Character design is the art of creating characters that are memorable and visually compelling. Understanding what makes a character iconic is crucial for anyone looking to break into the field of character design. The key elements include silhouette, color palette, and exaggeration, which help to establish the character’s personality and role in the story.
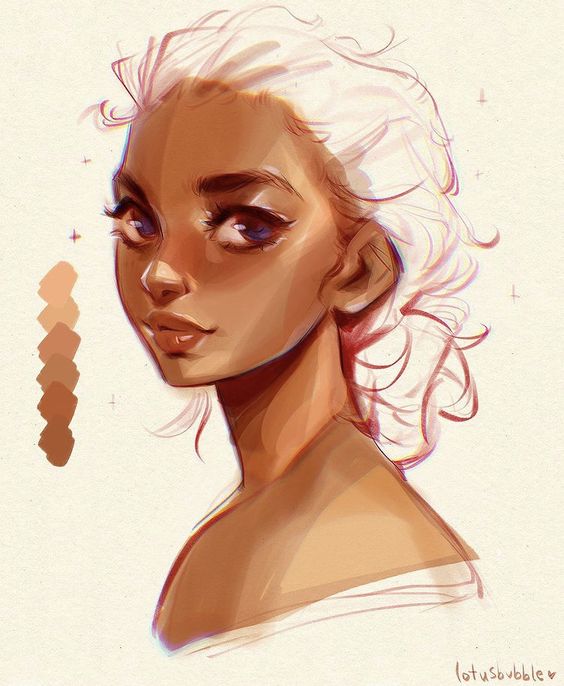
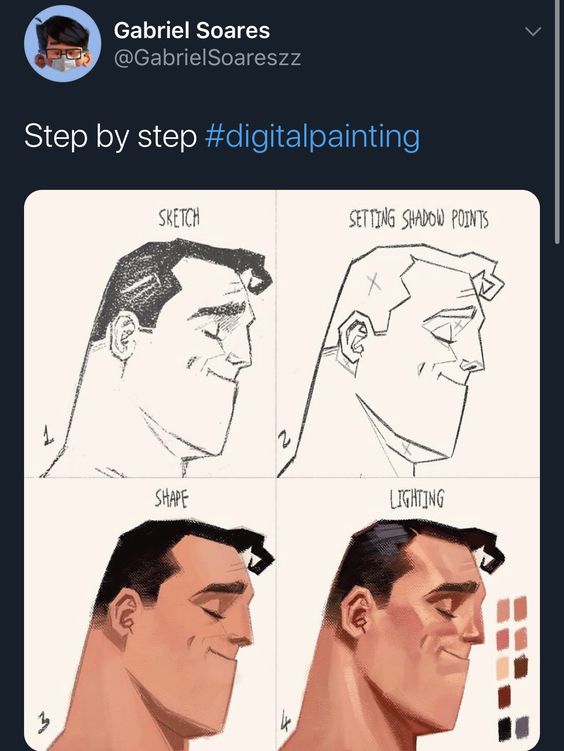

A well-designed character starts with a concept, often developed through a detailed profile and research into the target audience. Tools like sketching and rendering bring these initial ideas to life. Artists refine their characters by focusing on anatomy and proportions, ensuring they are both relatable and unique. Visual storytelling is also a major part of character design, as it helps convey the character’s story through their appearance and expressions.
For those looking to learn more, exploring various styles and genres can provide valuable insights. There are many resources available, including galleries and tutorials from professionals. These can offer tips and techniques to improve your own character designs.
Key Takeaways
- Character design focuses on creating memorable and compelling characters.
- Key elements include silhouette, color palette, and exaggeration.
- Resources like galleries and tutorials are valuable for learning character design skills.
The Basics of Character Design


Character design involves creating characters with unique appearances and personalities. Key elements include understanding character design principles, focusing on design elements, and the significance of line and form in creating characters.
Understanding Character Design
Character design is the process of crafting characters that fit a story or theme. Good character design gives personality and life to characters, making them memorable.
Designers begin with a concept. They consider factors like the character’s role, background, and traits. For instance, a hero might have a strong, symmetrical build, while a villain might have sharper features.
It’s helpful to use references and mood boards. These can include images, color samples, and various inspiration sources.
Elements of Design
Several elements shape a character’s appearance. These include shape, color, and texture.
Shapes define the character’s silhouette. Round shapes often imply friendliness, while sharp shapes might suggest danger.
Colors affect a character’s emotional impact. Bright colors often indicate an energetic personality, while dark colors might signify mystery or antagonism.
