
Fashion design clothing is about creating clothes that combine style, function, and creativity. Designers use their knowledge of fabrics, trends, and customer needs to develop garments that stand out. The main goal of fashion design clothing is to produce wearable art that appeals both visually and practically.
This process involves more than just sketching ideas. It includes understanding how clothes fit, choosing materials, and constructing patterns to bring a design to life. Fashion design is constantly evolving as it adapts to new trends and cultural influences.
The industry offers many paths, from high-end couture to mass-produced fashion. Designers also use shows and marketing to introduce their clothes to the world and build their reputation.
Key Takeaways
- Fashion design blends creativity and functionality to make appealing clothing.
- Designers work through steps like pattern making and material selection.
- Fashion trends and marketing shape the clothing industry globally.
Understanding Fashion Design
Fashion design involves creating clothing and accessories with a focus on style, function, and aesthetics. It includes many ideas, from the origins of design to how it differs from other fashion roles.
Defining Fashion Design
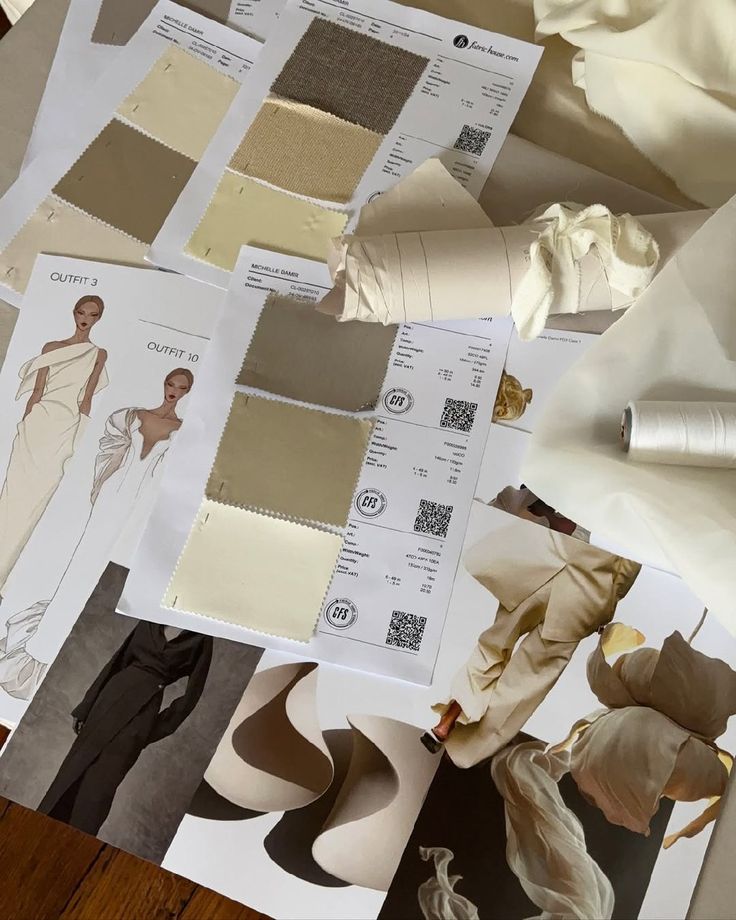


Fashion design is the art of making clothes that people will wear. Designers choose fabrics, colors, shapes, and details to create new looks. They blend creativity with practical skills like sewing and pattern-making.
Designers think about trends, culture, and comfort while making clothes. They often sketch ideas before building samples. Their goal is to produce pieces that fit well and express a unique style or message.
Fashion design covers many items, including dresses, jackets, shoes, and accessories. It requires understanding how clothes fit the body and how people move in them.
History of Fashion Design
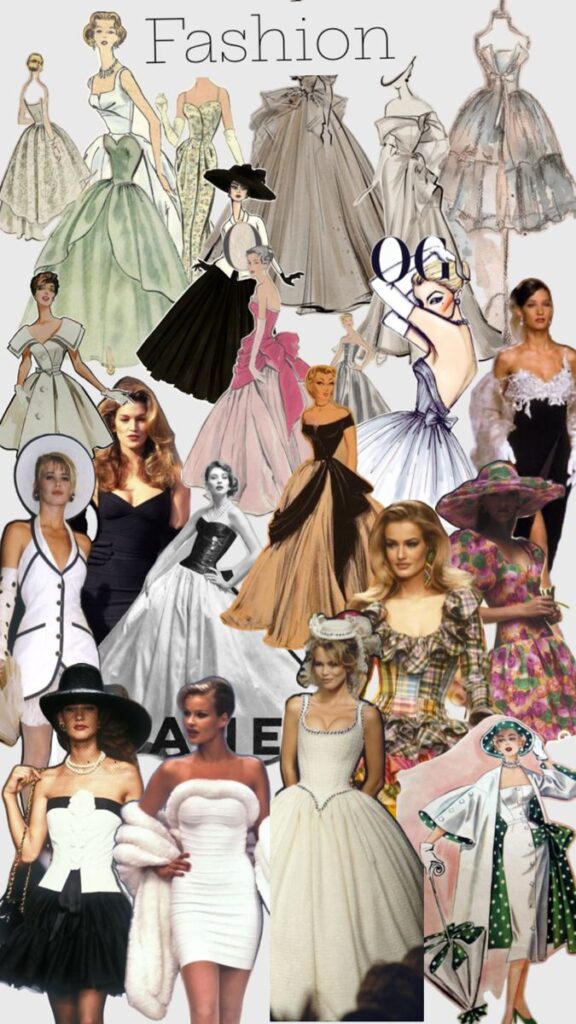
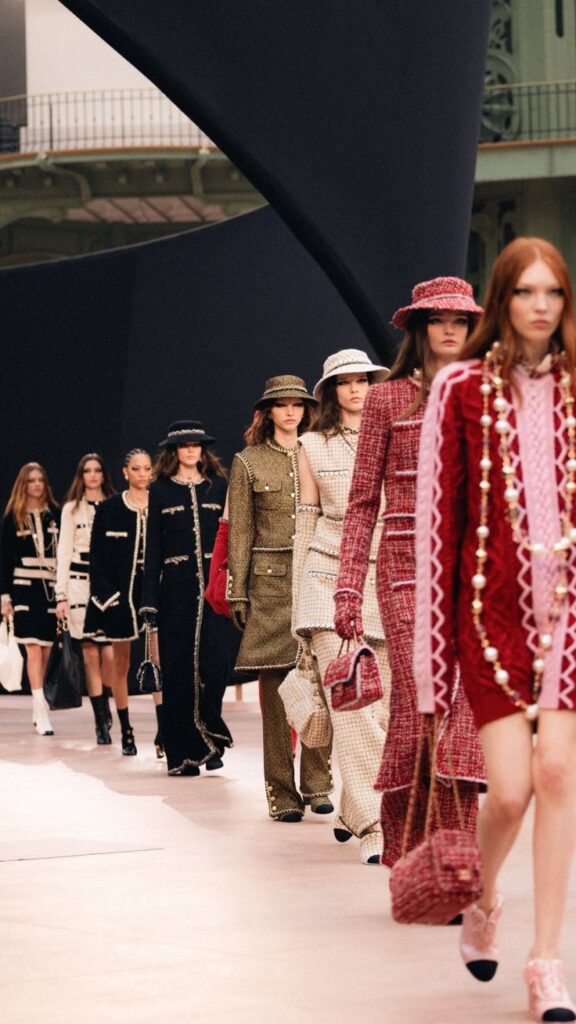


