3D printing sharks – the conversation needs to include them whenever we’re talking about creative, hands on innovation, because let’s be honest – it’s a project that initially might sound kinda quirky but it’s a real eye-opener on the intersection of design, tech, education, manufacturing and plain old imagination.
From detailed shark figurines and educational models that actually belong in a classroom, right through to prototypes being used by marine researchers and people getting new products off the ground – 3D printing sharks has turned into a pretty cool & genuinely useful application – and it’s exactly the kind of place where creativity and new tech come together to make learning, research, and design more fun and accessible.
- What Does “3D Printing Shark” Mean?
- Why Sharks Are Popular in 3D Printing
- The 3D Printing Process: Step by Step
- Educational Uses of 3D Printed Sharks
- 3D Printed Sharks in Product Design and Engineering
- Art, Collectibles, and Creative Projects
- Business and Marketing Applications
- Common Challenges (and How to Solve Them)
- Frequently Asked Questions (AEO-Optimized)
- Why 3D Printing Sharks Matter in the Bigger Picture
- Final Thoughts
In this in-depth guide, we’re going to take a closer look at what exactly “3D printing sharks” entails, how it all gets done step by step, the tools and materials that are involved and why this topic is still generating a lot of buzz between hobbyists, academics and business folk. Whether you’re a maker, an educator, a marketer or a business owner keeping up with the latest tech trends – this article breaks it all down in a clear, no nonsense way
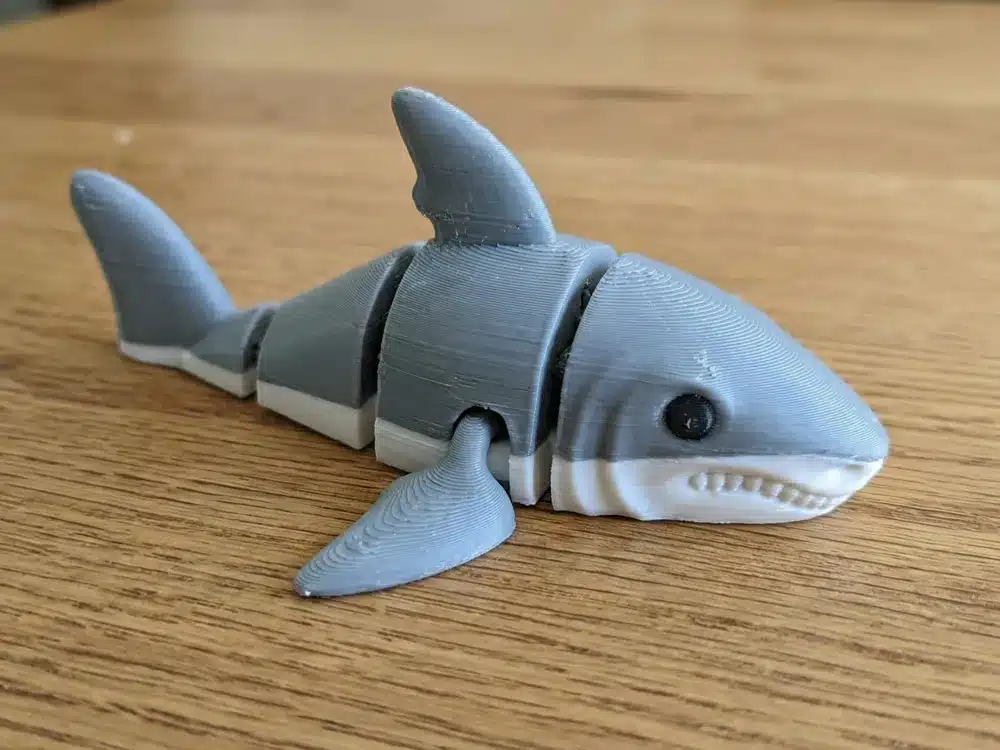