Textures add depth. Smooth textures can make a character look clean and modern, while rough textures might give them a rugged appearance.
Importance of Line and Form
Lines and forms are crucial in character design. The line of action is particularly important. It defines the character’s posture and movement, making them appear dynamic on the page.
Forms give volume to characters. They help in creating a three-dimensional feel.
Designers often start with simple forms and lines. Over time, they add details to refine the character. This process ensures that the final design is well-balanced and expressive.
Understanding the basics of line and form allows for effective communication of the character’s personality and role. These fundamentals are essential for bringing any character to life.
Developing Character Concepts
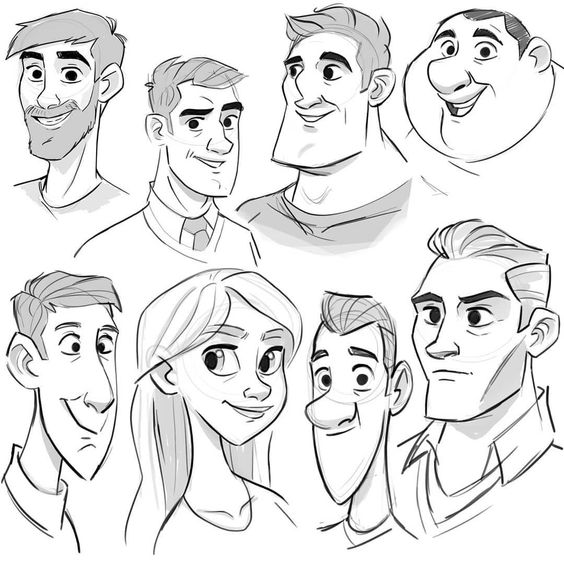
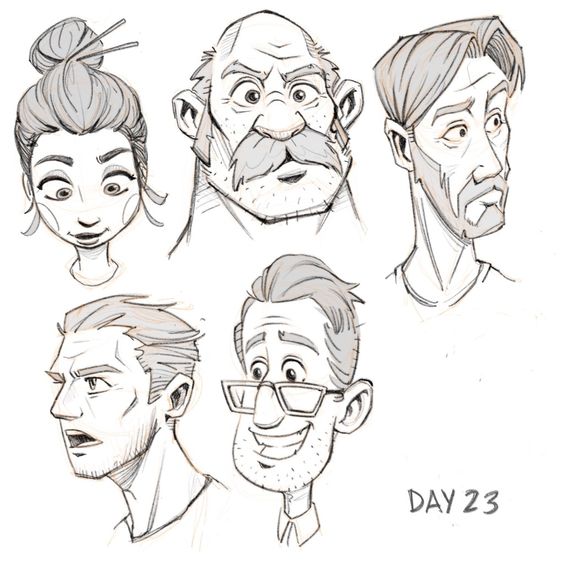

Creating character concepts involves drawing inspiration, generating memorable traits, and sketching ideas to life. It’s important to explore different approaches through research, creativity, and hands-on design.
Research and Inspiration
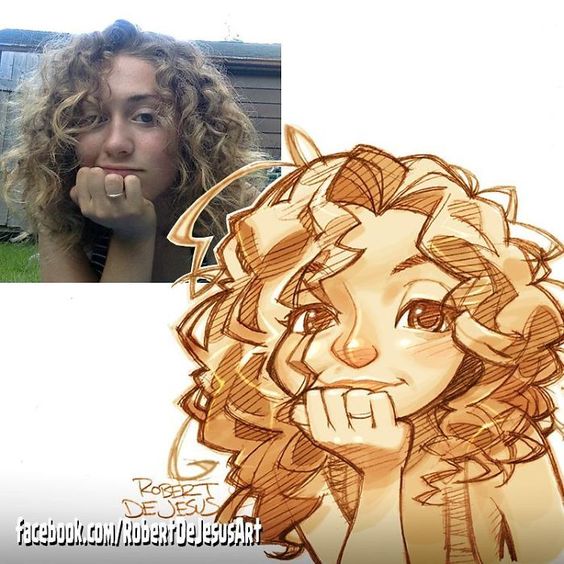
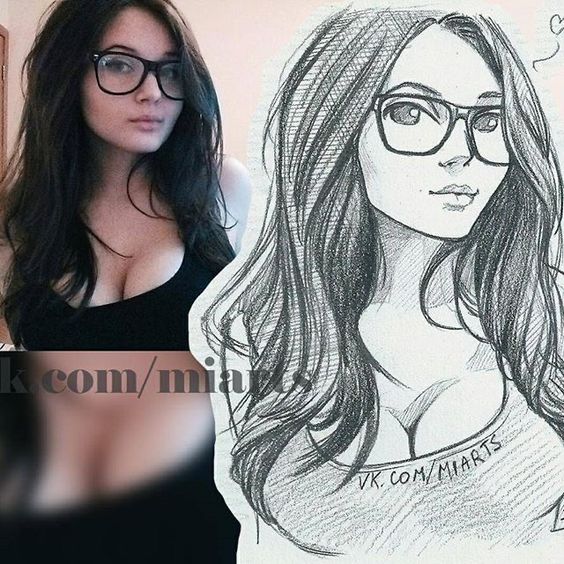


Inspiration can come from various places. Designers often look at books, magazines, and articles related to their character’s genre or theme. Observing real-life people, nature, and even other artworks can also spark ideas. By gathering diverse references, designers can create a unique vision for their character.
