra-Clean Minimal Style
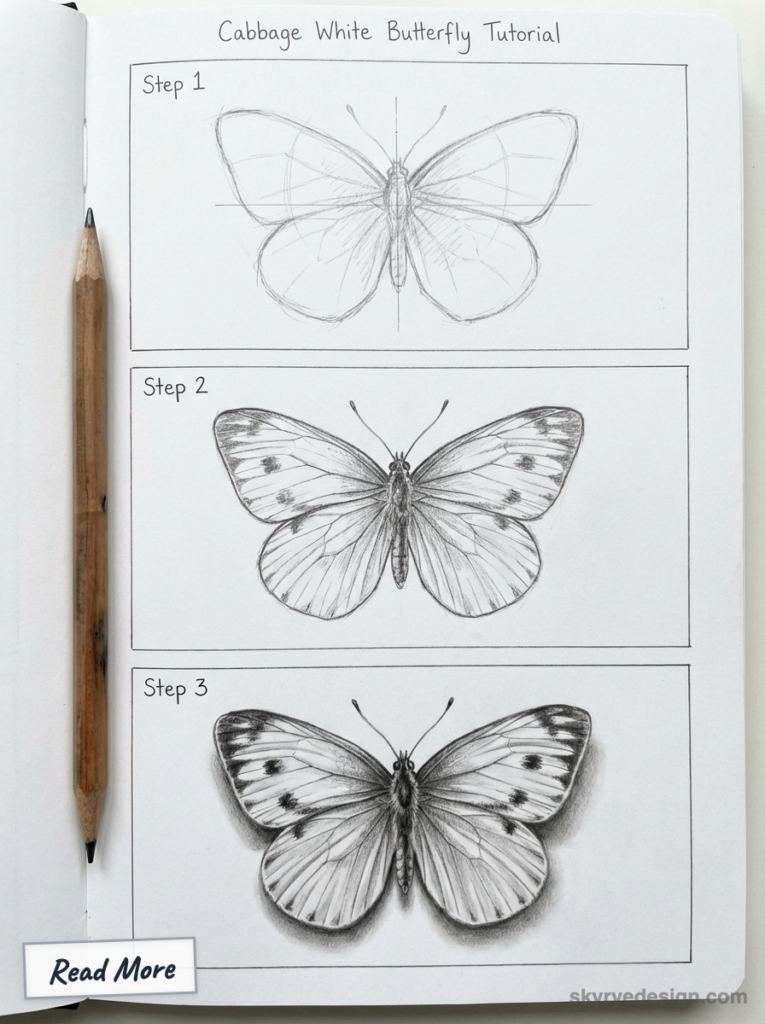

White or pale yellow wings with one or two small black spots near the forewing tip. Basically, the IKEA of butterflies — minimal, clean, satisfying. Great if you want to practice shading without worrying about complex patterns.
Swallowtail: When You Want a Challenge
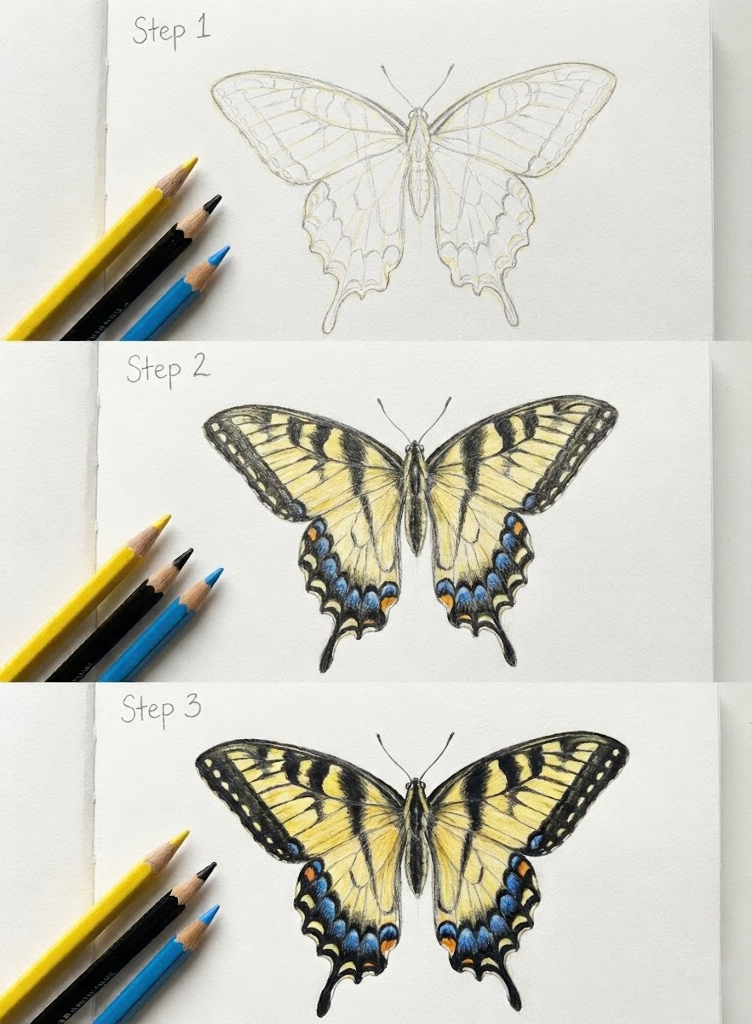

The Yellow Swallowtail (Papilio glaucus) has distinctive tail-like extensions on the hindwings — that’s the ‘swallowtail’ part. Yellow base with black tiger stripes and blue spots along the lower edges. More work, but visually dramatic. I’d tackle this after you’ve done 3-4 Monarchs first.
