Automotive UI design shapes how you interact with your vehicle’s technology, making it crucial for safety, efficiency, and comfort. A well-designed automotive UI prioritizes intuitive controls that minimize driver distraction while providing quick access to essential functions. This focus helps create a seamless connection between you and the car, improving both the driving experience and overall satisfaction.
Modern automotive interfaces go beyond simple controls, integrating real-time data, personalization options, and adaptive systems that respond to your preferences. Understanding these elements can help you appreciate the complexity behind the screens and buttons in your car.
You will also find that automotive UI design requires careful testing and iteration, balancing innovation with regulations and user needs. By paying attention to these details, you can better grasp how thoughtful design makes driving safer and more enjoyable.
Key Takeways
- Effective automotive UI reduces cognitive load for safer driving.
- Personalization enhances your connection to the vehicle’s system.
- Rigorous testing ensures functionality aligns with real-world use.

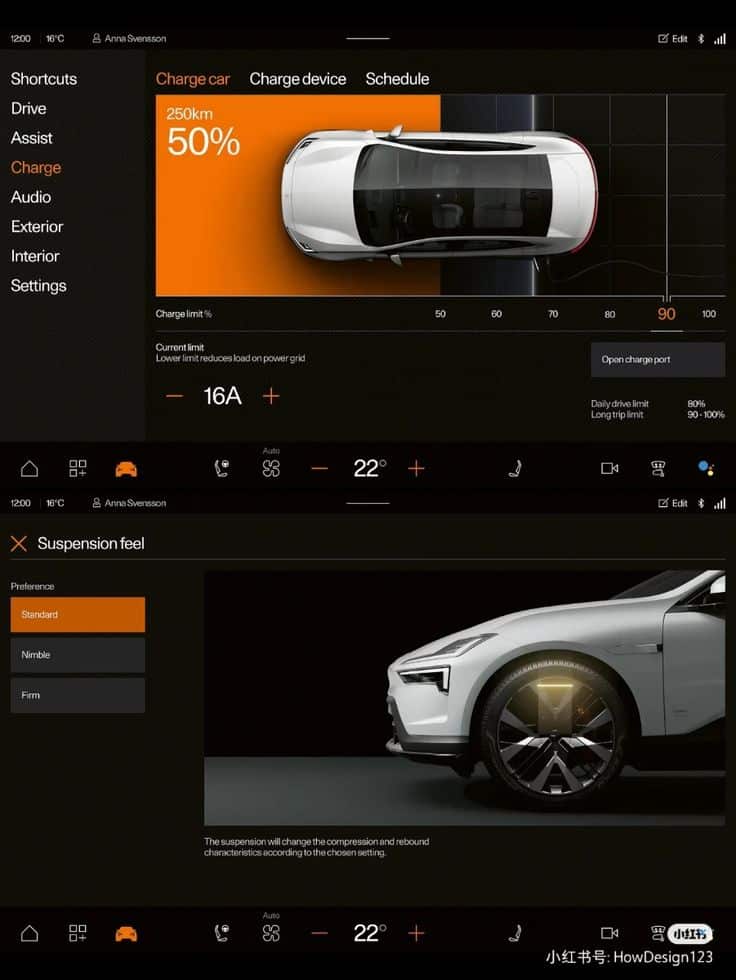
Principles of Automotive UI Design
When designing automotive UI, focus on delivering interfaces that support safety, ease of use, and minimal distraction. The experience should help you interact with the vehicle smoothly, keeping your attention on driving. Key areas include understanding user needs, managing interactions in dynamic environments, and ensuring the system is easy to learn and reliable.
Core Concepts of User Experience
Your automotive UI should prioritize clarity and context-awareness to enhance user experience (UX). This means presenting information precisely when you need it, avoiding overload or confusion. Sensory limitations—such as reduced attention and peripheral vision while driving—must be considered.
Accessibility factors like tactile feedback and voice recognition improve your interaction without taken away focus. The design should also balance automation and control, providing necessary information but avoiding unnecessary alerts that could cause distraction.
A consistent and predictable interface helps you build trust and confidence with the system. Feedback loops are essential—you need clear responses for every action, signaling success, failure, or system state changes effectively.
Interaction Design in Vehicle Environments
Automotive interaction design requires adapting to a fast-changing context and limited driver focus. Controls should be intuitive, minimizing the steps to achieve basic tasks like adjusting climate or navigation.
Physical interfaces (buttons, knobs) often supplement touchscreens to offer tactile confirmation without visual dependence. Gesture control and voice commands can supplement traditional inputs to reduce distraction but must be responsive and error-tolerant.
Timing and sequencing of interactions are critical. Your inputs must be registered swiftly, and the system should predict possible next steps to reduce the cognitive load. Prioritizing critical functions over secondary features maintains safety.