Brainstorming is another key part of this process. Writing down ideas and creating mind maps helps in organizing thoughts. Gathering visual references aids in visualizing the character’s look and feel. This stage sets the foundation for the creative process.
Creating Memorable Characters
Memorable characters are essential as they resonate with the audience. To achieve this, designers focus on distinct features, personality traits, and backstory. Physical attributes like shape, size, and color play a significant role. Unique outfits and accessories add to the character’s identity.
Designers also consider the character’s role in the story. Is the character a hero, villain, or sidekick? Defining these roles helps in setting the tone and mannerisms. A detailed backstory gives depth and makes the character relatable. Consistency in character traits ensures they stay memorable throughout the story.
The Role of Sketching
Sketching is a crucial step in developing character concepts. Initial thumbnail sketches help in brainstorming different poses and expressions. These quick drawings focus on capturing the overall shape and movement of the character.
Once a direction is chosen, more detailed sketches are created. These include close-ups of facial features, clothing details, and various angles. Sketching allows designers to experiment and refine their ideas before finalizing the character design. It’s a process that blends creativity with precision to bring concepts to life.
Character Design Principles


Effective character design relies on the interplay of color, shape, and personality. These elements work together to create memorable and relatable characters.
Color Theory and Palette
Color psychology plays a crucial role in character design. Different colors evoke different emotions and associations. For example, red can symbolize passion or danger, while blue often represents calmness and reliability.
Choosing the right color palette helps to highlight a character’s traits. Bright and vibrant colors can make a character appear energetic and youthful. In contrast, muted colors can suggest maturity or mystery. The balance of colors should be thoughtfully considered to maintain visual harmony and convey intended emotional responses.
Shape Language and Silhouette
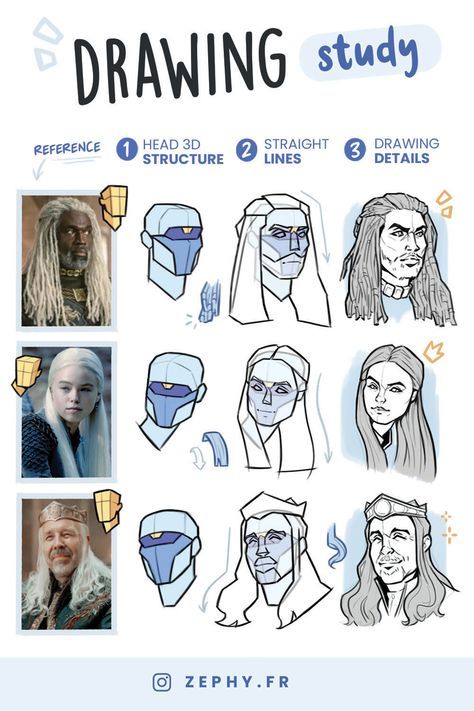

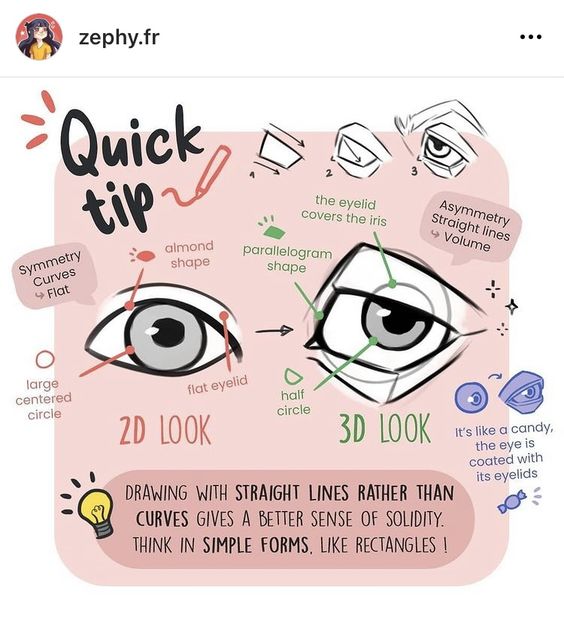
Shape language is another vital aspect of character design. Basic shapes like circles, squares, and triangles communicate different characteristics. Circles often suggest friendliness and approachability. Squares can convey stability and reliability, and triangles might indicate danger or excitement.