3. Materials That Make a Real Difference (Without Breaking the Bank)
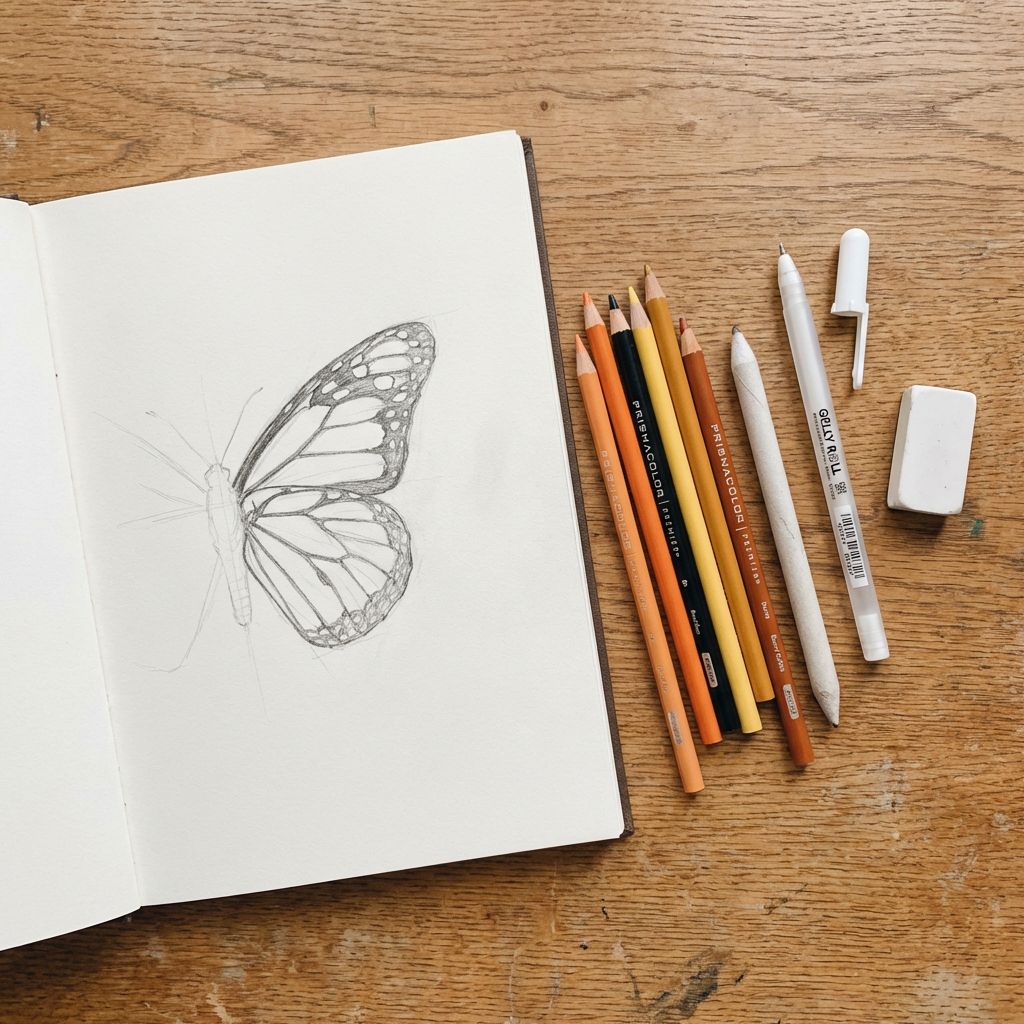

You don’t need expensive supplies to draw a good butterfly. But a few specific choices will save you a lot of frustration. I’ve drawn butterflies on printer paper with cheap pencils — and on Bristol board with Prismacolors. The gap in results is significant.
Paper: The Unsung Hero
For pencil sketching: Strathmore 400 Series Bristol (smooth surface, ~$15 for a 9×12 pad). Colored pencils glide on it without tearing, and erasing is clean. Regular printer paper works in a pinch, but tears if you layer colors.
For watercolor butterflies: Arches 140lb cold press. It doesn’t warp, and the texture adds natural depth to wing patterns.
Pencils: A Two-Tool System
Use an HB or 2B graphite pencil for the initial sketch — light enough to erase cleanly. For colored pencils, Prismacolor Premier ($25-35 for a 24-pack) gives you smooth layering and blending that cheaper sets can’t match. If the budget is tight, Faber-Castell Polychromos (~$40 for 24) is even better but costs more.