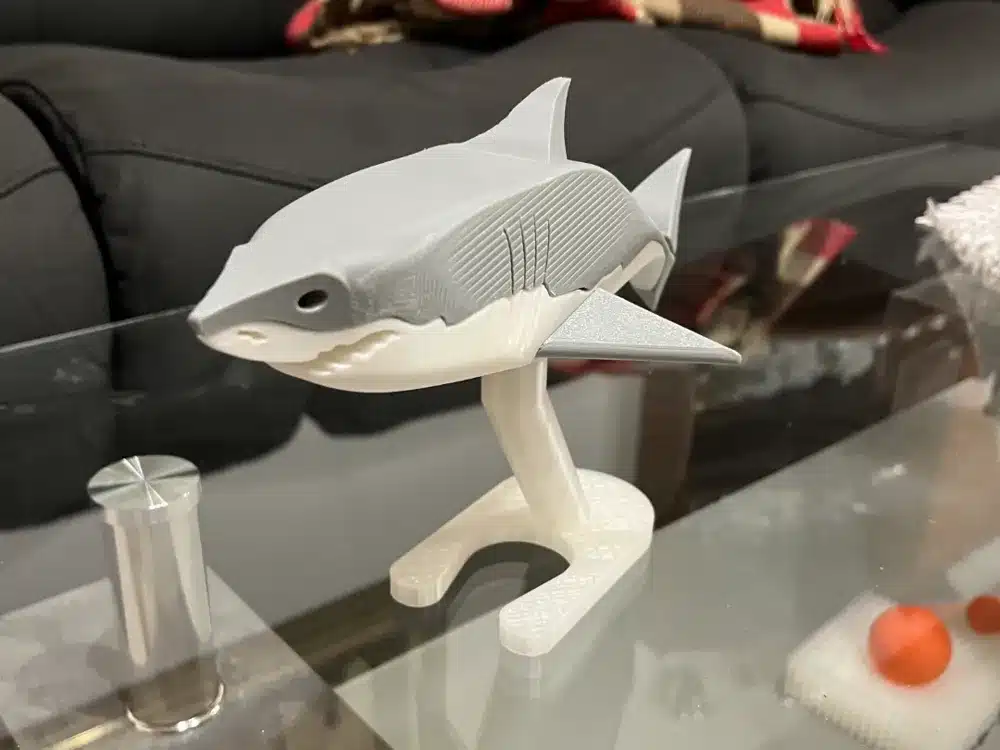


What Does “3D Printing Shark” Mean?
At its core, 3D printing shark involves creating a three-dimensional physical model of a shark using additive manufacturing technology. This process starts with a digital design file and builds the object layer by layer using materials such as plastic, resin, or composites.
However, the intent behind a 3D printed shark can vary widely:
- Decorative or collectible models for enthusiasts
- Educational anatomy models for classrooms and museums
- Engineering prototypes inspired by shark hydrodynamics
- Art installations or marketing displays
- Custom toys, figurines, or product mockups
The same underlying process supports all of these use cases—the difference lies in design complexity, scale, and material choice.
Why Sharks Are Popular in 3D Printing
Sharks are one of the most frequently modeled animals in 3D printing communities, and there are several reasons for this popularity:
1. Instantly Recognizable Form
The shark silhouette—streamlined body, dorsal fin, tail—is iconic. That makes it ideal for visual storytelling, branding, and display.
2. Complex Geometry (But Printable)
Sharks offer organic curves and dynamic shapes that showcase the strengths of 3D printing, while still being printable without extreme engineering challenges.
3. Cross-Industry Appeal
Shark models are relevant to:
- STEM education
- Marine biology
- Industrial design
- Pop culture and collectibles
- Marketing and experiential campaigns
4. Scalability
A shark model can be printed as a palm-sized figurine or scaled up into a large-format display piece—without changing the underlying design logic.