Usability and Learnability in Car Interfaces
Your automotive UI must be easy to understand and to use from the first experience. Usability focuses on simple navigation, clear labeling, and straightforward access to commonly used features, reducing the need for trial and error.
Learnability is enhanced by consistent layouts and familiar interaction patterns that reduce cognitive effort. Visual hierarchy, such as color contrast and font size, helps you identify important elements quickly.
Regular updates and user research refine usability by addressing real-world user behavior. Incorporating tutorials or onboarding aids helps you adapt to complex systems without frustration while driving.
Designing For Safety and Accessibility
When designing automotive UI, you must prioritize clear information delivery and ease of use to support driver focus and response times. Your design should address mental workload, ensure usability for diverse users, and integrate technology that actively improves safety.
Reducing Cognitive Load
Your interface should present information in a way that minimizes mental effort while driving. Use clear visual hierarchies and limit the number of simultaneous alerts to prevent distractions.
Simplify menu structures and rely on familiar icons to help your users navigate quickly without searching. Combine voice commands and tactile feedback to reduce the need for visual attention.
Prioritize critical driving data such as speed, navigation, and warnings on primary displays. Secondary information should appear only when relevant, avoiding clutter and enabling faster decision-making.
Accessibility in Automotive UI
Your automotive UI must accommodate users with varying physical and sensory abilities. This includes adjustable font sizes, high-contrast color schemes, and voice control features that aid drivers with limited vision or dexterity.
Ensure controls are reachable and operable without excessive effort. Incorporate customizable settings so users can tailor the experience to their specific needs, whether through haptic feedback or simplified interfaces.
Compliance with accessibility standards not only benefits drivers with disabilities but also improves overall usability. Your design should facilitate equal access without compromising safety or functionality.
Enhancing Safety Features
Integrate driver-assistance systems seamlessly into your UI to improve situational awareness without overwhelming the user. Visual and auditory alerts should be clear, timely, and distinguish between different levels of urgency.
Use real-time data to support proactive safety measures, such as collision warnings, lane departure alerts, and adaptive cruise control. Your interface must prioritize these features while maintaining intuitive control and avoiding distraction.
Design interfaces that encourage safe driving behavior by simplifying interaction during critical moments. Your UI should enable quick adjustments and reduce the risk of errors, directly contributing to crash prevention and improved road safety.
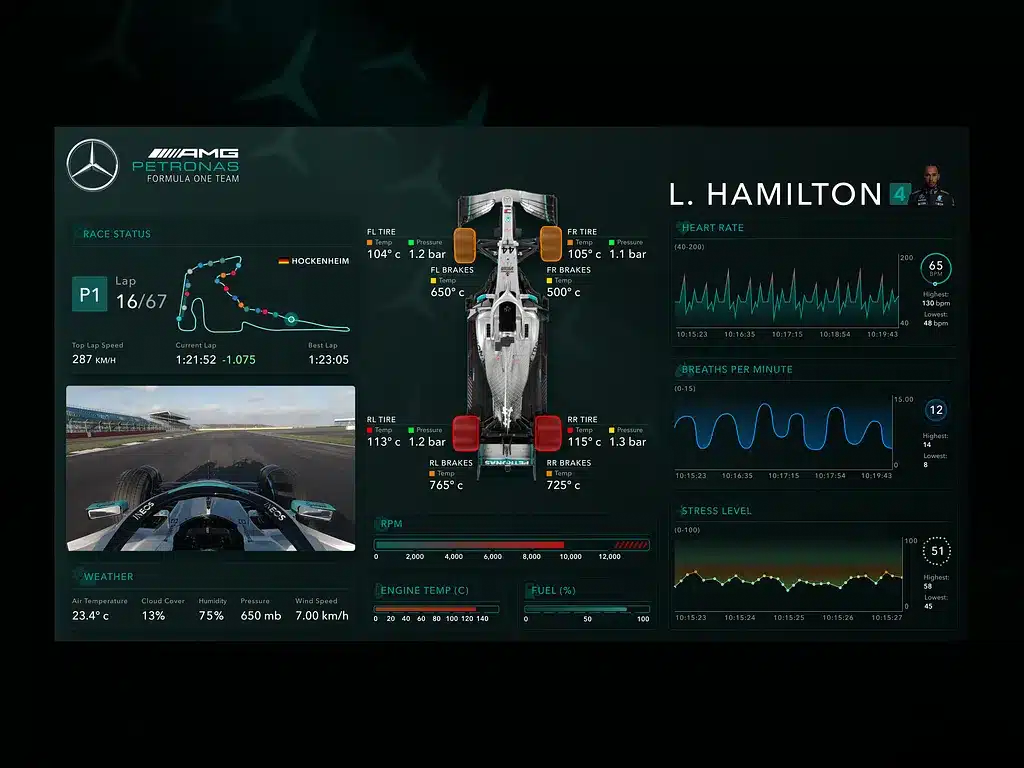
Infotainment and Real-Time Data Integration
You rely on automotive UI to provide seamless access to information and controls while driving. Efficient integration of real-time data in your infotainment system enhances safety, convenience, and interaction without distraction.
