The emergence of 3D printing has revolutionized the way you can design and produce drone parts. This technology allows for customization and rapid prototyping, enabling you to create components that meet your specific needs and preferences. Whether you are a hobbyist looking to enhance your flying experience or a professional aiming for efficiency, 3D printed drone parts present a viable and innovative solution.
As you explore the various materials and techniques available for creating these parts, you will find numerous options that cater to different performance requirements. From lightweight plastics to durable metals, understanding the properties of each material will help you make informed choices. Learning how to design and build your own drone parts opens up a world of possibilities for customization and innovation.
The growing trend of 3D printing in the drone sector not only enhances DIY projects but also supports educational initiatives aimed at teaching design and engineering principles. Embracing this technology can lead to exciting advancements and creative applications in your drone projects, making it an enticing field to explore.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing enables custom designs and rapid prototyping for drone parts.
- Various materials offer unique advantages for specific drone applications.
- This technology fosters creativity and learning in DIY and educational projects.


The Role of 3D Printing in Drone Technology
3D printing has fundamentally altered drone manufacturing by streamlining production processes and enabling innovative designs. This technology has advanced rapidly, impacting both the types of parts produced and the overall efficiency of the drone industry.
Evolution of 3D Printing in Drones
The journey of 3D printing in drone technology began with early prototypes using basic materials. As techniques like additive manufacturing matured, more complex and durable materials became available. Now, manufacturers can produce intricate components such as frames, propellers, and even sensor mounts with precision.
Key milestones in this evolution include:
- Material Diversity: Progress from plastics to advanced composites.
- Production Techniques: Adoption of methods like Multi Jet Fusion for greater efficiency.
- Customization: Ability to produce tailored parts that meet specific needs quickly.
These advancements have made it possible to streamline production and reduce waste, demonstrating the growing significance of 3D printing in this field.
Impacts on the Drone Industry
The integration of 3D printing into the drone sector offers several distinct advantages. First, it significantly reduces development costs by automating design processes and minimizing material waste. This allows for faster production times, enabling you to bring products to market more quickly.
- Customization: You can create unique designs that cater to specific applications.
- Rapid Prototyping: Testing new ideas can be expedited, allowing for iterative design improvements.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Localized production reduces reliance on external suppliers.
Overall, these impacts empower manufacturers to innovate and respond to market demands with agility, transforming the landscape of the drone industry.
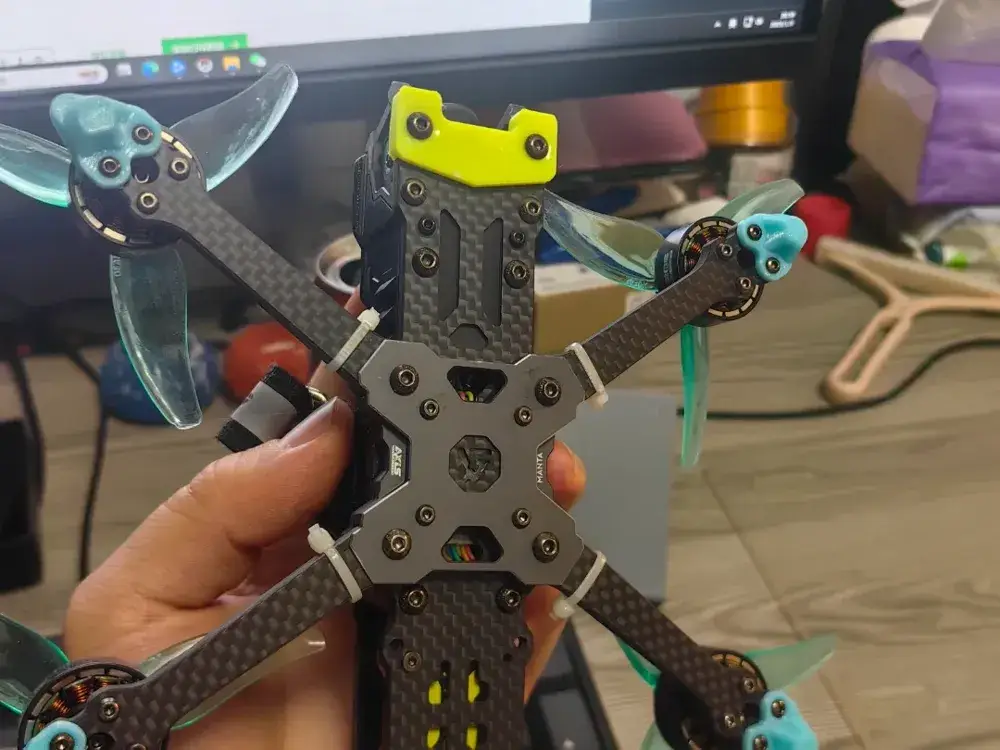