The silhouette of a character needs to be easily recognizable. This means that even when the character is viewed in shadow, their outline should be distinct. Designing a clear and unique silhouette helps in making the character easily identifiable and memorable.
Expressing Personality through Design
Expressing personality through design involves incorporating visual cues that communicate a character’s traits and behaviors. Features like facial expressions, body posture, and clothing style all contribute to this.
For example, large, expressive eyes can make a character appear more empathetic and relatable. In contrast, a more rigid stance might suggest a disciplined or serious personality. Elements like hairstyles, accessories, and unique markings further help define and differentiate a character.
Incorporating these elements thoughtfully ensures that the character’s personality resonates with the audience, creating a deeper connection and engagement.
Anatomy and Proportions
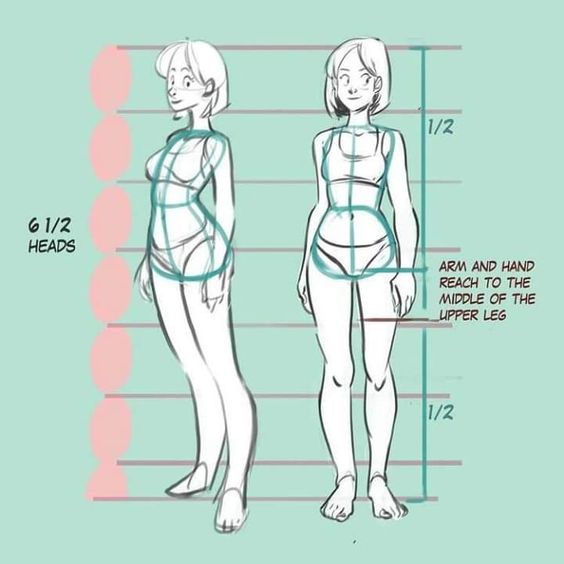
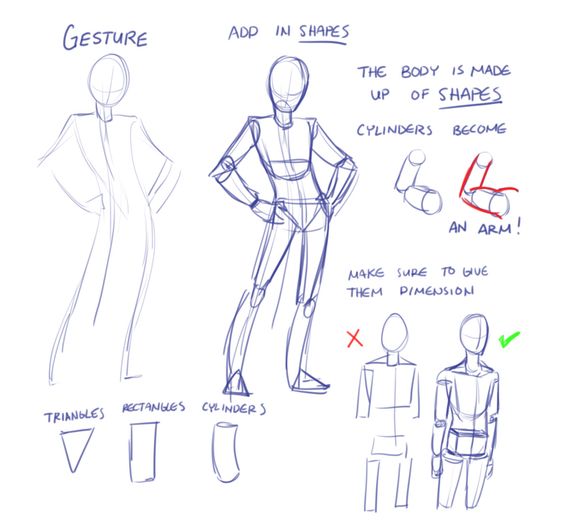
Understanding anatomy and proportions is essential for creating believable and expressive characters. By paying close attention to the structure of humans and creatures, you can craft designs that are both realistic and exaggerated where needed.