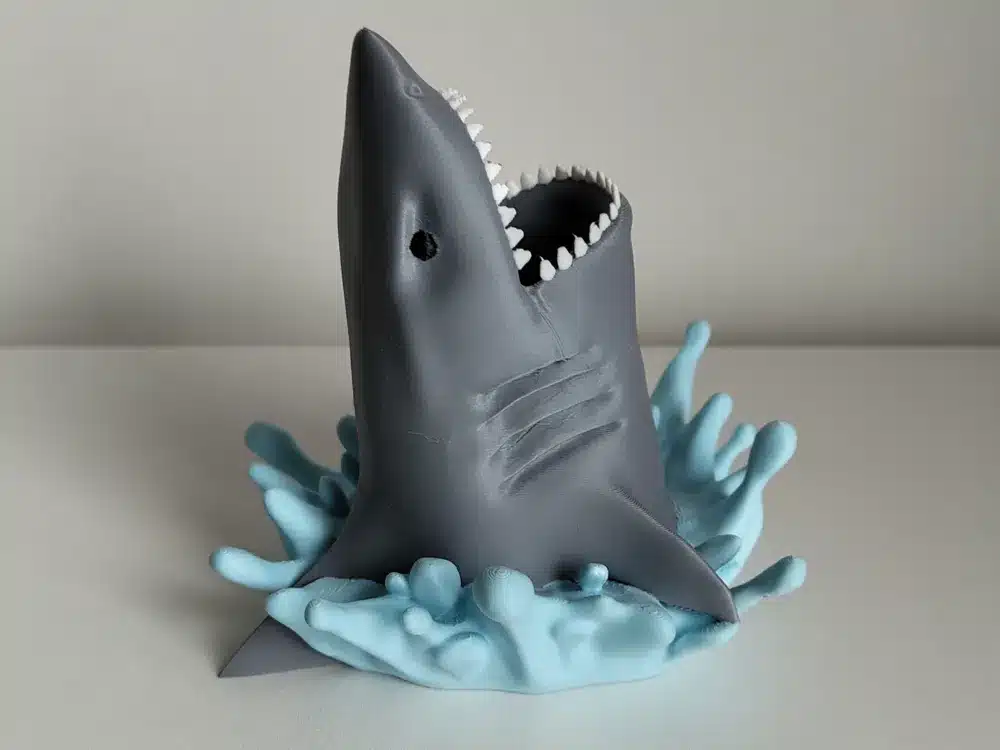
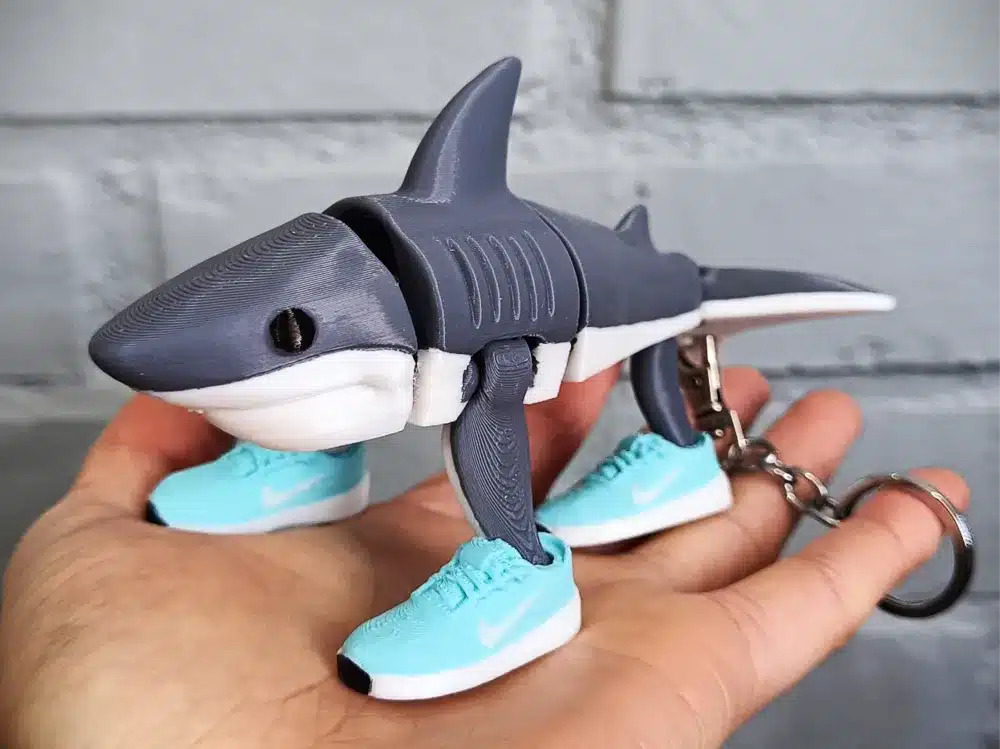


The 3D Printing Process: Step by Step
Let’s walk through the complete workflow for 3D printing shark, from idea to finished object.
Step 1: Choosing or Creating a Shark Model
You have two main options:
Download an existing model
Popular 3D model marketplaces and repositories offer thousands of shark designs, ranging from cartoon-style to hyper-realistic.