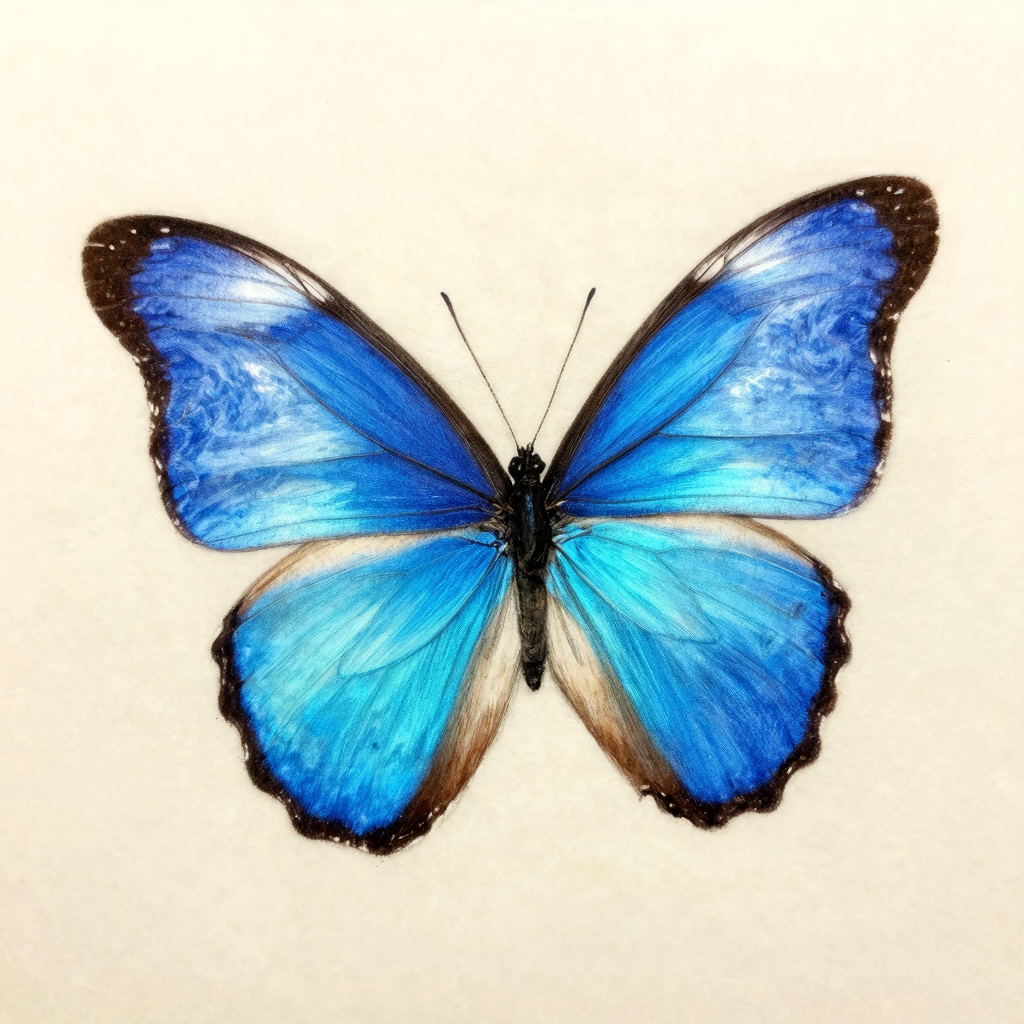
The three colors that carry most butterfly drawings: Yellow Ochre, Dark Brown/Black, and a vibrant Blue (Prismacolor ‘Denim Blue’ is underrated for Morpho butterflies).
The Two Tools Most Tutorials Don’t Mention
- White gel pen (Sakura Gelly Roll, ~$3) — for adding wing highlights and white spots that make drawings pop
- Blending stump (Prismacolor, ~$5 for a set) — smears colored pencil into smooth gradients; makes wings look translucent instead of flat.