Human and Creature Anatomy
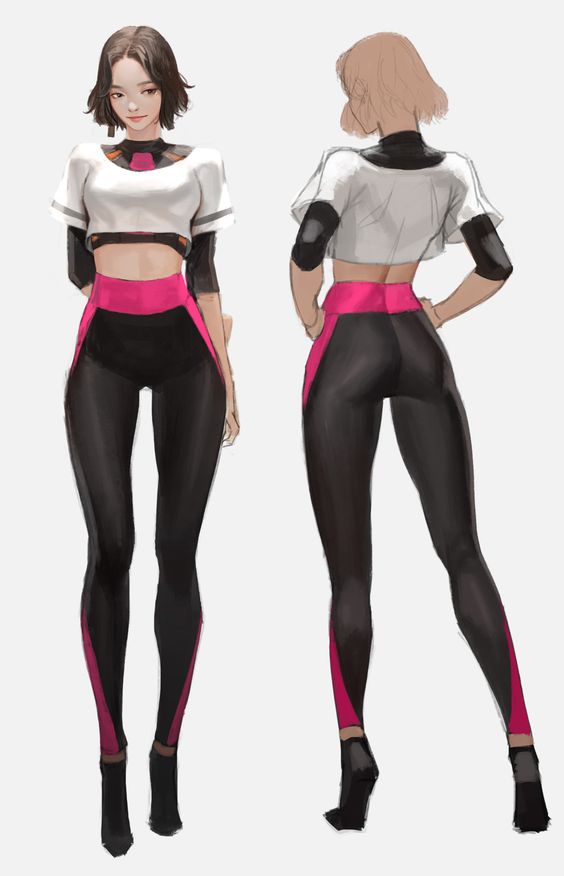


Knowing the basics of human anatomy is crucial. This includes understanding muscle placement, bone structure, and joint alignment. Artists should study how these elements interact during different movements.
For creatures, anatomy can vary widely. Researching real-world animals helps in learning muscle distribution and skeletal forms. Creatures should feel believable, even if they are fantastical. This means understanding how their anatomy might function in real life.
Character Proportions and Exaggeration
Proportions are key in defining a character’s look. Standard human proportions involve aligning joints and maintaining size ratios among body parts. In character design, these proportions can be exaggerated to emphasize traits. For example, larger eyes or exaggerated limbs can convey certain emotions or characteristics.
Different styles demand different approaches. In cartoon styles, proportions often deviate significantly from reality to enhance expressiveness. Meanwhile, more realistic styles maintain closer adherence to true anatomical proportions. Balancing realism and exaggeration is an art form, requiring careful observation and practice.
By mastering anatomy and proportions, character designs become more dynamic and engaging, capturing both realism and creativity.
Visual Storytelling
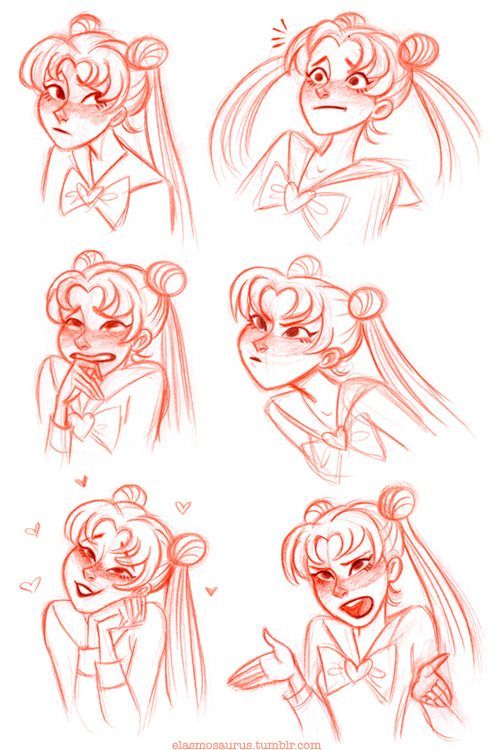
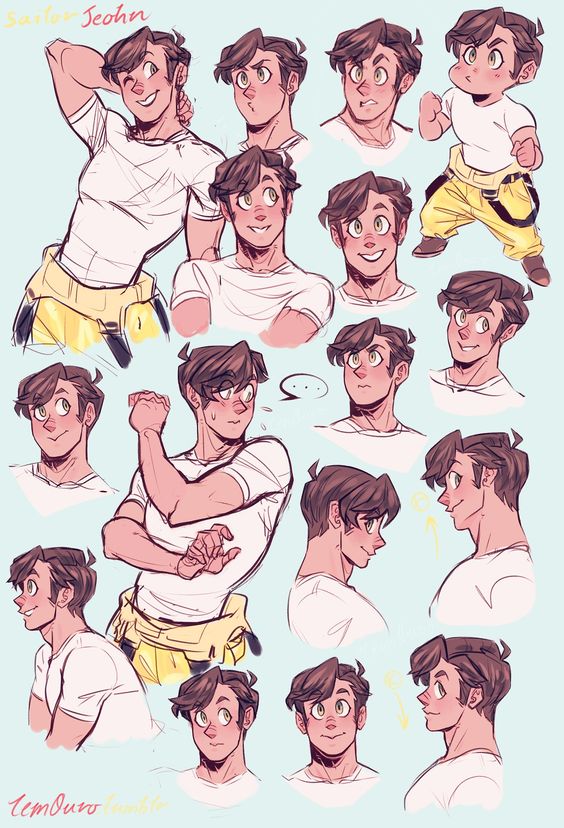


Visual storytelling uses images to tell a story effectively. It’s important to convey character backstories and illustrate their personality and behavior through visual elements. This section breaks down these crucial aspects.