Fashion design has been around for centuries but became a formal profession in the 19th century. Early clothes were handmade by local tailors and seamstresses. The rise of industrial sewing machines changed how clothes were made.
The first fashion house opened in Paris in the 1850s. Designers like Charles Frederick Worth started creating collections for wealthy clients. This marked the start of fashion as a business.
Over time, fashion design included more styles and designers from around the world. Today, it reflects different cultures and modern technology. The history shows a shift from simple handmade clothes to complex global industries.
Fashion Design Versus Fashion Styling
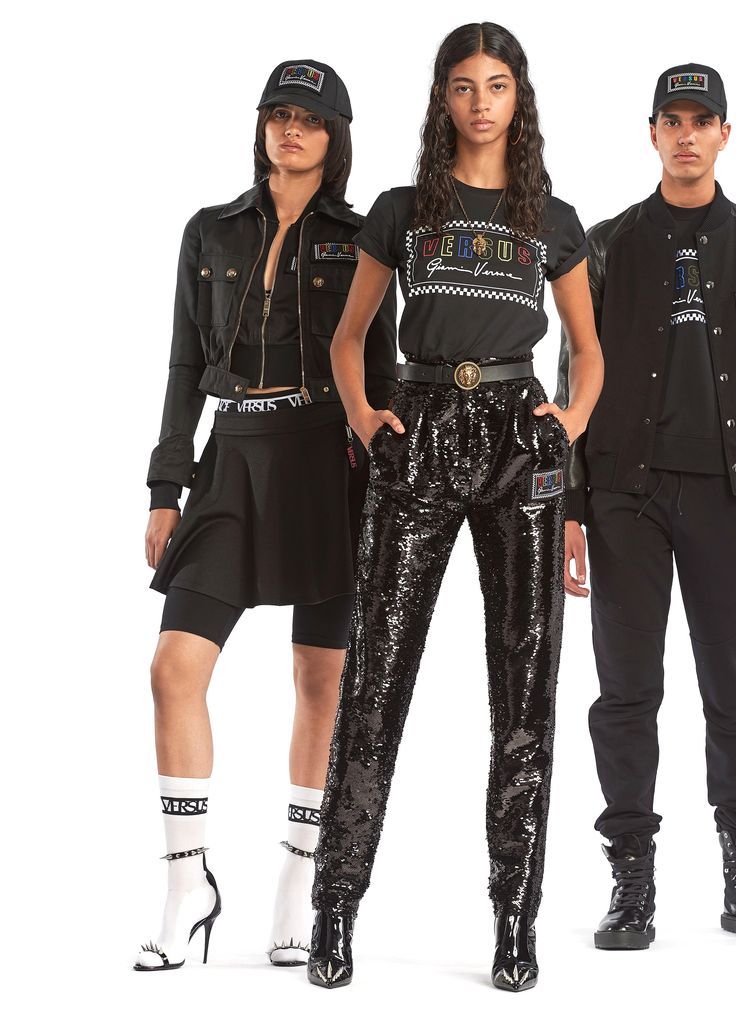
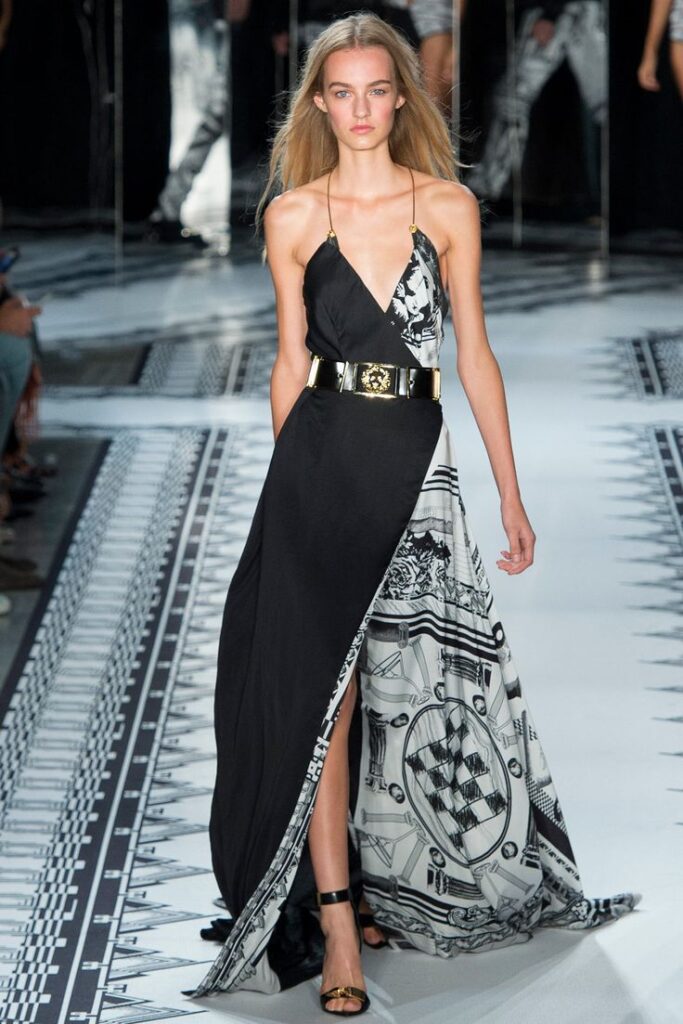