✦ Total beginner kit cost: under $40. Sketchbook ($8) + basic colored pencils ($20) + blending stump ($5) + white gel pen ($3) = results that look like you know what you’re doing.
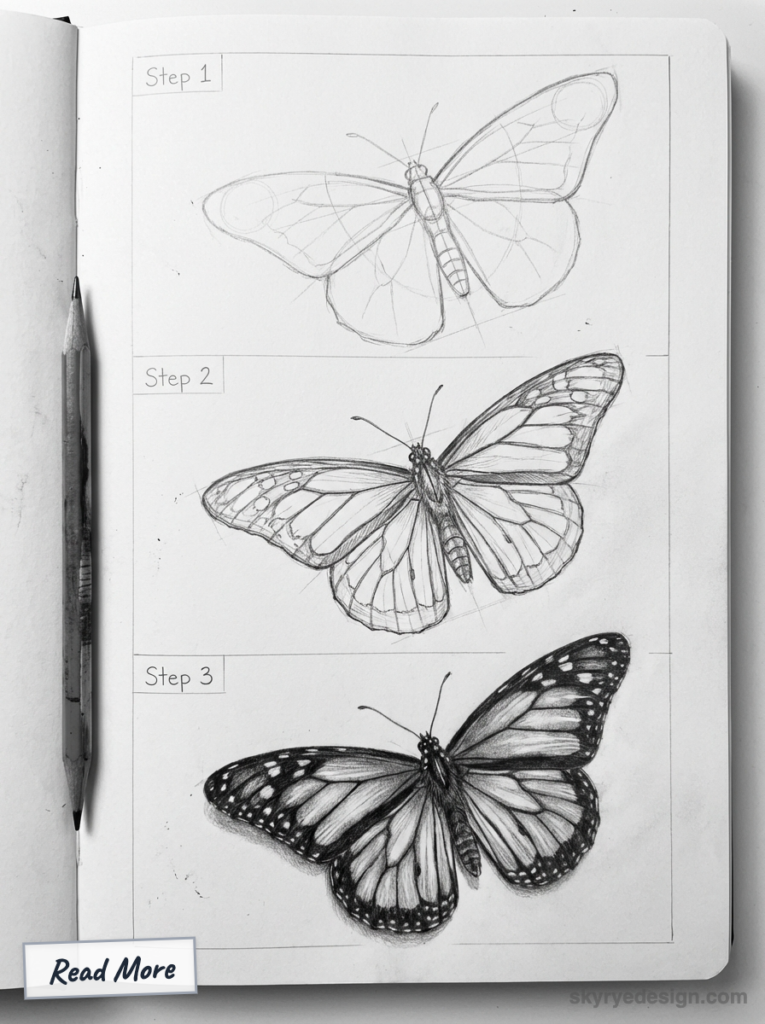
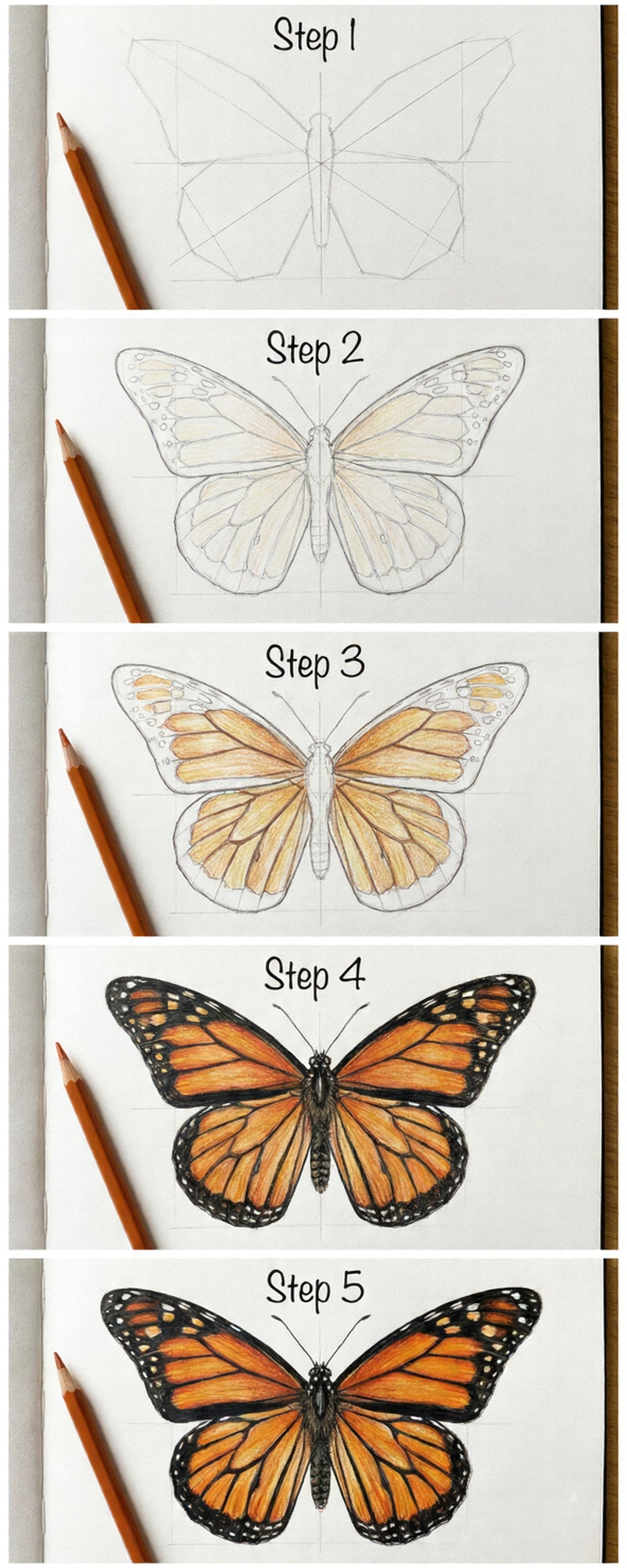
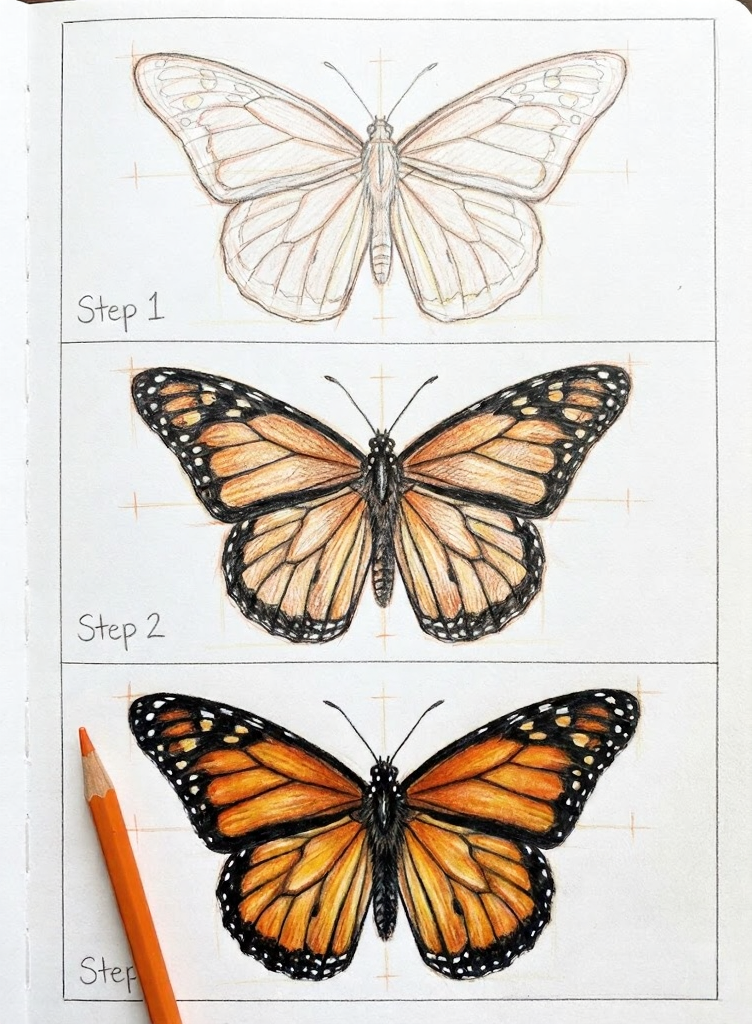
4. Drawing a Butterfly Step by Step: The 5-Step Method
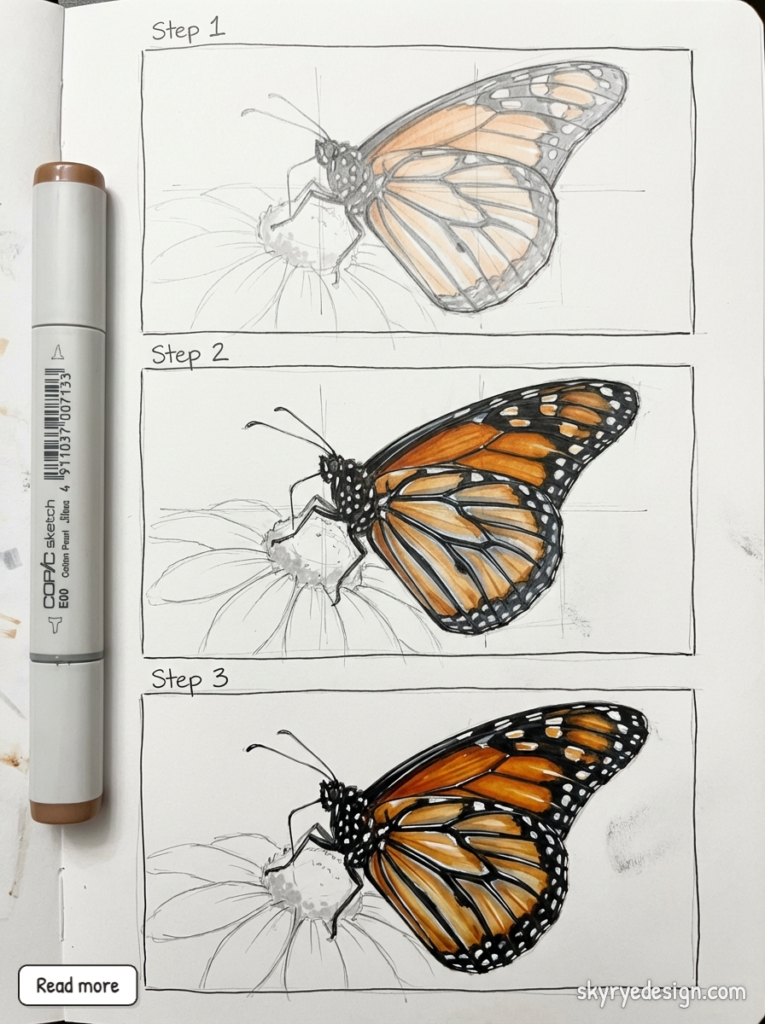
We’re going to draw a Monarch — the most recognizable butterfly and the most forgiving for beginners. Clear your space, use