Conveying Character Backstories
Character backstories are key to making the story more engaging. Artists can use visual cues like clothing, accessories, and surroundings to provide hints about a character’s history.
For example, a character with worn-out clothes and a rugged appearance might suggest a tough past or a life of hardship. Settings such as a cluttered room can indicate a chaotic lifestyle or a busy mind.
Color choices also play a significant role. Dark colors can imply a troubled past, while bright colors can indicate a more positive background. Subtle details like scars or tattoos can hint at past experiences and add depth to the character.
Illustrating Personality and Behavior
Illustrating a character’s personality and behavior can make them more relatable. Body language, facial expressions, and poses are effective tools in achieving this.
A confident character might be shown with an upright posture and direct eye contact. In contrast, a shy character may have a hunched posture and avoid eye contact. Clothing styles can also reflect personality traits; vibrant, unique outfits may indicate a bold personality, while plain, simple clothes might suggest a reserved nature.
In addition, integrating specific actions like fidgeting, smiling, or aggressive stances helps to clearly present character behavior. Movement within the scenes can show whether a character is energetic, sluggish, or graceful, making their behavior more visible to the audience.
By focusing on these visual details, artists make characters come alive, enriching the storytelling experience.
Design Execution
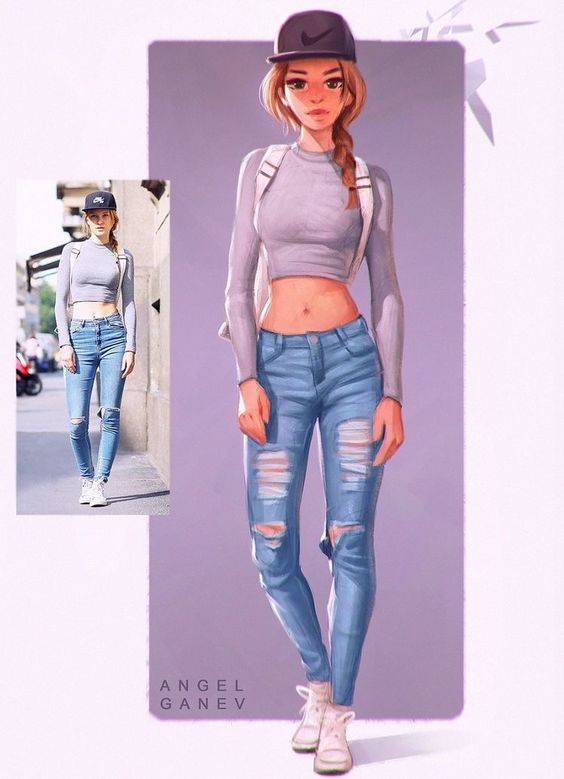


A successful character design hinges on the right tools, detailed model sheets, and thorough refinement. The three main areas to focus on are software selection, model sheet creation, and the final refinement steps.
Choosing the Right Software and Tools
Selecting the correct software is critical. Programs like Adobe Illustrator and Adobe Photoshop are popular for 2D design. ZBrush and Blender are excellent options for 3D modeling. Each software provides unique tools that can help bring a character to life.
Illustrator offers vector-based tools, allowing for scalable designs without loss of quality. Photoshop provides powerful raster editing capabilities which are ideal for detailed texture work.
For 3D design, ZBrush excels in sculpting highly detailed models, while Blender allows for both modeling and animation workflows. Tutorials and resources are abundant online, making it easier to learn these programs.
Drafting Model Sheets
Model sheets are essential for consistency. These sheets typically include multiple views of the character: front, side, and back. They can also include various expressions and poses to capture the character’s personality and range of motion.
Creating clean and precise sketches on these sheets is key. Color palettes and initial costume designs can be tested at this stage to see how they fit with the overall character concept. Adding notes for textures, accessories, and other details guides the future stages of design.
Model sheets act as a blueprint that ensures every aspect of the character is accounted for.
Refinement and Finalization
Once the base design is complete, it’s time to refine and finalize it. This involves adding intricate details and making any necessary adjustments for realism and consistency. Fine-tuning elements like shadows, highlights, and textures can make a significant difference.
Feedback from peers or clients during this stage is invaluable. Adjust colors, tweak proportions, and refine facial expressions based on this feedback. Final touches might also include setting up the character for animation if needed.