Fashion design and fashion styling are related but different jobs. Designers create and make the clothes. Stylists choose outfits and accessories for people to wear on specific occasions or shoots.
Designers focus on the production process. Stylists work with finished clothes to create looks for photos, events, or daily wear. Stylists must understand current trends and how to combine pieces well.
Both roles require creativity but serve different parts of the fashion world. Designers make the products, while stylists show how those products can be worn.
Clothing Design Principles
Clothing design relies on key ideas to create garments that look balanced, pleasing, and functional. These ideas include the basic parts of design, how those parts work together, and the effect of color on fashion.
Elements of Design


Elements of design are the building blocks of any garment. These include line, shape, form, texture, and space.
Line directs the eye and can make a figure look longer, shorter, wider, or thinner.
Shape refers to the outline of a garment, such as A-line or pencil shapes.
Form is the three-dimensional structure of clothing.
Texture adds interest through how the surface feels or looks, like smooth silk or rough wool.
Space is the area around and between elements, affecting how a design feels—open or crowded.
Together, these elements create the foundation for every piece of clothing.
Principles of Design in Apparel


Design principles guide how the elements are used to make clothing attractive and useful. They include balance, proportion, emphasis, rhythm, and harmony.
Balance makes sure the garment feels stable and evenly weighted, either symmetrical or asymmetrical.
Proportion compares the size of different parts of a garment to avoid awkward looks.
Emphasis highlights one area, like a bold collar or detailed stitching.
Rhythm creates movement by repeating shapes or colors across the design.
Harmony ensures all parts of the design fit well together for a unified look.
These principles help designers shape clothes that work well on the body and look intentional.
Color Theory in Fashion


Color theory in fashion focuses on how colors interact and affect perception. It helps designers select colors that work well together to create a desired mood or style.
Primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. They mix to form secondary colors like green, orange, and purple.
Complementary colors are opposite each other on the color wheel and create strong contrast.
Analogous colors sit next to each other and offer a harmonious look.
Color can show season, mood, and even personality. For example, cool blues suggest calm, while bright reds feel energetic. Designers use color to attract attention, match trends, and flatter different skin tones.
The Fashion Design Process
Fashion design involves several clear steps to create clothing. It starts with ideas and inspiration, moves to drawing out those ideas, and ends with picking the right materials to bring the designs to life.
Inspiration and Concept Development

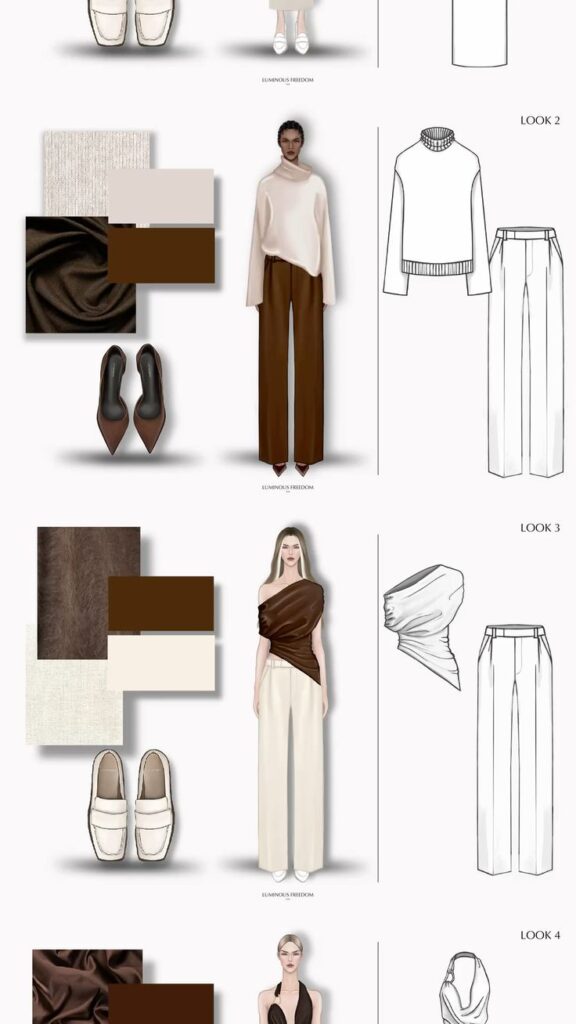
Designers look for inspiration everywhere, like nature, art, culture, or current trends. They gather images, colors, and textures to build a mood board. This board helps shape the theme or story behind a collection.
The concept defines the style and purpose of the clothing. Designers decide on details like the target audience, season, and overall look. This early stage directs all future decisions in the design process.
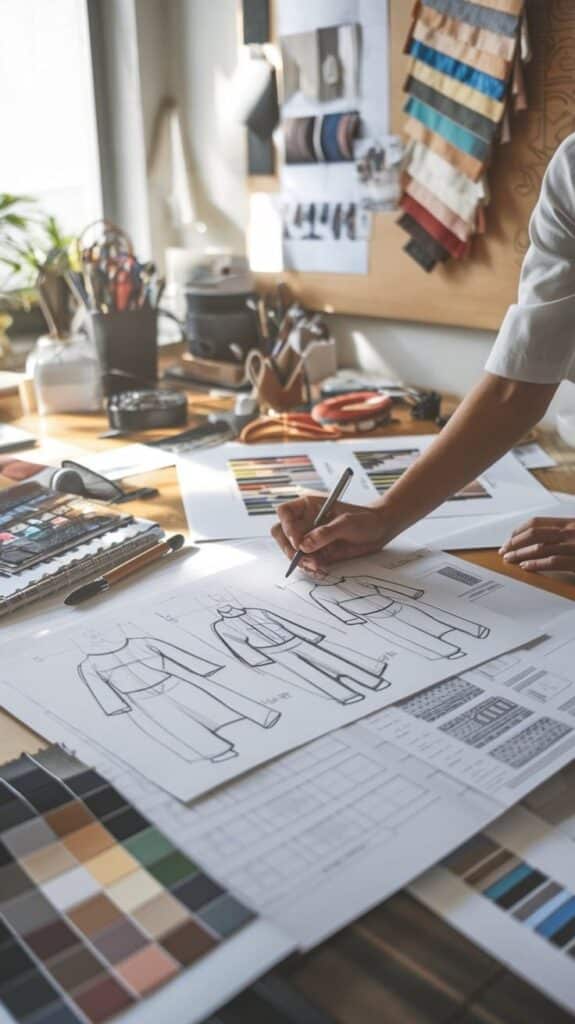
Sketching and Illustration


Designers create rough sketches to visualize their ideas. These can be quick drawings or detailed illustrations showing how a garment will look. They often include notes on shapes, lengths, and key features.
Sketching helps refine the design by testing proportions and styles on paper. Sometimes, designers use digital tools to improve accuracy and share ideas easily with their team.
Choosing Fabrics and Materials