Design your own shark
Using CAD or sculpting software allows for full customization. This is common for:
- Educational accuracy
- Branding-specific designs
- Product prototypes
Key design considerations:
- Wall thickness
- Overhang angles
- Print orientation
- Internal supports
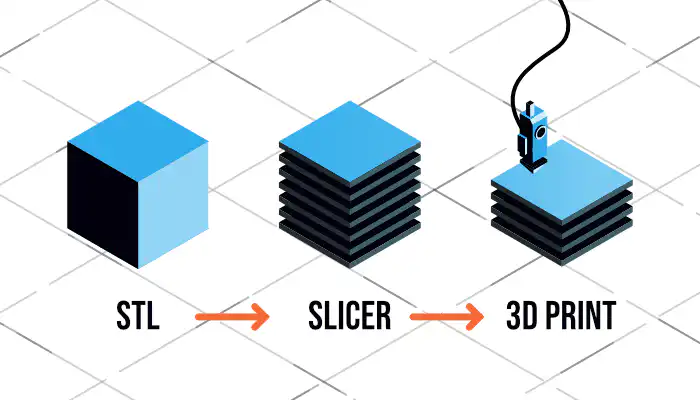
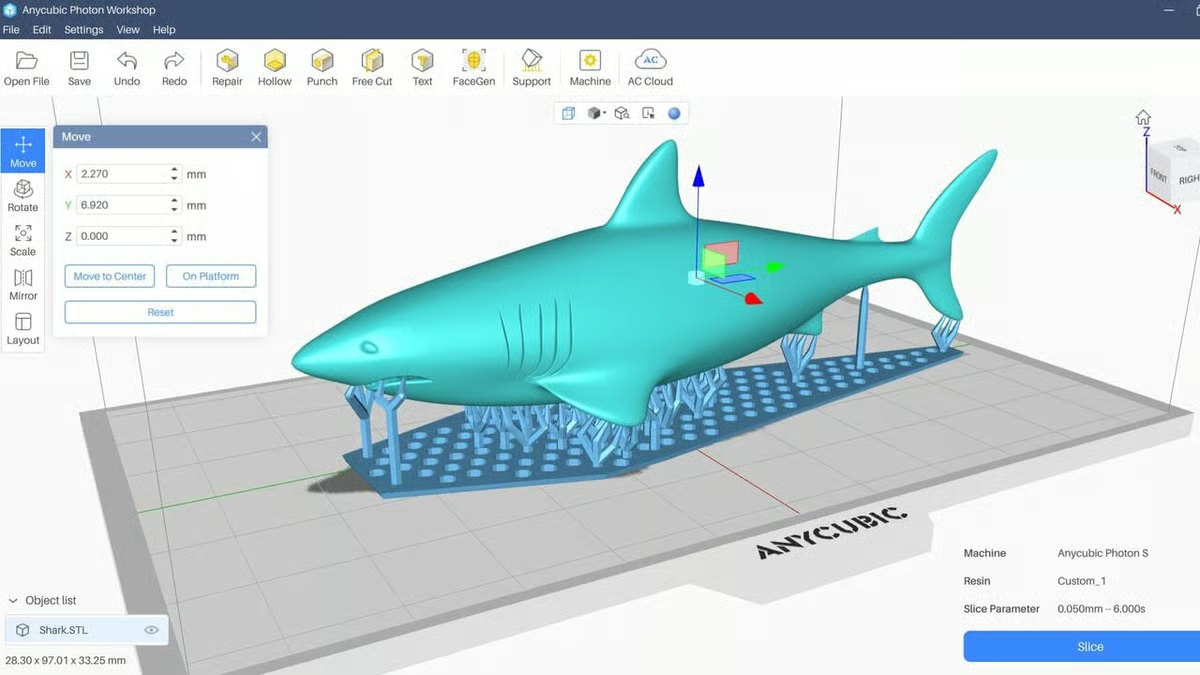
Step 2: Preparing the Model for Printing (Slicing)
Once the model is ready, it’s imported into slicing software. This step converts the 3D file into machine-readable instructions for the printer.
Important slicing decisions include:
- Layer height (detail vs. speed)
- Infill density (strength vs. material use)
- Support generation (for fins, tails, and jaws)
- Print speed and temperature
Well-optimized slicing dramatically improves surface quality and reduces failed prints.