Ultimately, having a well-defined process from software choice to final tweaks results in a polished and appealing character design that aligns with the project’s goals.
Industry Insights

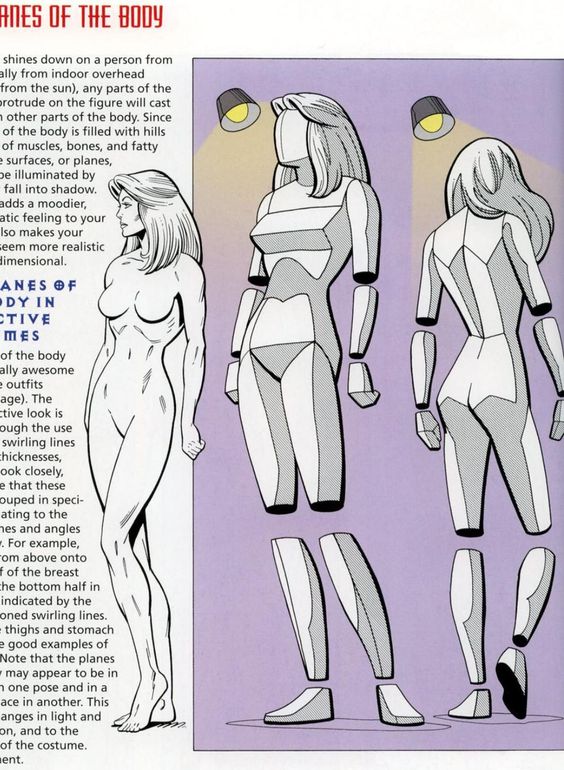
Understanding the character design industry is crucial for aspiring designers. Key areas include the demands in animation and comics, the professional life of a character designer, and tips for building a compelling portfolio.
Character Design in Animation and Comics
Character design plays a vital role in both animation and comics. Characters need to be visually appealing and expressive, embodying the story’s essence. In animated movies, characters are brought to life through motion, requiring designers to focus on how characters move and interact.
In comics, the focus shifts to static illustrations that still must convey dynamic actions and emotions. This means designers have to create poses and expressions that tell a story without movement. Creating a character that can do both effectively reflects a designer’s skill and experience.
Working as a Professional Character Designer
A professional character designer has a multifaceted job that includes more than just drawing. They participate in brainstorming sessions, collaborate with directors and writers, and often revise their work multiple times.
In the TV and film industries, designers must adhere to production schedules and work in sync with other departments like animation and production art. A designer’s ability to take feedback and make changes quickly is crucial to their success. Networking and continuous learning play a key role in maintaining and advancing their career.
Building a Strong Portfolio
A strong portfolio is essential to showcasing a character designer’s skills and experience. It should include a range of different character styles, from simple sketches to fully realized designs. Including production art can demonstrate an understanding of how characters fit into broader projects.
Portfolios should also highlight work done in various mediums, such as animated movies, TV, and comics. This diversity shows versatility and the ability to adapt. Adding brief descriptions to each piece can give potential employers insights into the thought process and techniques behind the designs.
Additional Resources
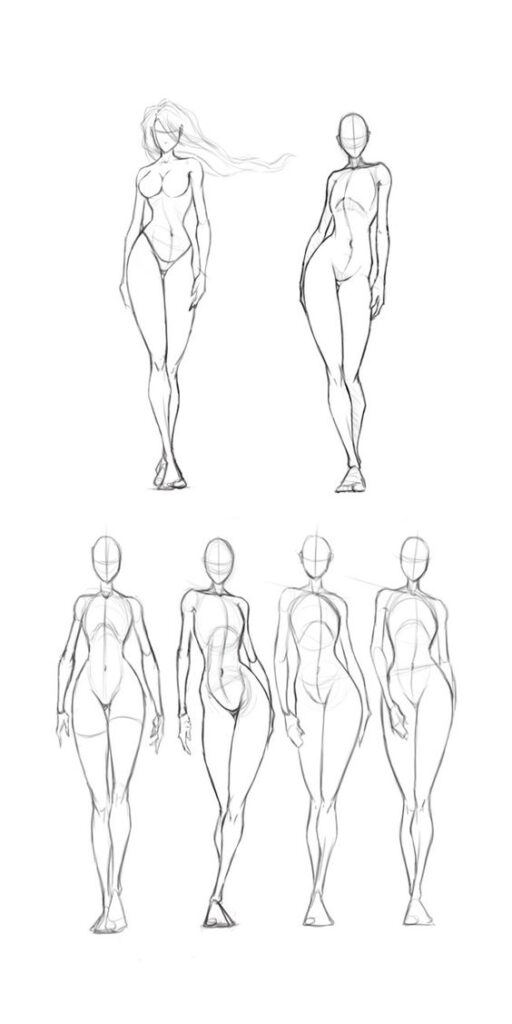
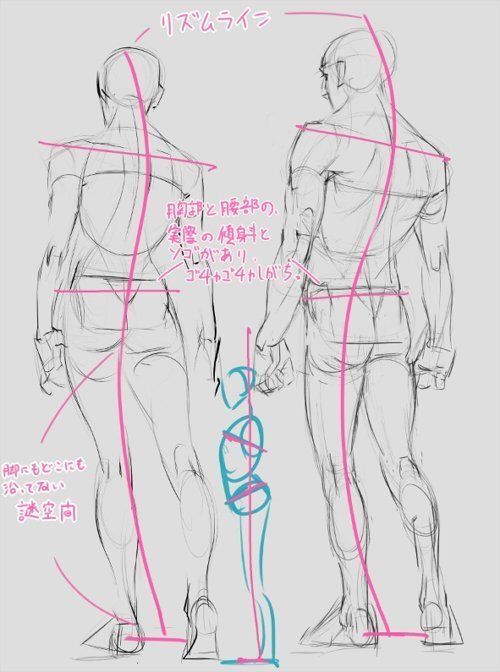
Character designers have many tools and communities at their disposal to grow and improve their skills. These resources include books, articles, and online content; opportunities for community and networking; and options for continued education and improvement.