Picking the right fabric is essential. Designers consider texture, weight, and durability when choosing materials. Fabrics must fit the design’s purpose, such as comfort for casual wear or strength for outerwear.
They also think about colors and patterns that will enhance the design. Sustainable and affordable materials are often part of the decision, especially for modern collections.
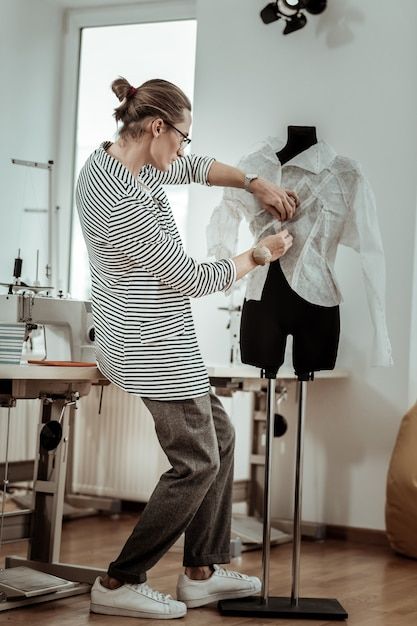
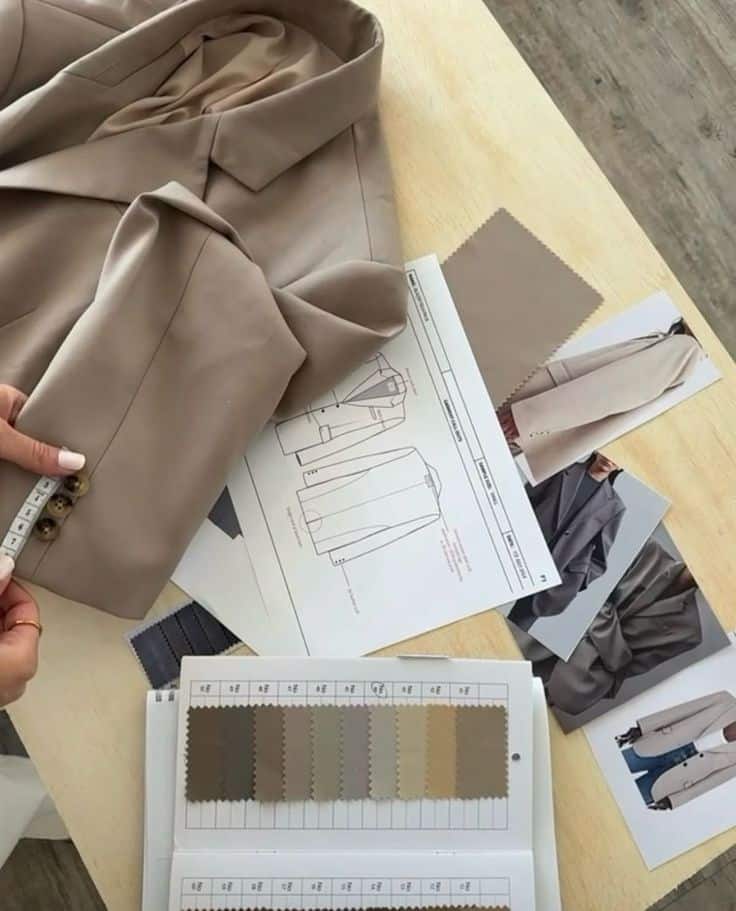
Pattern Making and Construction
Pattern making and construction are key steps in turning clothing ideas into wearable pieces. These steps involve precise measurement, cutting, and sewing to ensure the garment fits and looks as intended.
Pattern Drafting Techniques
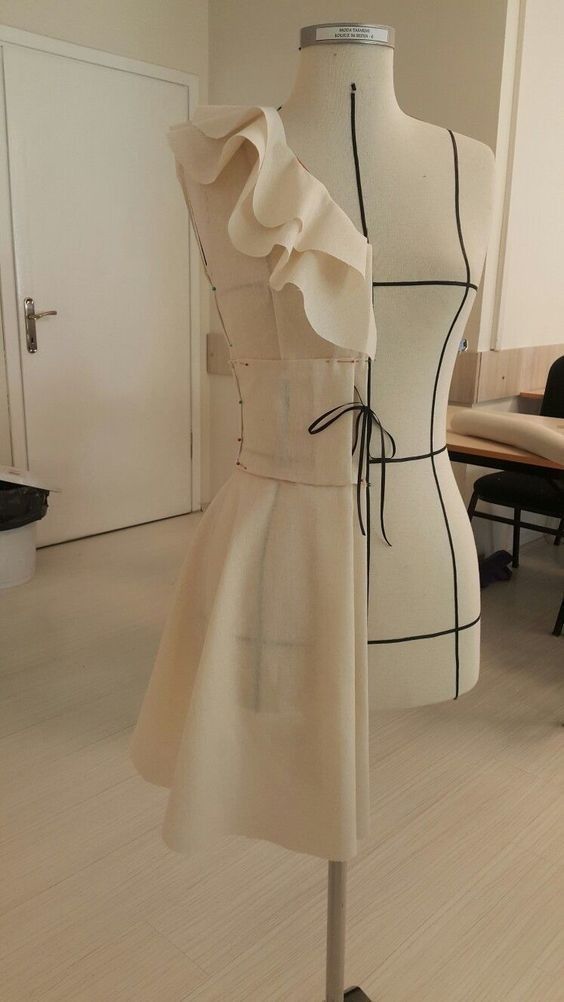