Modern Infotainment Systems
Your vehicle’s infotainment system serves as the central hub for entertainment, communication, and control features. These systems typically have large infotainment screens designed for easy readability and accessibility.
You can expect support for multimedia playback, phone connectivity, climate control, and sometimes vehicle settings. Integration with embedded Linux or other operating systems supports flexibility in updates and third-party apps.
Modern design prioritizes reducing driver distraction by using clear layouts, minimal taps, and predictable navigation flows. Multimodal inputs such as touch, voice, and physical controls give you multiple ways to interact safely.
Real-Time Navigation and Data
Your navigation system now uses real-time data to improve route accuracy and adapt to changing conditions instantly. Access to traffic updates, road hazards, and weather informs route recalculations.
This data often comes from external sources through cellular or satellite connections, ensuring you get the latest information directly on your digital interface. Real-time navigation also includes lane guidance and points of interest tailored to your preferences.
Efficient use of this data can reduce travel time and stress. Real-time data animations and alerts are displayed clearly, avoiding information overload that could distract you from the road.
Voice User Interfaces in Cars
Voice user interfaces (VUIs) allow you to control various functions using natural speech. This enables hands-free operation of navigation, media, phone calls, and climate settings.
Effective VUIs understand context and intent, allowing complex commands like “Find the nearest gas station open now.” They also provide audible feedback to confirm actions, keeping your eyes on driving.
Privacy, noise handling, and system responsiveness are key design considerations. Your system should minimize false triggers and support multilingual commands if needed.
Digital Displays and Interfaces
Digital displays in your vehicle vary from touchscreens to instrument clusters and heads-up displays. These interfaces consolidate information, offering you intuitive control points.
A clear and consistent graphical interface helps you quickly interpret vehicle status, incoming alerts, or media controls. The design uses high contrast, legible fonts, and logical grouping of functions.
Customization options let you prioritize what you want to see, like trip data or media info. Some systems support gesture control, enhancing interaction flexibility while maintaining focus on driving.
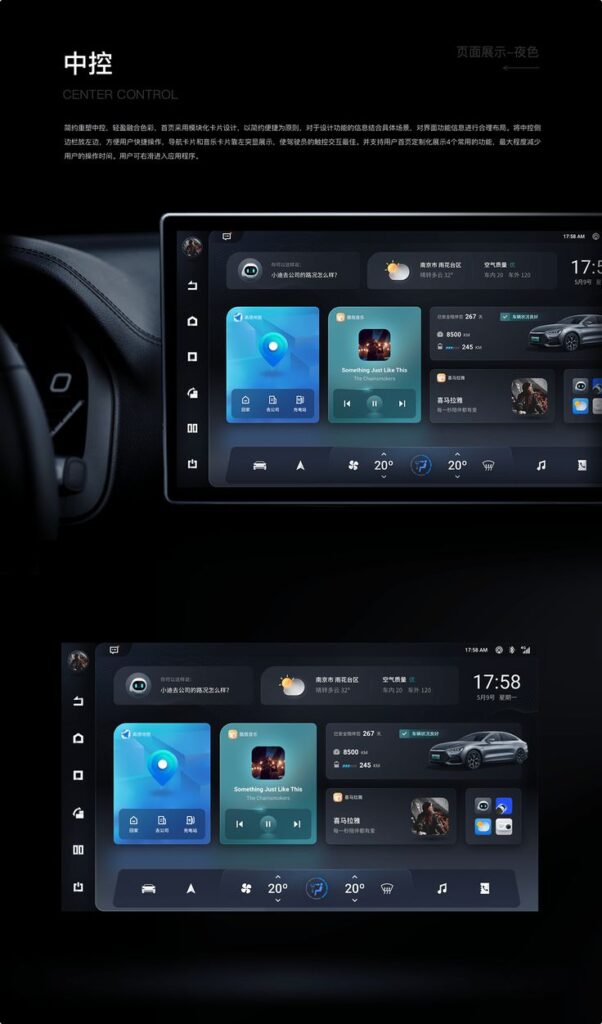
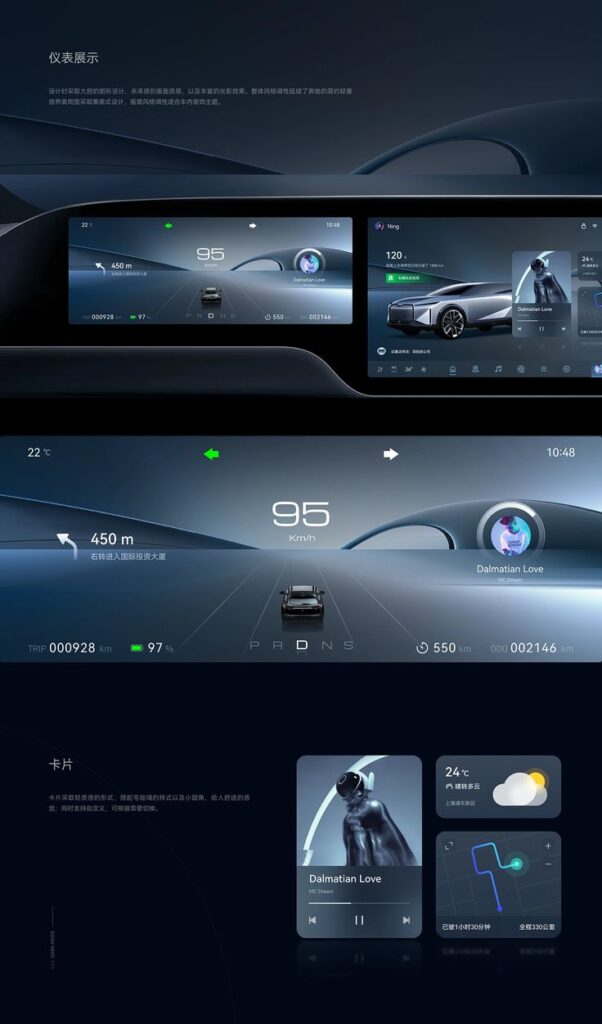
Personalization and Emotional Connection
Your interaction with a vehicle goes beyond functionality; it involves how well the design fits your preferences and creates a bond. Tailoring settings to your needs and evoking emotional responses through design elements are critical to enhancing your driving experience.
User-Centric Customization
You can make the vehicle truly your own by adjusting settings based on your preferences. Automotive UI design often includes customizable climate controls, seat positions, lighting, and infotainment options. These features allow you to modify the environment so it reflects your comfort and style.