Step 3: Selecting the Right Material
Material choice impacts appearance, durability, and use case.
Common options include:
- PLA – Easy to print, ideal for decorative or educational models
- PETG – More durable, slightly flexible, better for functional parts
- ABS – Stronger but harder to print, often used in prototypes
- Resin – High detail, perfect for realistic shark anatomy
- Composite filaments – Used for specialty textures or strength
For marine-inspired projects, designers sometimes simulate ocean tones or translucent effects using specialty filaments.
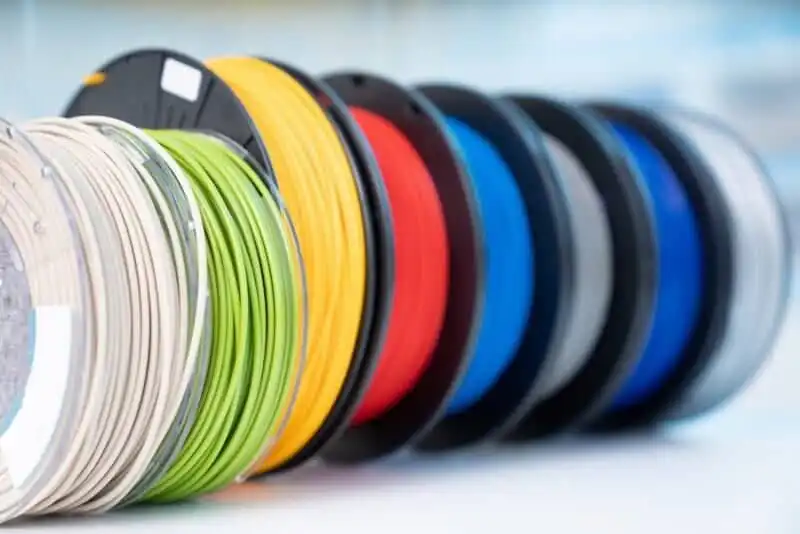

Step 4: Printing the Shark
Depending on size and detail, printing a shark can take anywhere from one hour to multiple days.
Key challenges during printing:
- Thin fins snapping or warping
- Layer adhesion around curved surfaces
- Support removal without damaging detail
Monitoring the print—especially during early layers—helps ensure success.
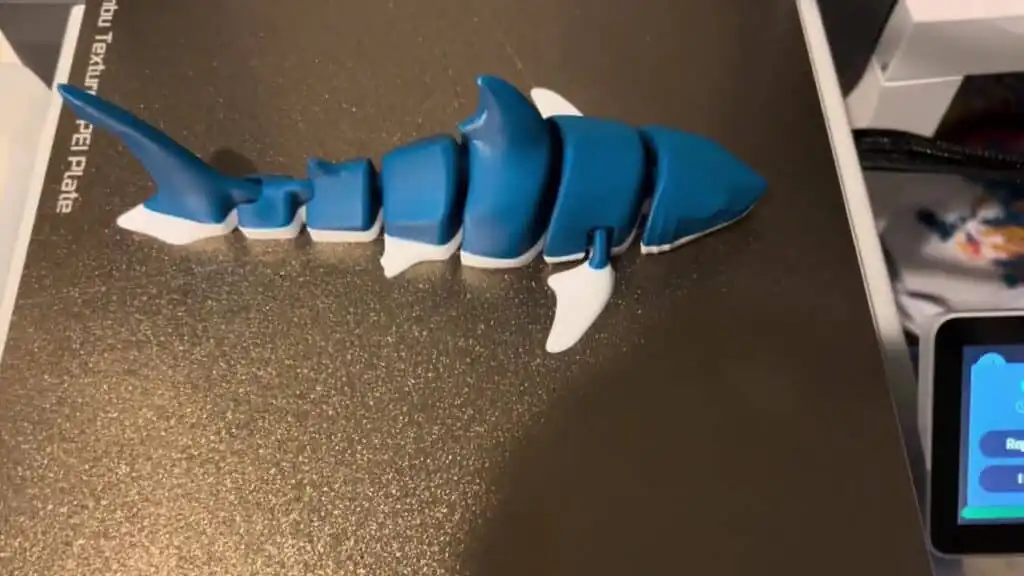

Step 5: Post-Processing and Finishing
After printing, most shark models benefit from post-processing:
- Support removal
- Sanding and smoothing
- Painting or airbrushing
- Clear coating or sealing
For educational or display purposes, finishing can transform a basic print into a professional-grade model.