Pattern drafting begins with taking detailed body measurements or using standard sizing charts. Designers create flat templates called patterns that represent each part of the garment.
Common methods include the block method, where basic shapes (blocks) are adjusted to design new styles, and the draping method, which involves pinning fabric directly on a dress form to shape the garment.
Patterns are made on paper or digitally. The accuracy of these patterns affects how well the final garment fits. Alterations to the pattern allow for style changes without starting from scratch.
Garment Construction Methods
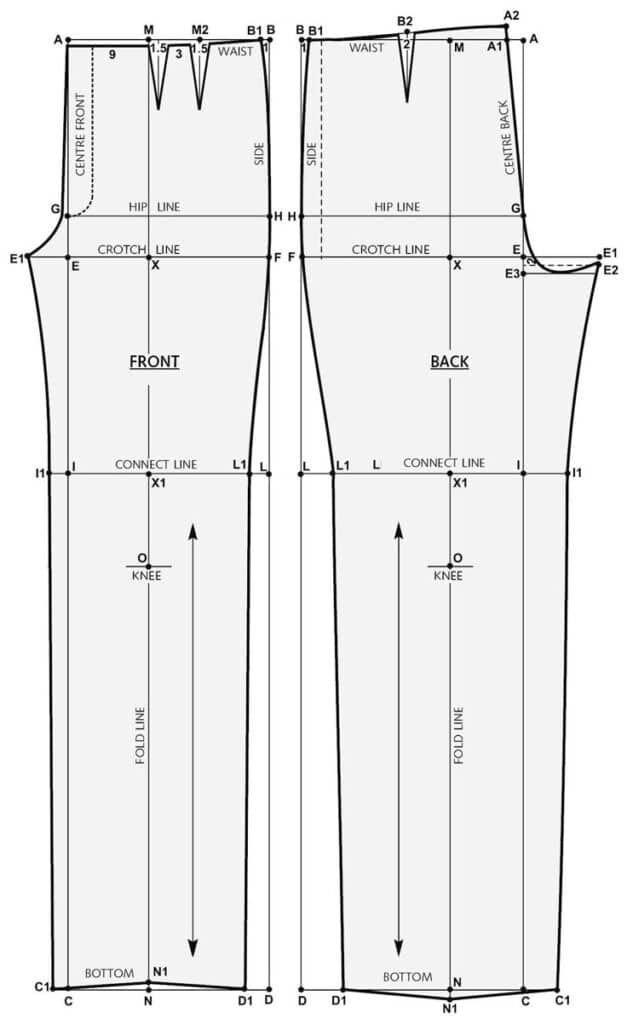

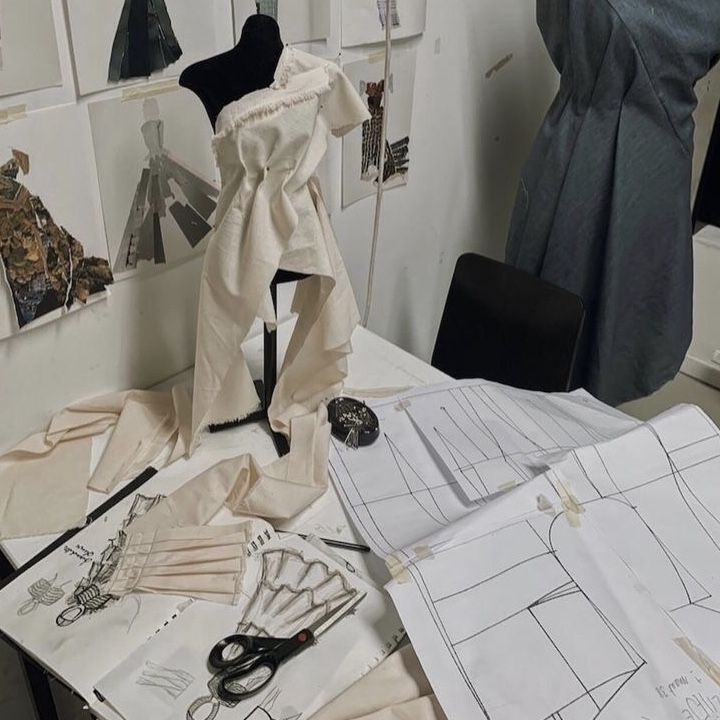
Construction covers sewing the pattern pieces into a finished garment. It starts with fabric cutting based on the pattern.
Seams join fabric pieces, with common types like plain seams and French seams chosen for their strength and finish. Stitch types and seam allowances vary depending on fabric weight and design requirements.
Details like darts, pleats, and hems shape the garment and improve fit. Proper pressing during sewing helps achieve clean lines. Finally, fasteners like zippers or buttons complete the clothing assembly.
Types of Fashion Design Clothing
Fashion design clothing comes in different forms, each with unique features and target audiences. Some focus on exclusivity and craftsmanship, while others emphasize accessibility and trends. The way clothes are made, sold, and worn varies widely.
Ready-to-Wear
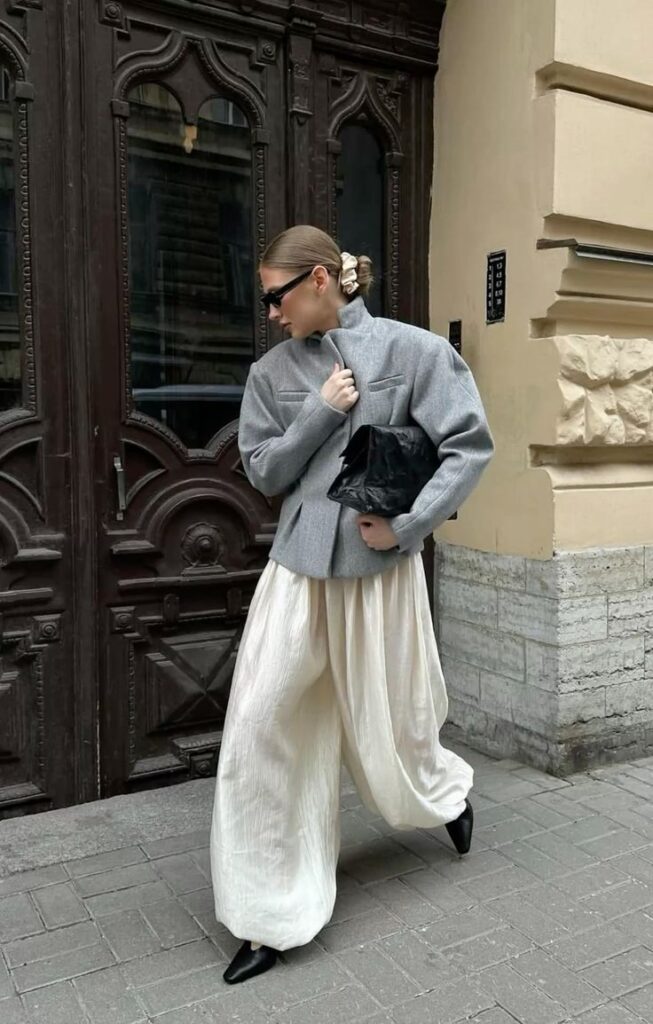
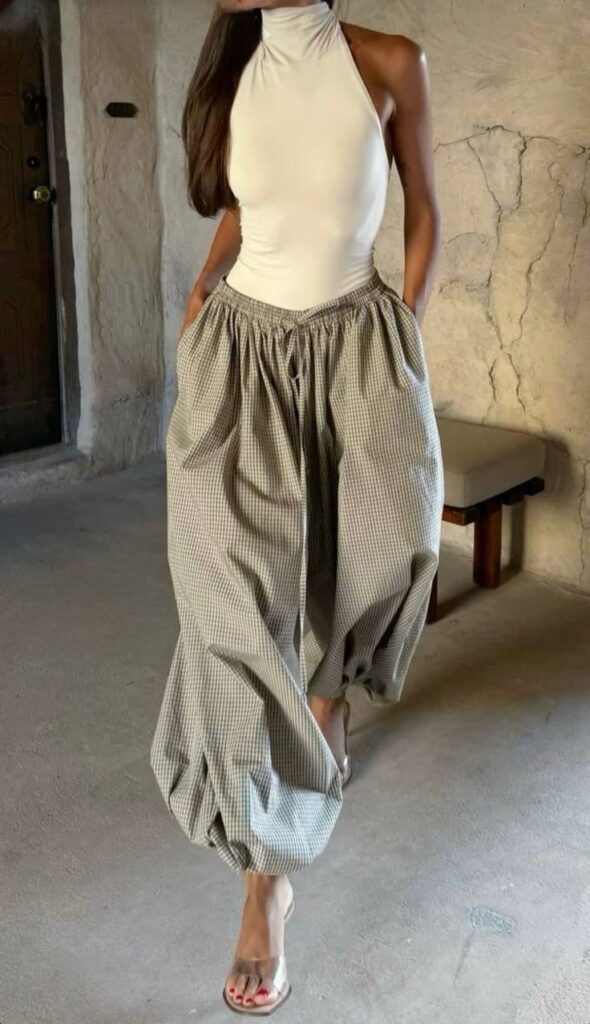