light pencil pressure, and don’t skip step 1 (most people do, and it shows).
Step 1 — Build the Geometric Framework
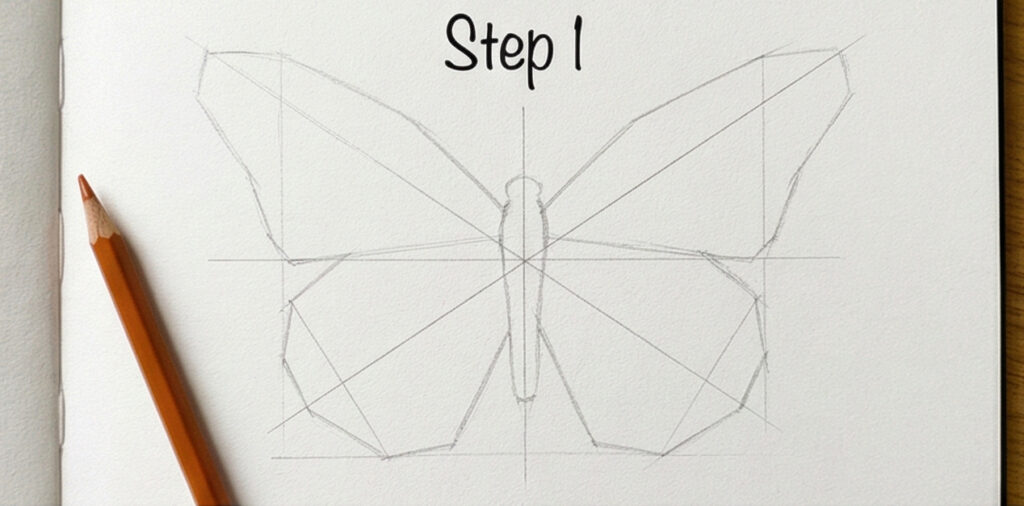
Resist the urge to draw curves right away. Start with straight angular lines — think of the wings as faceted crystal shapes, not soft organic forms. Draw your center axis first, then map out the wing silhouette with flat geometric segments. Press lightly; these lines disappear later. This angular skeleton is what keeps your final butterfly symmetrical.