Materials and Techniques for 3D Printed Drone Parts
Choosing the right materials and techniques is essential for optimizing the performance and durability of your 3D printed drone parts. In this section, key considerations for material selection and advanced manufacturing techniques will be discussed.
Selecting Materials for Durability and Performance
Selecting the appropriate material is critical for 3D printed drone parts. Common options include:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): Easy to print but less durable than other materials. Best for prototypes.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Offers better strength and heat resistance but can warp during printing.
- Nylon: Known for its toughness and flexibility, making it a good choice for parts that experience stress.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified): Combines ease of printing with strength and flexibility.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Ideal for parts requiring flexibility, such as landing gear.
When choosing materials, consider factors like weight, impact resistance, and environmental conditions. Make sure the material’s specifications align with your drone’s performance needs.
Advanced Techniques in Additive Manufacturing
Advanced additive manufacturing techniques enhance the quality and functionality of drone parts. Some techniques include:
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Utilizes powdered materials and laser energy to create highly intricate structures with excellent mechanical properties.
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Common for hobbyists and offers versatility in material choice. Ideal for one-off prints.
- DLP (Digital Light Processing): Provides high-resolution prints suitable for smaller detailed components.
Additionally, techniques like multi-material printing allow you to combine strengths of different materials, enhancing overall performance. Employing these advanced methods can facilitate the production of lightweight yet durable drone components.

Designing Drone Parts for 3D Printing
When creating drone parts for 3D printing, it’s essential to focus on both structural integrity and design flexibility. This involves understanding how to optimize your designs to minimize weight while maximizing strength, and incorporating customization options to suit specific flight needs.
Optimizing Structures for Strength and Weight
To design durable drone components, you should prioritize the balance between strength and weight. Using lightweight materials like PLA+ or carbon fiber composites can enhance performance.
Key Design Techniques:
- Honeycomb Structures: This design significantly reduces weight while maintaining strength.
- Reinforcement Ribs: Integrate ribs in high-stress areas to distribute loads more evenly.
It’s also critical to ensure that wall thickness is consistently optimized. Aim for a thickness of at least 2-3 mm in load-bearing parts but adjust according to the design’s requirements. CAD software can assist in simulating stress points, ensuring your designs are both functional and reliable.
Customization and Modular Design
Customization is a major advantage of 3D printing. You can tailor drone parts to specific needs, improving both performance and functionality. Consider modular designs that allow for easy upgrades or repairs.
Benefits of Modular Designs:
- Interchangeability: Easily swap out damaged components without replacing the entire frame.
- Adaptability: Modify parts according to changes in technology or specific missions.
Make use of 3D modeling software to create designs that can accommodate future enhancements. By keeping a modular approach in mind, you ensure that your drone parts evolve with your requirements, providing longevity to your projects.