Ready-to-wear clothing is made in standard sizes and sold through retail stores. Designers create collections each season that are produced in factories. This type balances style, quality, and affordability.
It is more exclusive than mass market fashion but more accessible than custom pieces. Ready-to-wear offers current trends that customers can buy off the rack without waiting. Brands often release new lines seasonally to keep up with demand.
Haute Couture
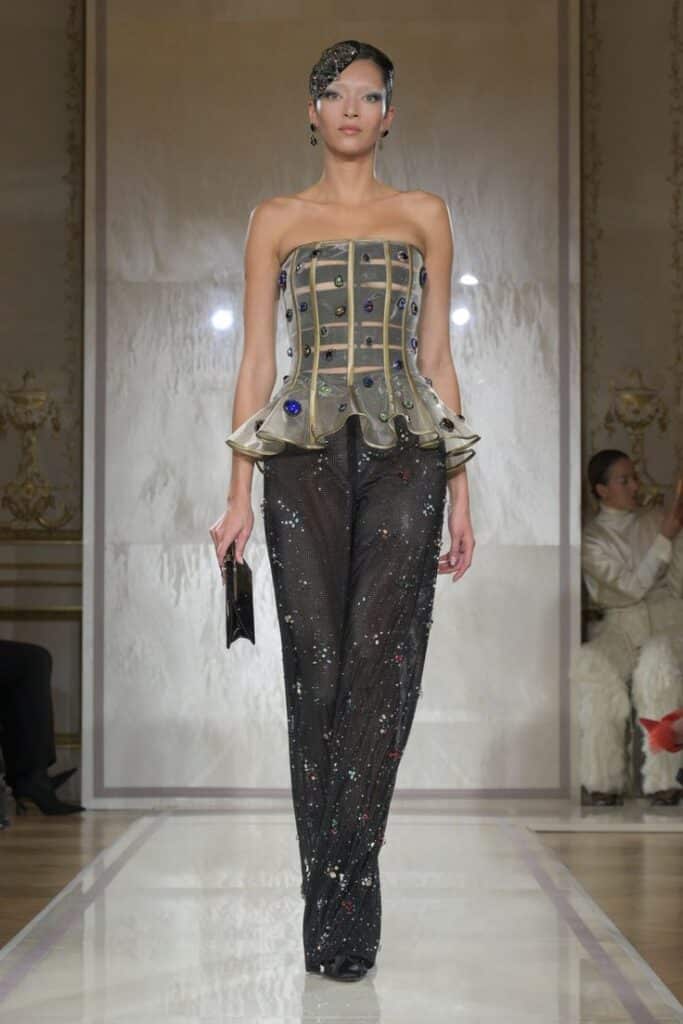
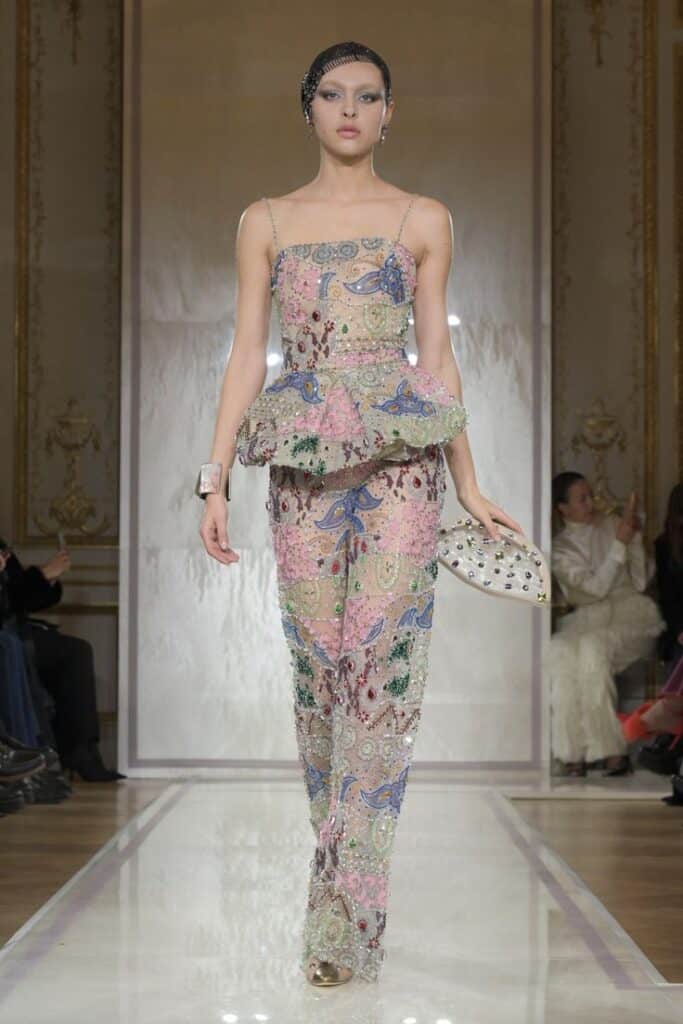