✦ Symmetry trick: draw a light vertical center line first. Measure the width of one wing at three points, mark the same distances on the other side. Much more accurate than eyeballing.
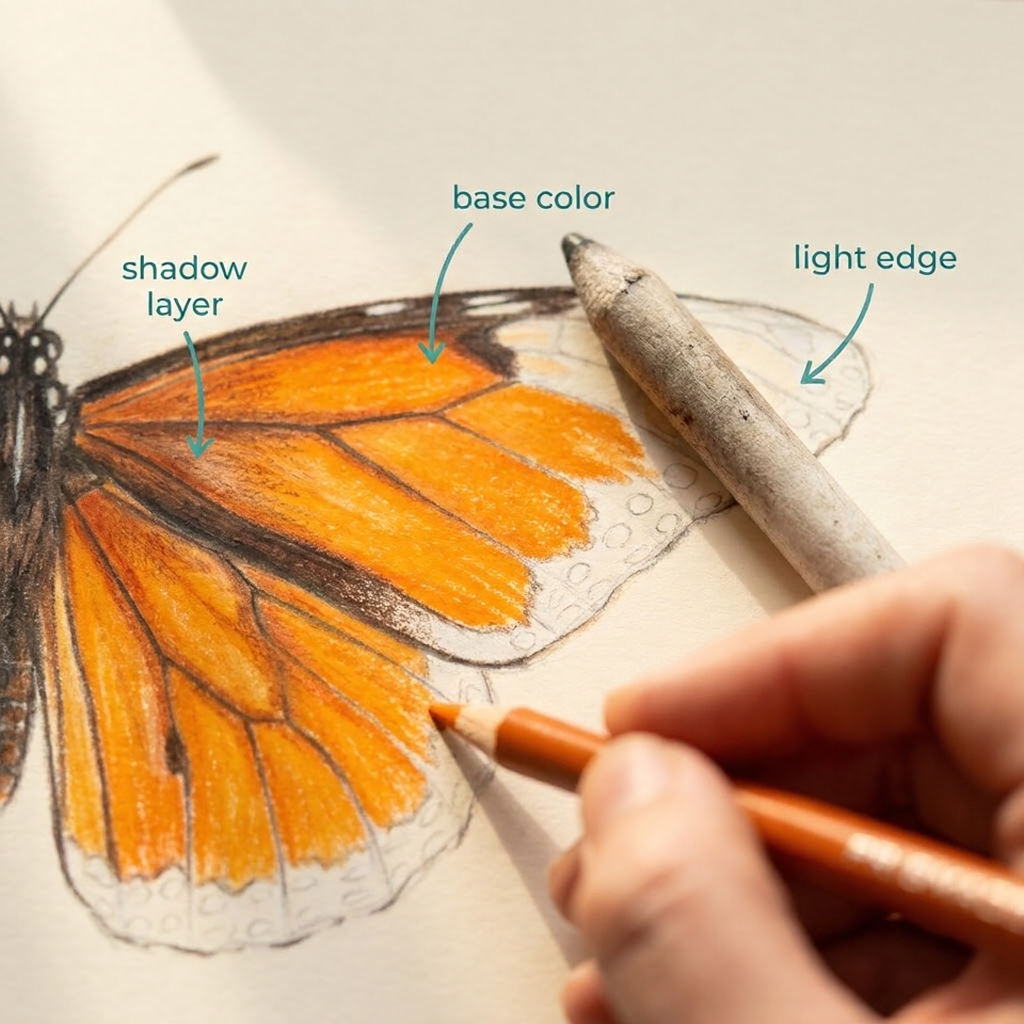
Step 2 — Lay Down the Base Color
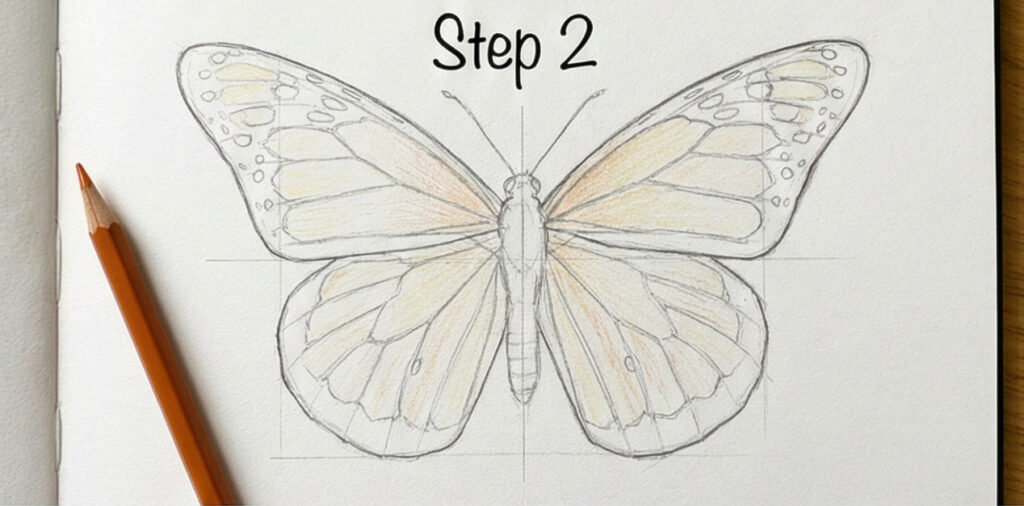
Cover the entire wing area with a very light warm yellow — almost cream. This isn’t the final color, it’s a primer. That underlayer makes the orange you add next look richer and more saturated than if you’d applied it to bare paper. Leave the veins and body untouched for now. At this stage your butterfly should look pale and unfinished. That’s correct.
