Every object you touch, from your phone to your coffee mug, has been shaped by industrial design. Millions of people rely on products crafted through this blend of creativity, technology, and problem-solving every day. Industrial design influences how we live, work, and connect by turning ideas into practical, beautiful, and user-friendly experiences. Discover how this discipline transforms everyday life and why it matters more than most people realize.
Table of Contents
- Defining Industrial Design And Its Scope
- Types Of Industrial Design Disciplines
- The Industrial Design Process Explained
- Key Characteristics And Core Principles
- Industrial Design In Everyday Products
- Skills, Education, And Career Pathways
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
| Holistic Design Approach | Industrial design encompasses creativity, technology, and user experience, focusing on functional and aesthetically pleasing products. |
| Diverse Disciplines | The field includes various specializations such as interaction design, biodesign, and medical device design, each addressing unique challenges. |
| Iterative Design Process | The industrial design process is an iterative journey involving research, concept development, prototyping, and refinement, essential for effective solutions. |
| Career Skills | Successful industrial designers need a blend of technical, creative, and user-centered design skills to navigate the evolving landscape of technology. |
Defining Industrial Design and Its Scope
Industrial design represents a fascinating intersection of creativity, technology, and human experience. According to the Industrial Designers Society of America (IDSA), industrial design is the professional practice of designing products, devices, objects, and services that millions of people worldwide interact with daily.
Industrial designers are creative problem solvers who focus on transforming conceptual ideas into functional, aesthetically pleasing, and user-friendly products. Their work goes beyond mere appearance – they carefully consider multiple dimensions including physical form, functionality, manufacturing processes, and user interaction.

This holistic approach ensures that products not only look appealing but also solve real-world challenges efficiently.
The scope of industrial design is incredibly broad and touches nearly every aspect of our manufactured environment. From the smartphone in your pocket to the chair you’re sitting on, from medical devices to transportation systems, industrial designers play a critical role in shaping how we interact with the objects and systems around us. They blend artistic vision with practical engineering, creating solutions that are both innovative and pragmatic.
Key aspects of industrial design include:
- User-Centered Design: Prioritizing human experience and ergonomics
- Aesthetic Innovation: Creating visually compelling product experiences
- Functional Engineering: Ensuring products work seamlessly and efficiently
- Sustainability Considerations: Designing with environmental impact in mind
While many people might not recognize the term “industrial design,” its impact is omnipresent in our daily lives. Industrial design from IDSA highlights how these professionals serve as crucial bridge builders between raw conceptual ideas and tangible, marketable products that enhance human capabilities and experiences.
Types of Industrial Design Disciplines
Industrial design encompasses a rich and diverse range of specialized disciplines, each addressing unique challenges and opportunities across different sectors. These specialized areas demonstrate the incredible versatility and depth of industrial design as a professional practice.Interaction Design stands out as a critical discipline that focuses on creating meaningful digital experiences. According to Wikipedia, interaction design integrates principles from psychology, human-computer interaction, and information architecture to develop user-centered designs that prioritize human behavior and experience. This discipline is particularly crucial in our increasingly digital world, where seamless technology interfaces can dramatically improve how we work, communicate, and live.
Biodesign represents another fascinating frontier in industrial design. As described by Wikipedia, this interdisciplinary field combines design principles with biological sciences and emerging biotechnologies. Biodesign professionals are pioneering innovative approaches that leverage living organisms to create sustainable, adaptive products and systems that can transform industries from healthcare to environmental conservation.
Key industrial design disciplines include:
- Product Design: Creating physical objects for consumer and industrial markets
- Transportation Design: Developing vehicles, from automobiles to spacecraft
- Interaction Design: Crafting digital interfaces and user experiences
- Biodesign: Integrating biological principles into design solutions
- Medical Device Design: Developing specialized healthcare technologies
- Sustainable Design: Creating environmentally responsible products and systems
These diverse disciplines demonstrate that industrial design is far more than just making things look good. It’s about solving complex problems, improving human experiences, and creating innovative solutions that push the boundaries of technology, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Explore our dedicated industrial design category to dive deeper into these fascinating design domains.