Haute couture includes custom-made, hand-stitched clothing designed for individual clients. It involves high-end materials and extreme attention to detail. Each garment is one of a kind, created to fit perfectly.
Only a few fashion houses qualify as haute couture under strict rules, mostly in Paris. These pieces carry a high price due to the luxury fabrics and time-intensive craftsmanship. Haute couture is about artistry, often seen on runways rather than in everyday wear.
Mass Market Fashion


Mass market fashion targets a wide audience with affordable, trendy clothes made in large quantities. Brands use quick production methods to follow fast-changing style trends. This category sells mainly through department stores and online platforms.
Quality may be lower compared to ready-to-wear and haute couture, focusing instead on volume and low cost. Clothing is often seasonal and designed to appeal to the general public. Mass market fashion allows many consumers to access current styles quickly.
Trends and Innovations in Fashion Design
Fashion design is changing fast, with new ideas shaping what people wear. These changes focus on using eco-friendly methods, smart materials, and digital tools to create clothes in smarter ways.
Sustainable Fashion


Sustainable fashion aims to reduce harm to the environment. Designers use natural fibers like organic cotton and hemp that need fewer chemicals and water. Recycling old clothes into new fabrics also cuts waste.
Brands are also focusing on fair labor practices, making sure workers get safe conditions and fair pay. Consumers now expect transparency about where and how clothes are made.
Some companies use plant-based dyes that avoid toxic chemicals. Others design clothes to last longer or be easily repaired.
Technological Advances in Fabrics

New fabrics now have special features like being water-resistant, wrinkle-free, or temperature-regulating. These materials improve comfort and durability.
Nanotechnology allows fabrics to resist stains and bacteria. Some textiles can even adapt to the wearer’s body heat or moisture.
Smart fabrics include sensors woven into clothes to track health or movement. These advances make clothes more functional for sports and daily life.
Materials like recycled polyester and bio-fabricated leather reduce reliance on oil-based products and animal materials.
Digital Fashion and 3D Design


Digital tools help designers create virtual clothes before making physical samples. This reduces waste by lowering the number of prototypes needed.
3D design software allows for precise pattern making and fitting. It helps designers experiment with shapes and textures quickly.
Brands use digital fashion for virtual try-ons in online stores, improving the shopping experience. Some also sell digital-only clothes for use in social media or games.
This technology speeds up production and offers new creative possibilities.
Fashion Design Careers
Fashion design careers include learning skills, working in studios, and starting brands. Each path requires different steps but focuses on creativity, technical know-how, and business sense.
Becoming a Fashion Designer
To become a fashion designer, one usually studies fashion design or a related field. Many attend art or design schools to learn about fabrics, sewing, and fashion history.
Designers often start by making sketches and sewing sample clothes. Internships at fashion houses help build real-world experience. Strong skills in drawing and software like Adobe Illustrator are important.
A good designer also needs to know the market and current trends. Patience and persistence help, since breaking into fashion is competitive. Building a portfolio of original work is key to getting hired.
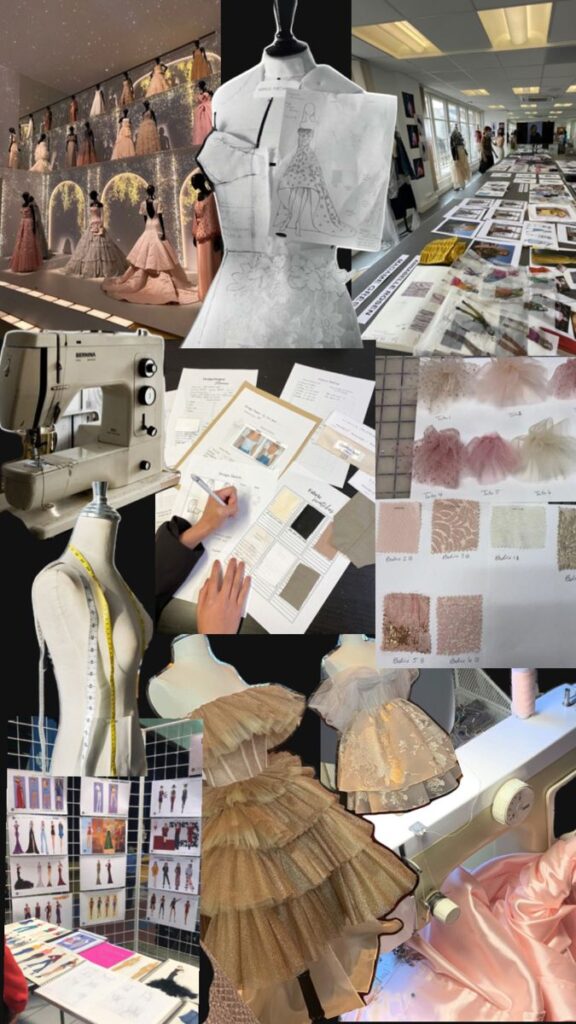


Roles in Fashion Design Studios
Fashion design studios have many jobs beyond creating clothes. Designers focus on concepts and looks. Pattern makers turn designs into templates for cutting fabric.
Sample makers sew the first versions of clothes to check fit and style. Technicians test materials and suggest changes. Sales and marketing teams promote the collections to buyers and stores.
Teamwork and good communication are important in studios. Each member plays a part in bringing a fashion line to life, from ideas to final store displays.
Building a Clothing Brand
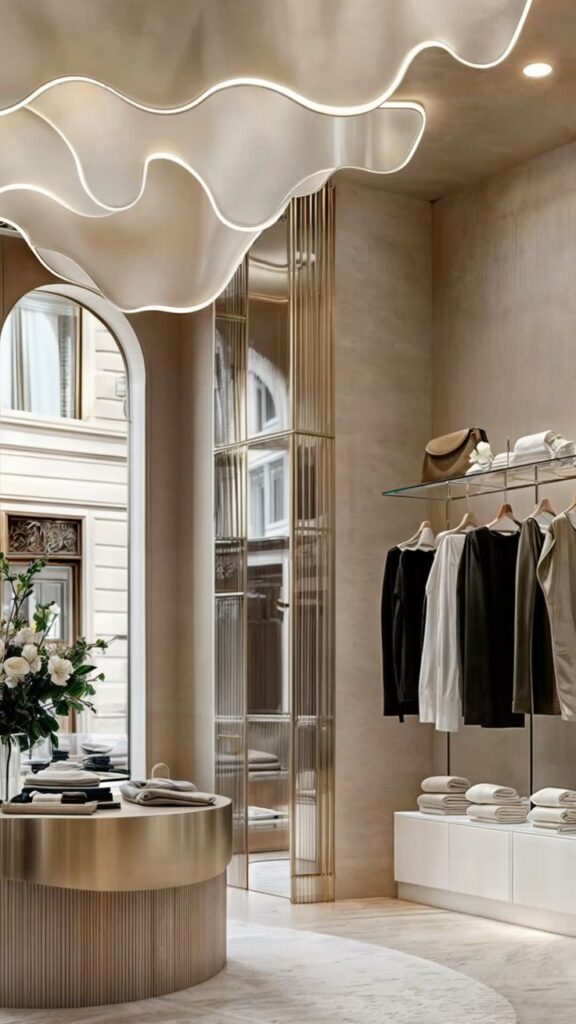