Educational Uses of 3D Printed Sharks
3D printed sharks play a growing role in STEM education and marine science.
Classroom Learning
Teachers use shark models to explain:
- Anatomy and skeletal structure
- Predator-prey dynamics
- Evolution and adaptation
Unlike flat images, 3D prints allow hands-on exploration.
Museums and Aquariums
Institutions use printed sharks for:
- Interactive exhibits
- Touch-safe displays
- Custom scale models
Accessibility Benefits
3D models help visually impaired learners understand shape and structure through touch—something traditional displays can’t provide.
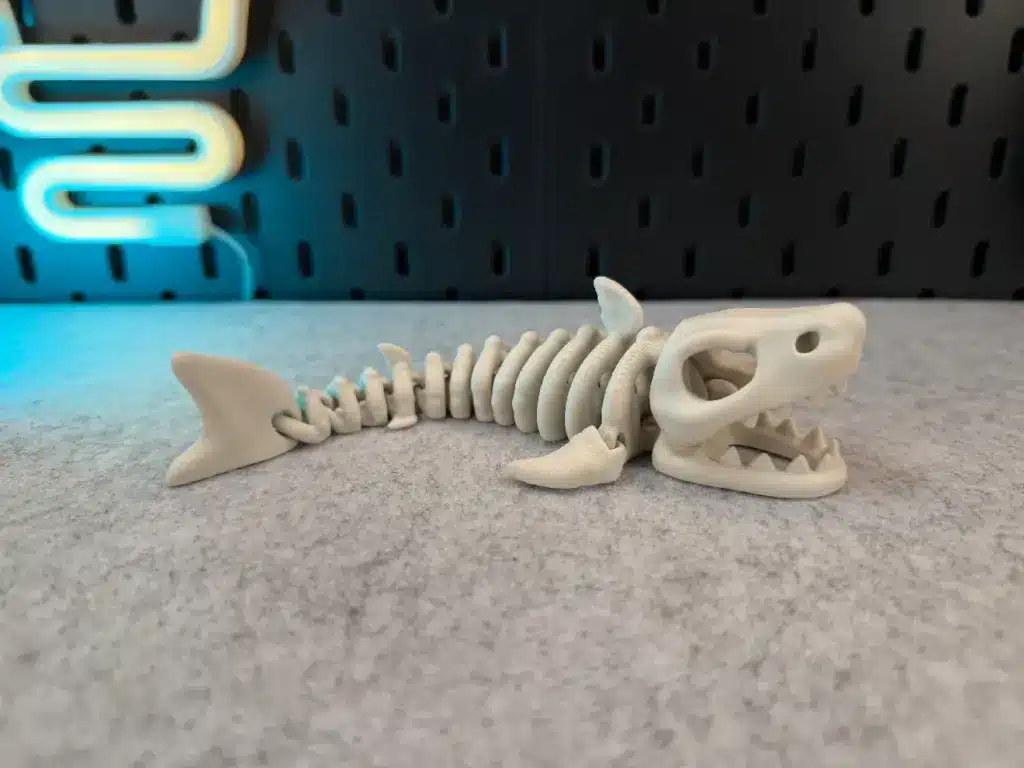
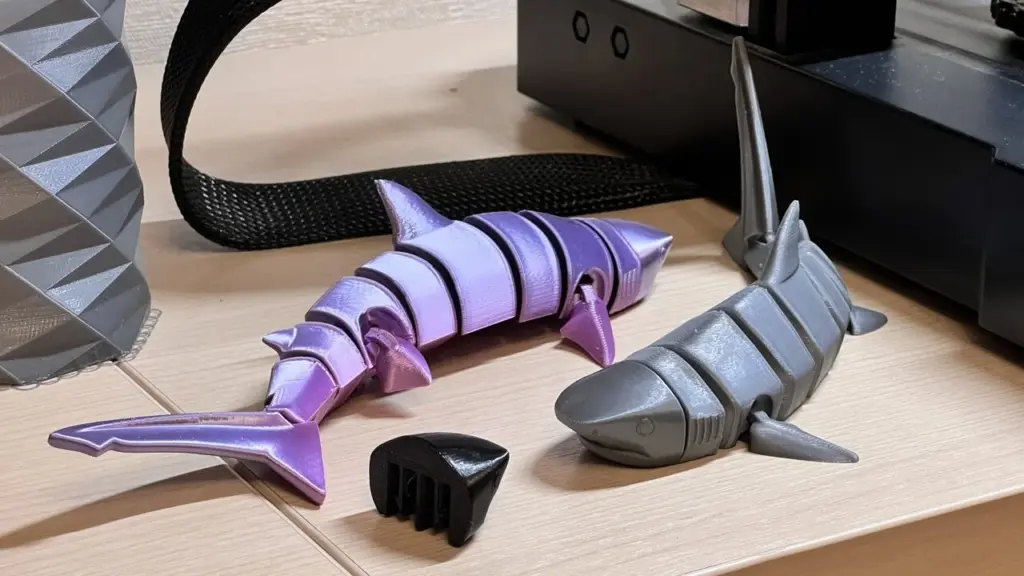


3D Printed Sharks in Product Design and Engineering
Sharks are not just animals—they’re engineering inspirations.