Step 3 — Build Orange Cell by Cell
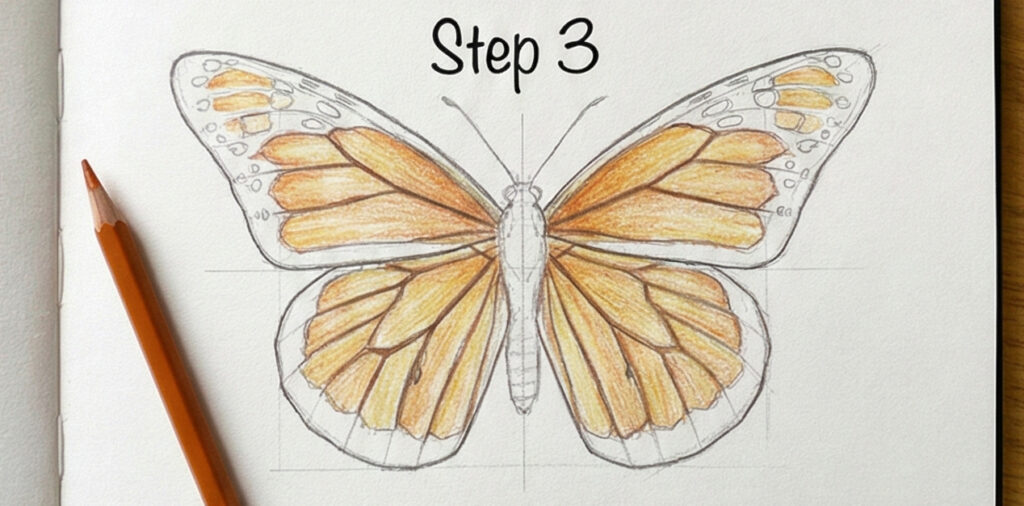
Work between the veins, not over them — each cell gets its own layer of orange. Go slightly darker near the body, lighter toward the wing tips. Don’t try to make it vibrant yet; you’re just establishing the value structure. The veins still read as light lines at this point. If it looks a bit flat and washed out, you’re on track.
Step 4 — Add the Black and Watch It Transform

This is the step where everything clicks. Using dark brown or black, draw all the veins, the wide scalloped border along the wing edges, and the body. Add small white oval spots inside the border. The whole drawing snaps into focus — this is the moment it stops looking like a sketch and starts looking like a Monarch butterfly.
Step 5 — Deepen, Saturate, and Add Light

Go back into each orange cell and push the color darker, especially near the body and along the vein edges. Add a warm brown shadow just inside each vein line. Then use a white colored pencil or gel pen for highlights on the body and spots. Finally — and this is the detail most people skip — leave the outer wing tips slightly lighter than the rest. That subtle fade is what makes the wings look translucent, not painted.
✦The translucency trick: leave the area near the wing edges very light — almost white in some spots. Real butterfly wings let light through. This single technique makes colored pencil butterflies look 10x more realistic.

5. Coloring Techniques That Make Wings Look Real
Flat orange is how a beginner colors a Monarch. Layered orange with brown undertones, light edges, and dark veins is how a finished drawing looks. The difference is technique, not talent — and it takes about 10 extra minutes.
The Layering Method
Apply color in 3-4 thin layers rather than one thick one. First pass: 30% pressure, cover the whole wing. Second pass: 50% pressure, add shading near the body and vein edges. Third pass: 70% pressure on the darkest areas only. Blend with a stump between passes.


This is what Prismacolor tutorials call ‘burnishing’ when you do a final heavy pass — but for butterflies, I find stopping at medium pressure keeps the wing looking delicate rather than waxy.
Making Wings Look Transparent

Butterfly wings aren’t opaque — they’re made of tiny scales that let light through. To replicate this: (1) keep your lightest areas very light, almost untouched paper near the wing tips; (2) add a light layer of the background color (white or cream) over the lighter parts using a white Prismacolor pencil; (3) use your blending stump to feather the edges of darker areas into lighter ones. The result reads as translucency, not just gradient.