Personalization also extends to digital interfaces, where you might set preferred routes, music playlists, and voice commands. By addressing your unique needs, the design reduces frustration and increases ease of use.
Designers incorporate adaptive systems that learn your habits and automatically adjust. The goal is to minimize effort while maximizing your sense of control over the vehicle.
Building Emotional Engagement
Designing for emotional connection involves more than customization; it taps into how the vehicle makes you feel. Visual elements, sounds, and tactile feedback are chosen to foster a positive emotional response.
You might notice how ambient lighting changes to suit driving conditions or how a smooth, intuitive interface builds trust. TheseDetails contribute to making each drive feel personal and engaging.
Emotional design in automotive UI also emphasizes clarity and transparency, ensuring you understand data practices and system functions. This transparency helps establish confidence, which strengthens your emotional bond with the vehicle.

Prototyping, Testing, and Industry Trends
You rely on detailed prototyping and user-centered testing to refine automotive UI design. Keeping pace with emerging technologies like augmented reality and addressing UX design challenges is essential for creating interfaces that meet modern drivers’ needs.
Prototyping and UI Research
Start by building high-fidelity prototypes using tools like Figma or ProtoPie, which allow integration with real car data for realistic simulations. This approach helps you visualize interactions in a genuine driving context.
Component-driven prototyping accelerates iterations and improves accuracy. You can test interface elements individually and ensure consistency across systems.
Combine in-car user testing with digital UI research to capture both practical behavior and analytical insights. This dual method enhances your understanding of user needs and system performance.
UX Testing and User Feedback
You gather user feedback through structured UX testing protocols that simulate real driving scenarios. Testing in actual vehicles ensures that usability issues are detected under realistic conditions.
Collect quantitative and qualitative data during tests. Metrics might include task completion time, error rates, and subjective comfort or satisfaction.
Iterate your design based on this feedback to address pain points such as distraction, complexity, or responsiveness. Effective user testing reduces risk and enhances safety.
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends
Augmented reality is increasingly integrated into automotive UI, offering heads-up displays that deliver critical information without diverting attention. You should explore AR-driven interfaces for navigation and safety alerts.
Connectivity and AI-driven personalization are shaping the future of automotive UI. Systems like Tesla’s leverage continuous software updates and machine learning to enhance user experience over time.
Stay informed on evolving standards and technologies to ensure your designs remain competitive and compliant with industry expectations.
- 116shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest113
- Twitter3
- Reddit0