Designers study shark skin, fins, and movement to improve:
- Hydrodynamics
- Drag reduction
- Aerodynamic surfaces
3D printing allows rapid prototyping of shark-inspired forms, enabling:
- Faster design iteration
- Lower R&D costs
- Physical testing before mass production
This is especially useful in industries like sports equipment, automotive design, and robotics.
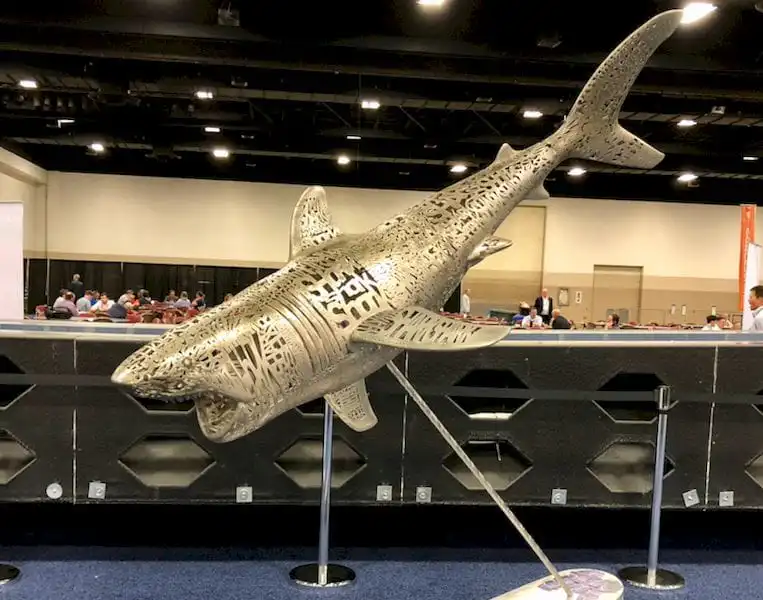

Art, Collectibles, and Creative Projects
For artists and creators, 3D printing shark opens up endless creative possibilities.
Examples include:
- Stylized or abstract shark sculptures
- Custom toy designs
- Limited-edition collectibles
- Pop culture mashups
Because digital files are easily modified, artists can:
- Change poses
- Add textures or patterns
- Create themed collections quickly
This flexibility is one reason shark models perform well in online marketplaces and social platforms.