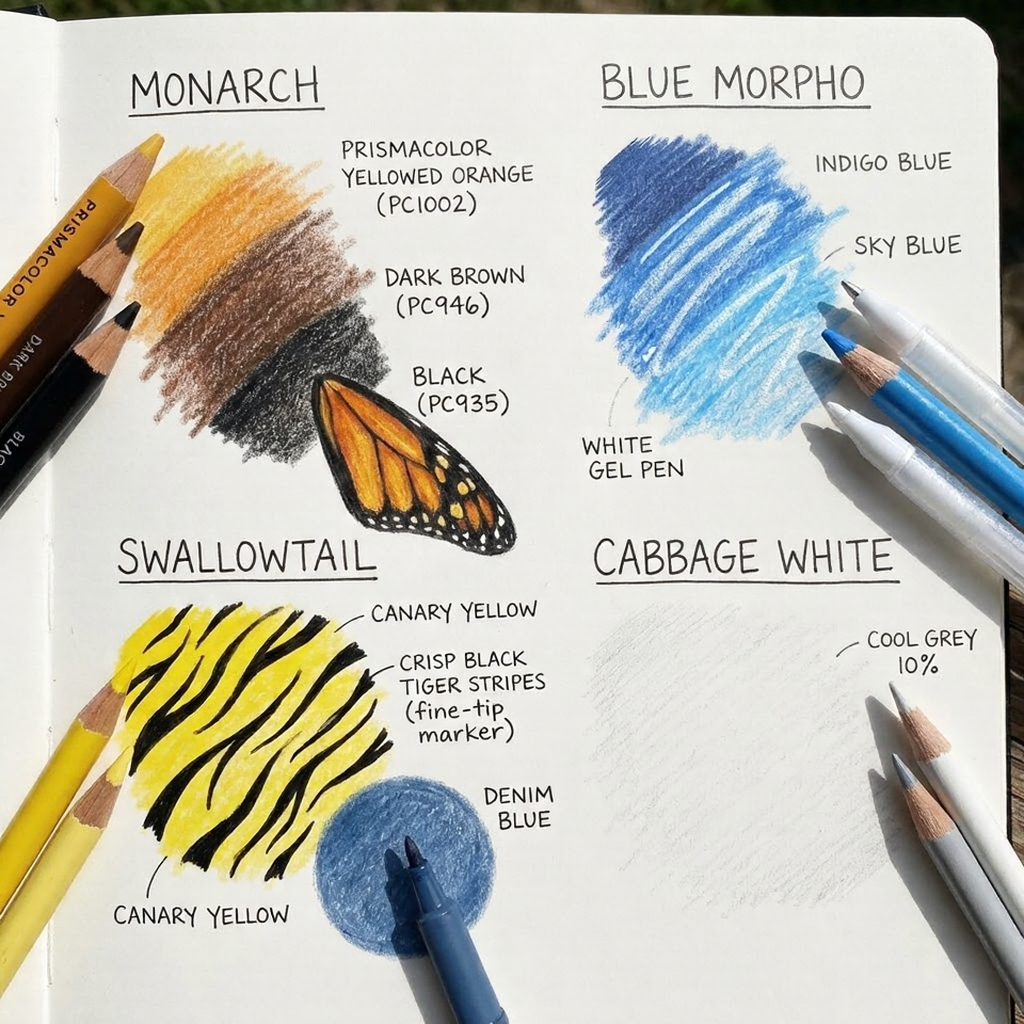

Species-Specific Color Notes
- Monarch: Prismacolor Yellowed Orange (PC1002) + Dark Brown (PC946) + Black (PC935)
- Blue Morpho: Start with Indigo Blue, add Sky Blue highlights, White gel pen for iridescence shimmer
- Swallowtail: Canary Yellow base, then black tiger stripes with a fine-tip marker for crispness; Denim Blue for the hindwing eyespots
- Cabbage White: Barely-there Cool Grey 10% for shadowed areas; otherwise mostly white paper showing through
FAQ: Butterfly Drawing Questions People Actually Ask
Q: How do I draw a butterfly that looks symmetrical?

Draw a vertical center line first. After completing one wing, fold the paper in half and trace through to the other side — or hold it up to a window and trace the mirror image. Symmetry is a technique, not a talent. Even professional illustrators use this trick.
Q: What’s the easiest butterfly to draw for beginners?
The Monarch butterfly. Its pattern is bold and follows the wing veins, so you have a natural grid to work within. The colors are straightforward — orange, black, white — and the shape is the classic butterfly silhouette most people picture when they think of butterflies.
Q: How do you make butterfly wings look realistic?
Three things: (1) Layer colors instead of applying them all at once. (2) Leave the outer wing edges lighter than the center — wings are translucent. (3) Add a white gel pen dot in each wing eye spot for that wet, luminous effect. These three changes alone shift a drawing from ‘student sketch’ to ‘finished artwork.’
Q: Do I need expensive colored pencils for butterfly drawing?
Not for starting. Crayola colored pencils work fine for practice. But if you want blendable, layerable results, Prismacolor Premier ($25 for 24 colors) or Faber-Castell Polychromos are worth the upgrade. The single most impactful cheap tool: a $3 white gel pen for highlights.
Q: How long does it take to draw a butterfly?
A simple pencil sketch: 10-20 minutes. A fully colored, detailed Monarch with realistic wing texture: 1.5 to 3 hours, depending on how much detail you add. Most of that time is in the coloring, not the line work. Start with just the line drawing — coloring is a separate skill you can build separately.
Q: Can kids learn to draw butterflies easily?
Yes — in fact, butterflies are one of the best subjects for kids ages 6+ because the symmetry makes them forgiving. If one side isn’t perfect, it still reads as a butterfly. Start with a simple oval body and two wing shapes. The Cabbage White (mostly white with two dots) is the absolute simplest version.
Your First Butterfly is 5 Steps Away


The thing about butterfly drawing isn’t that it’s hard — it’s that most tutorials make it look harder than it needs to be. Start with the gesture line. Build the body. Add wings. Follow the patterns. Layer the color.
I’d recommend starting with a Monarch sketch in graphite. Don’t add color yet. Just get comfortable with the symmetry and the anatomy. Do three or four of those, then bring in the colored pencils.
Your first one will be rough. Your fifth one will surprise you.




- 5.2Kshares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest5.2K
- Twitter0
- Reddit0