Books, Articles, and Online Content
Books and articles are essential for in-depth learning. “Creating Characters with Personality” by Tom Bancroft is a highly recommended book. It covers basics to advanced techniques. Websites like Creative Bloq offer expert tips, useful for both beginners and experienced designers.
Magazines such as ImagineFX provide regular updates on industry trends. Online content, including Character Design References and CharacterDesigns.com, offer comprehensive visual libraries and image references to assist with the creative process.
Pinterest is another valuable platform for gathering inspiration and discovering new techniques. It allows designers to create boards filled with diverse artistic styles and resources that can be easily accessed and organized.
Community and Networking
Networking is key in the art community. Joining platforms like ArtStation or DeviantArt can offer interaction with other artists. These communities provide critiques and feedback, essential for growth. Following industry professionals on platforms such as Instagram or subscribing to relevant YouTube channels also helps stay updated.
Reddit‘s forums like r/CharacterDesign and r/ArtCrit, allow for sharing work and receiving feedback from a broader community. Participating in character design challenges and contests, such as those on CGSociety, can also be greatly beneficial.
Podcasts like “The Oatley Academy of Visual Storytelling” and “Character Creator Podcast” are useful resources. They discuss topics ranging from character design tips to industry interviews, providing valuable insights.
Continued Education and Improvement
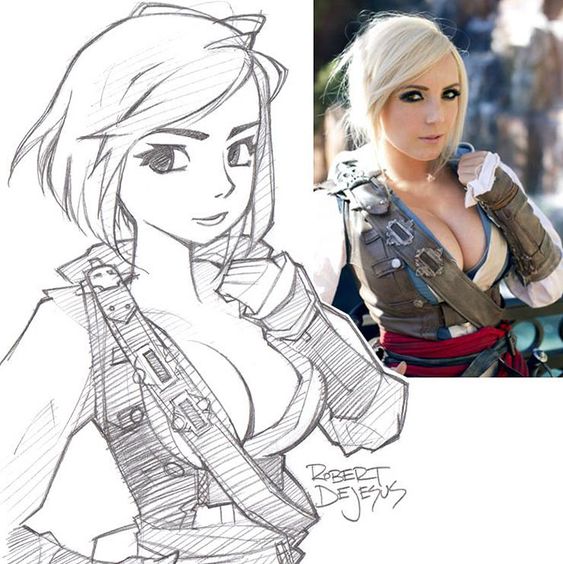


Continuous learning is essential. Enrolling in online courses from platforms like Skillshare and Udemy can provide structured learning paths. Websites like 21 Draw offer ultimate character design tips focusing on practical skills.
Workshops and webinars, often hosted by professional artists, present opportunities for live learning and immediate feedback. Mentorship programs can provide personalized guidance, which is invaluable for serious learners.
Following dedicated tutorials on YouTube and other platforms is another way to improve. Engaging with educational content and regularly practicing new techniques can lead to significant improvement in character design skills.
- 492shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest492
- Twitter0