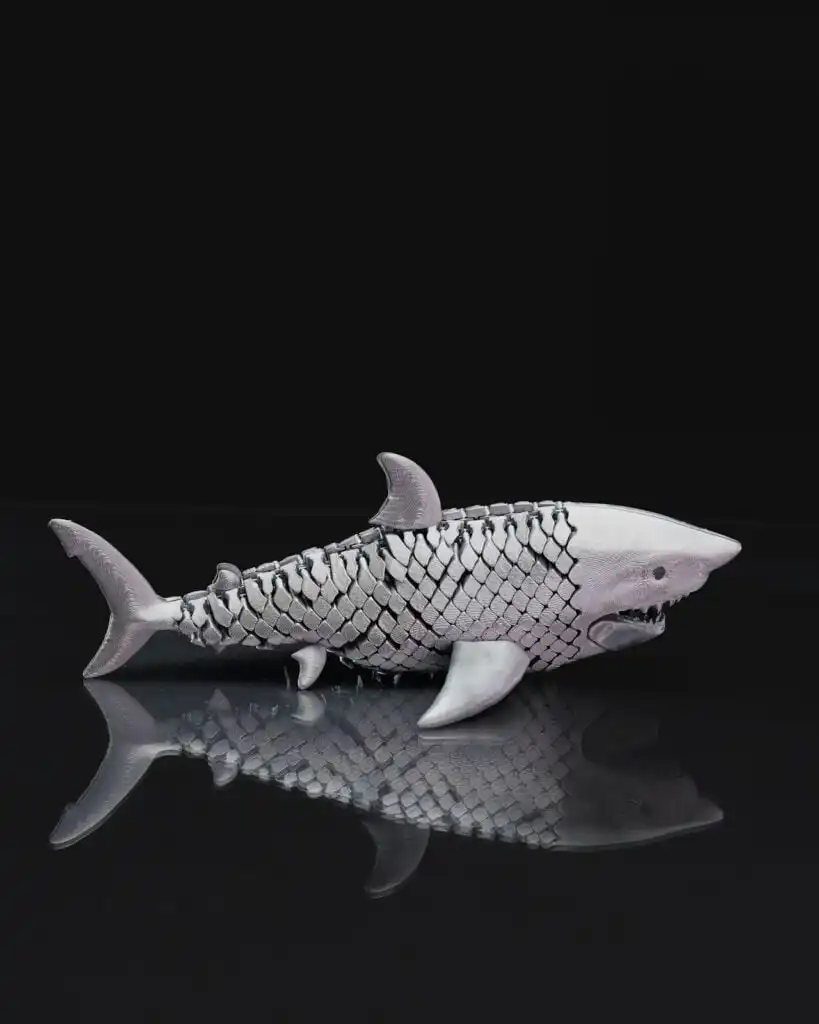


Business and Marketing Applications
From a business perspective, 3D printed sharks can be powerful visual assets.
Branding and Displays
A shark model can symbolize:
- Strength
- Speed
- Innovation
- Market leadership
Companies use them for:
- Trade show displays
- Office decor
- Experiential marketing
Rapid Prototyping for Campaigns
Marketing teams can test physical concepts quickly—without waiting weeks for traditional manufacturing.
Content and SEO Value
Topics like “3D printing shark” generate interest because they combine:
- Visual appeal
- Emerging technology
- Curiosity-driven search intent
This makes them ideal for blog content, video demonstrations, and social media storytelling.
Common Challenges (and How to Solve Them)
Problem: Thin fins breaking
Solution: Increase wall thickness or print at a different orientation
Problem: Poor surface detail
Solution: Lower layer height or switch to resin printing
Problem: Long print times
Solution: Split the model into sections or adjust infill density
Problem: Support scars
Solution: Use custom supports or refine post-processing techniques
Understanding these challenges upfront saves time and material.
Frequently Asked Questions (AEO-Optimized)
Can you 3D print a realistic shark?
Yes. With high-resolution resin printers and detailed models, it’s possible to create extremely realistic shark prints suitable for education or display.
What is the best material for a 3D printed shark?
PLA is best for beginners, while resin is ideal for high-detail models. PETG works well for durability.
How long does it take to 3D print a shark?
Small models can take 1–3 hours. Large or detailed sharks may take 24 hours or more.
Are 3D-printed sharks food-safe or waterproof?
Standard prints are not food-safe. Waterproofing requires sealing and proper material selection.
Why 3D Printing Sharks Matter in the Bigger Picture
3D printing shark isn’t just about creating a cool object—it reflects how digital design, physical production, and storytelling come together.
For educators, it enhances learning.
For designers, it accelerates innovation.
For businesses, it creates memorable experiences.
And for anyone exploring additive manufacturing, it’s a powerful reminder of what modern technology makes possible—one layer at a time.
Final Thoughts
The popularity of “3D printing shark” highlights a broader trend: people want tangible, visual, and interactive experiences—not just ideas on a screen. As 3D printing becomes more accessible, shark models will continue to surface in classrooms, studios, labs, and marketing campaigns worldwide.
Whether you’re printing your first shark or scaling up a professional project, the process offers creativity, learning, and impact far beyond the finished model.
- 16shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest16
- Twitter0
- Reddit0