Building a clothing brand means blending design with business. Designers create original styles that fit a target market. Branding includes logo design, packaging, and advertising.
Secure funding is necessary for production and marketing. Many start small with online stores or local boutiques. Social media helps reach customers and build a following.
Consistent quality and clear brand identity grow customer loyalty. Managing supply chains and pricing are critical to staying profitable. Success often depends on balancing creativity with smart business decisions.
Fashion Shows and Marketing
Fashion shows require careful planning to display designs effectively. Marketing strategies help brands reach the right audience and build their image.
Preparing Collections for Runway
Designers choose pieces that show their season’s theme clearly. The collection must have a mix of standout looks and wearable staples.
Models are cast to fit the style and mood of the show. Hair, makeup, and music are selected to create a consistent atmosphere.
Logistics like timing, venue, and lighting are arranged to make sure every detail enhances the clothing. Designers often work closely with stylists and production teams.
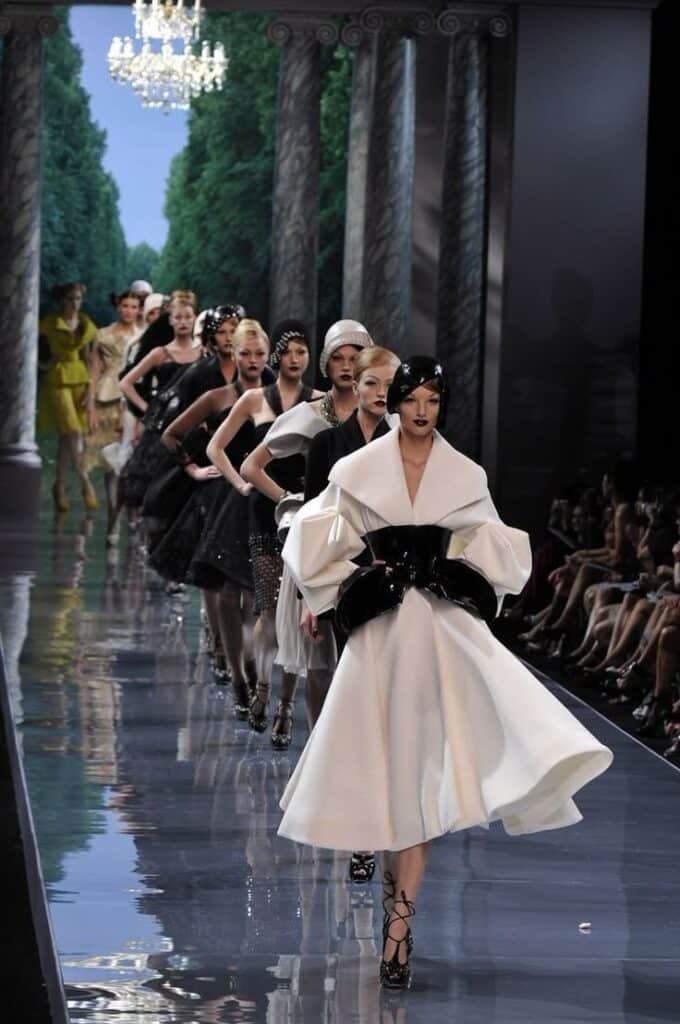
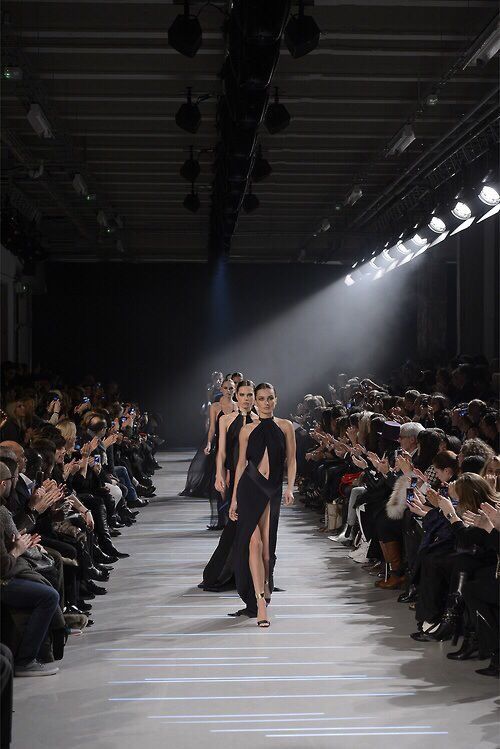


Fashion Marketing Strategies
Marketing in fashion focuses on building brand identity and driving sales. Social media campaigns and influencer partnerships are common tools.
Brands use events, advertisements, and online content to showcase their collections. Email marketing and special discounts help keep customers engaged.
Data analytics track customer preferences, guiding future designs and promotions. Effective marketing creates a connection between the clothing and its buyers.
Global Influence in Fashion Design Clothing
Fashion design today reflects a mix of ideas from many parts of the world. Different cultures and cities shape styles, materials, and trends that influence designers globally.
Cultural Influences in Fashion
Fashion borrows a lot from cultural traditions. For example, Japanese kimono patterns and fabrics have inspired many modern collections.
Many designers use elements like embroidery, prints, and colors that represent specific cultures. These details make clothes more meaningful and unique.
Cultural exchange happens when designers travel or work with artisans from other countries. This collaboration creates fresh looks while preserving traditional crafts.


International Fashion Capitals
Cities like Paris, Milan, New York, and London are key hubs where new fashion trends start. These cities host big fashion weeks that grab attention worldwide.
Each capital has its style. Paris is known for haute couture, Milan for luxury brands, New York for streetwear, and London for edgy, experimental fashion.
Designers from other countries often move to these cities to grow their careers. The mix of talent and cultures in these places drives innovation in fashion design.
- 1.7Kshares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest1.7K
- Twitter0
- Reddit0