Building Drones with 3D Printed Parts
Creating a drone with 3D printed parts involves careful planning and execution. By focusing on assembly processes and proper integration of electronics, you can build a functional and efficient drone tailored to your specifications.
Assembly Processes and Techniques
The assembly of a drone begins with designing the frame. Use CAD software to model your drone’s frame, ensuring it meets required dimensions and weight specifications. Select appropriate materials such as PLA or ABS plastic for printing, as they balance weight and durability effectively.
Once your parts are printed, pay attention to the finishing touches. You may need to sand edges for a smooth fit and enhance aerodynamics. Use screws, nuts, and bolts to join printed components, ensuring secure connections. Consider utilizing adhesives for additional stability where necessary.
It’s important to test fit all parts before final assembly. This ensures that the components align correctly and promotes ease during integration with electronics. Creating a checklist of all necessary parts can be helpful in keeping your assembly organized.
Integrating Electronics and Accessories
After completing the frame assembly, the next step is integrating the electronics. This typically includes the flight controller, motors, electronic speed controllers (ESC), and battery. Choose a flight controller compatible with your design for optimum performance.
Wiring is a critical aspect. Use heat-shrink tubing for cable organization and to protect connections from wear. Ensure that the motors are mounted securely to prevent vibrations from affecting flight performance.
Incorporate accessories such as cameras or GPS modules as needed. Pay attention to the weight distribution; proper balancing is key to stable flight. Finally, perform thorough testing of all systems to ensure everything operates cohesively before your first flight.

https://makerworld.com/en/models/737944-rekon5-3d-printed-parts?from=search#profileId-670105
3D Printing for Educational and DIY Drone Projects
3D printing opens up exciting possibilities in education and DIY projects, particularly in the realm of drones. You can create custom parts that fit specific designs, enhancing both learning and practical application.
When working on a DIY drone project, consider the following 3D printed parts:
- Chassis: The framework that supports all components.
- Arms: Connecting sections that hold the propellers.
- Blade Protection: Shields the blades from damage during flight.
- Landing Feet: Provides stability when the drone lands.
Many educational institutions utilize 3D printing to support robotics programs. Access to printers often allows students to design and prototype their own components. Local libraries frequently offer low-cost printing services, making it accessible for you to create parts without high expenses.
For learning, building a drone project can deepen your understanding of engineering concepts. You get hands-on experience with design, assembly, and testing. This practical approach helps reinforce theoretical knowledge in a fun and engaging manner.
Using 3D printed parts fosters creativity and innovation. You can iterate designs quickly, troubleshoot issues, and improve overall functionality. Your skills and knowledge can grow significantly through this hands-on experience in a supportive environment like a school or maker space.

https://makerworld.com/en/models/1160762-dji-tello-underbelly-pouch?from=search#profileId-1166940
Challenges and Future Perspectives
As the use of 3D printed parts in drone manufacturing expands, several challenges must be addressed. Understanding these hurdles will help you navigate the landscape effectively and leverage the emerging trends that will shape the industry’s future.
Overcoming Technical Limitations
One significant challenge in using 3D printed drone parts is the technical limitations of materials and machinery. While many plastics and composites are available, their properties may not meet the rigorous demands of aviation.
Examples of key limitations include:
- Strength-to-weight ratio: Many 3D printed materials do not have adequate tensile strength.
- Durability: Parts may wear out faster than traditionally manufactured components.
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting aviation standards is critical but complex.
Investing in research to develop advanced materials will be essential. Improvements in materials science can lead to stronger, lighter printed components, making them more viable for critical applications.
Emerging Trends in Drone Manufacturing
The future of drone manufacturing is poised to embrace several emerging trends that can enhance the effectiveness of 3D printing.
Highlight trends such as:
- Customization: You can easily create tailored parts that fit specific needs, improving functionality and reducing waste.
- Mass production: Scalability through 3D printing could lower costs and streamline production processes.
- Integration of AI: Utilizing AI to optimize designs can lead to more efficient manufacturing, allowing for innovative features in drones.
With these trends, the industry will likely see an increased adoption of 3D printing in various sectors such as logistics, surveillance, and agriculture.
- 4shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest4
- Twitter0
- Reddit0