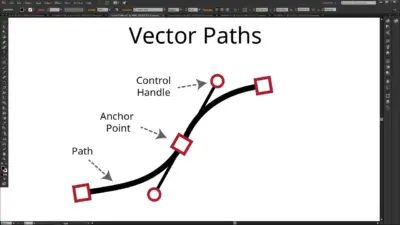
If you’ve ever wondered how to take your art skills to the next level, creating vector illustrations is a fantastic place to start. Whether you’re designing a logo, crafting icons, or just improving your overall drawing skills, vector-based artwork keeps your designs crisp and clear—no matter the size. That crisp, scalable quality sets vector graphics apart, and once you master them, you will find your creative toolkit expanding in powerful ways.


Explore the power of creating vector illustrations
When you create vector art, you draw using paths and shapes instead of pixels. Vector lines remain flawlessly sharp when scaled up or down, so you never have to worry about pixelation or blurriness. This is perfect for brand logos, large posters, or even small icons. According to Penji, vector illustrations are ideal for design work that requires high-quality, crisp edges at any resolution.
Compared to raster images that rely on specific pixel dimensions, vector files often have smaller sizes because they are essentially mathematical instructions. This makes them easier to store, share, and edit. And if you ever need to reposition a curve or change a shape’s color, everything is fully adjustable without degrading the artwork.
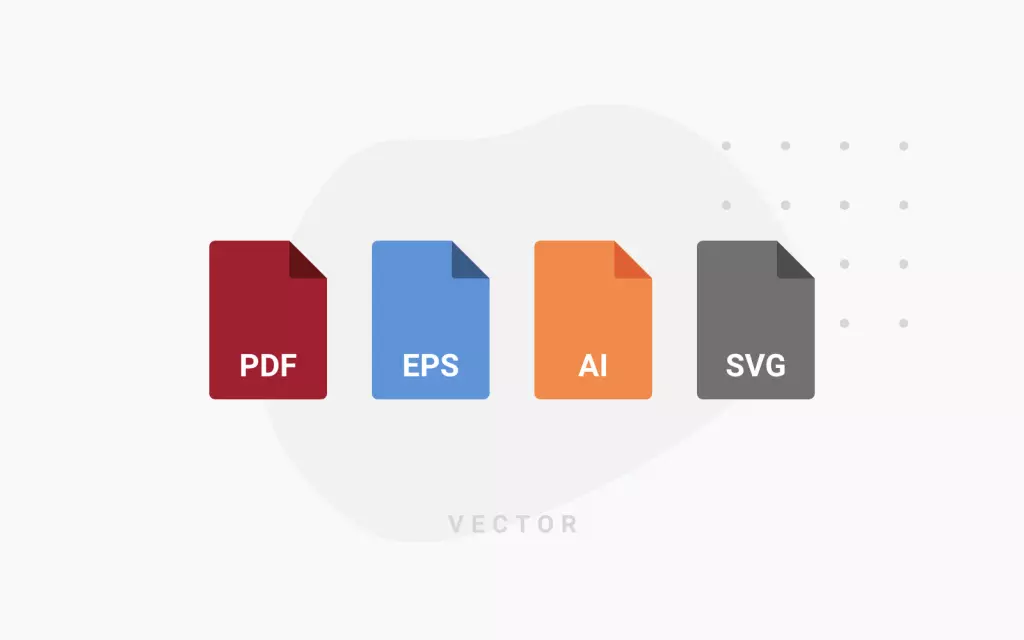
Understand the difference in file formats
To get the most out of your vector designs, it helps to know the key file formats:
- AI: Adobe Illustrator’s native format, widely used by professionals.
- SVG: Scalable Vector Graphics, a popular open standard for web-friendly visuals.
- EPS: Encapsulated PostScript, often leveraged for logos and print designs.
- PDF: Can contain both vector and raster elements, making it versatile for sharing.
Penji points out that PDF can handle vectors and pixels in the same document. Meanwhile, GeeksforGeeks highlights that formats like AI and SVG preserve scalability and editability, ensuring details remain sharp whether you are zooming in or printing large.
Review key software choices
When you are ready to invest in the right tool for vector artwork, you have several standout options. Each software package has its pros, potential costs, and device compatibility.
| Software | Cost Options | Key Features | Device Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Illustrator | Subscription (approx. $20/mo) | Industry standard, powerful vector tools | Windows, Mac |
| CorelDRAW | One-time purchase or subscription | PowerTRACE for quick bitmap-to-vector conversion | Windows, Mac, iPad/web app (CorelDRAW) |
| Inkscape | Free, open-source | Beginner-friendly, solid set of drawing tools | Windows, Mac, Linux |
| Canva | Free with paid premium features | Easy templates, basic vector capabilities | Web-based, limited offline functionality |
- Adobe Illustrator delivers a deep feature set, but you will pay for monthly access.
- CorelDRAW offers both subscription and one-time purchase options, along with user-friendly tools such as quick perspective drawing and color replacement (CorelDRAW).
- Inkscape stands out as a free solution, well-suited to beginners.
- Canva is best for quick social media graphics, though it lacks the more advanced vector-editing precision found in Illustrator or CorelDRAW.
Optimize your setup
You do not need a fancy machine to begin, but having a decent processor, a graphics card, and a drawing tablet or stylus can make your creative process smoother. CorelDRAW recommends a multi-core processor for speedy rendering and suggests using accessories like a 2-in-1 laptop or graphic tablet to sketch ideas directly. If you plan to do detailed illustrations, layering, or advanced shading, the extra hardware boost is well worth it.
It helps to organize your workspace, too. Use layers and grouping in whichever software you choose. That way, you can easily manage complex designs and keep your final artwork tidy.
Address common FAQs
Should I always choose vector over raster?
It depends on your project. Vector images shine for graphics like logos or icons that need resizing without losing clarity. Raster images are better for detailed photographs or photo-realistic art.Is free software enough for serious work?
Tools like Inkscape can handle professional-grade tasks. However, paid options such as Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW often come with extra features, ongoing support, and frequent updates.What is the difference between AI, SVG, and EPS?
AI is Adobe’s native format, SVG is a widely compatible web standard, and EPS is an older print-based format. All three maintain vector data, so your artwork remains scalable.How do I learn vector drawing faster?
Practice is key. Focus on mastering the pen tool, shape building, and layering. Big Red Illustration suggests keeping lines clean, using fewer anchor points, and experimenting with color gradients to add depth.What if I need photo-realism?
For complex photo-realistic images, raster graphics remain the stronger choice. But you can blend both approaches. If your design has large text or shapes, use vector elements alongside raster images for a versatile result.
Creating vector illustrations enhances your skill set by offering a unique combination of flexibility, scalability, and professional polish. When your art looks crisp at any size, you boost your creative confidence and open the door to more advanced design opportunities. Explore different software, refine your technique, and watch your work transform into stunning, scalable art.
- 4shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest4
- Twitter0
- Reddit0