The Industrial Design Process Explained
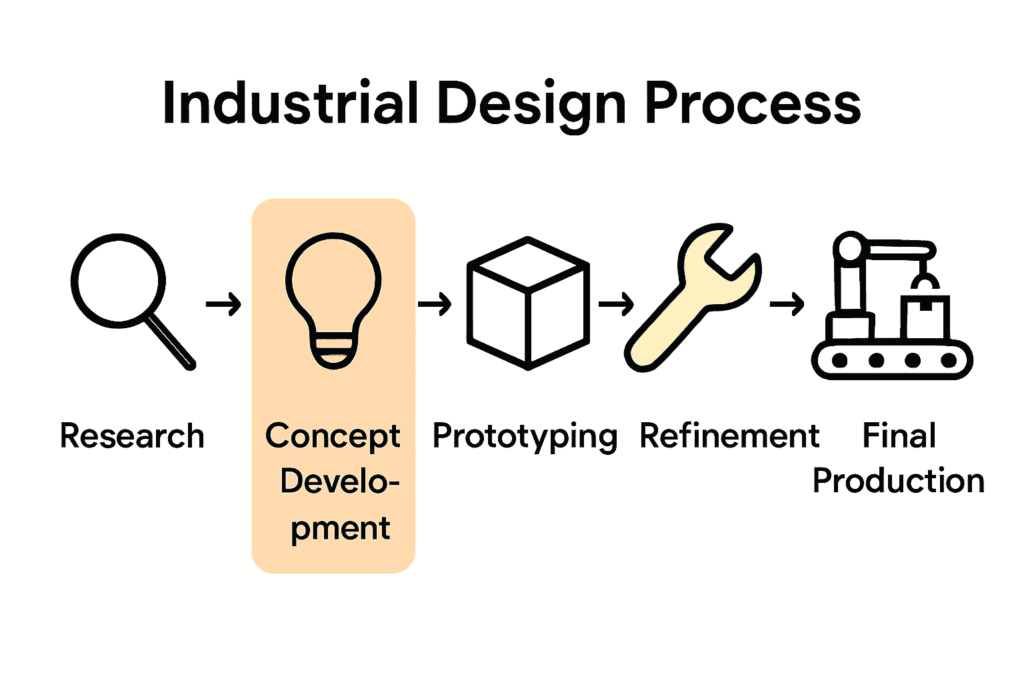
The industrial design process is a sophisticated, iterative journey that transforms abstract ideas into tangible, functional products. It’s a strategic approach that combines creativity, technical expertise, and systematic problem-solving to develop innovative solutions that meet user needs and market demands.
Data-driven intelligent computational design (DICD) has revolutionized how designers approach product development. According to research from ArXiv, this emerging approach utilizes deep learning algorithms to extract and represent design features from historical data. By analyzing past design solutions, these computational methods support the generation, optimization, and evaluation of new designs, dramatically enhancing the efficiency and innovative potential of the industrial design process.
Platform-based design (PBD) offers another powerful framework for streamlining product development. Research from ArXiv highlights how this systematic approach, originally developed in the electronic industry, promotes the reuse of hardware and software systems. PBD enables designers to explore design spaces more efficiently, optimize performance, and create more adaptable and scalable product solutions.
The typical industrial design process typically involves these key stages:
- Research and Insight Gathering: Understanding user needs, market trends, and technological possibilities
- Concept Development: Brainstorming and sketching initial design ideas
- Prototyping: Creating physical or digital models to test design concepts
- Refinement: Iterating and improving designs based on feedback and testing
- Final Production: Preparing designs for manufacturing
Learn more about transforming design ideas into reality with our sketch design tutorial, which can help you understand how initial concepts evolve into sophisticated design solutions. The industrial design process is ultimately about bridging imagination and functionality, creating products that are not just visually appealing, but also meaningful, user-friendly, and technologically advanced.
Key Characteristics and Core Principles
Industrial design is fundamentally about creating meaningful connections between human needs, technological possibilities, and aesthetic experiences. At its core, the discipline goes far beyond simply making things look attractive – it’s a strategic approach to problem-solving that synthesizes functionality, user experience, and innovative thinking.Systemic design represents a profound approach to understanding complex design challenges. According to Wikipedia, this methodology integrates systems thinking with design practices to address multi-disciplinary challenges. By emphasizing holistic approaches and considering the intricate interactions between different components, systemic design enables designers to develop sustainable and adaptive solutions that go beyond traditional linear problem-solving.
The principles of industrial design are built on a foundation of user-centric innovation, where every design decision is carefully evaluated through the lens of human experience, technological feasibility, and environmental responsibility. This approach requires designers to balance multiple, often competing considerations – from ergonomic functionality and manufacturing constraints to aesthetic appeal and cultural relevance.
Key characteristics of industrial design include:
- User-Centered Approach: Prioritizing human needs and experiences
- Interdisciplinary Integration: Blending insights from psychology, engineering, and art
- Sustainable Innovation: Designing with environmental and social impact in mind
- Iterative Problem-Solving: Continuously refining solutions through feedback and testing
- Technological Adaptability: Embracing emerging technologies and design methodologies
These principles demonstrate that industrial design is a dynamic and evolving discipline, constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible by transforming abstract concepts into tangible, meaningful products that enhance our daily lives.
Industrial Design in Everyday Products

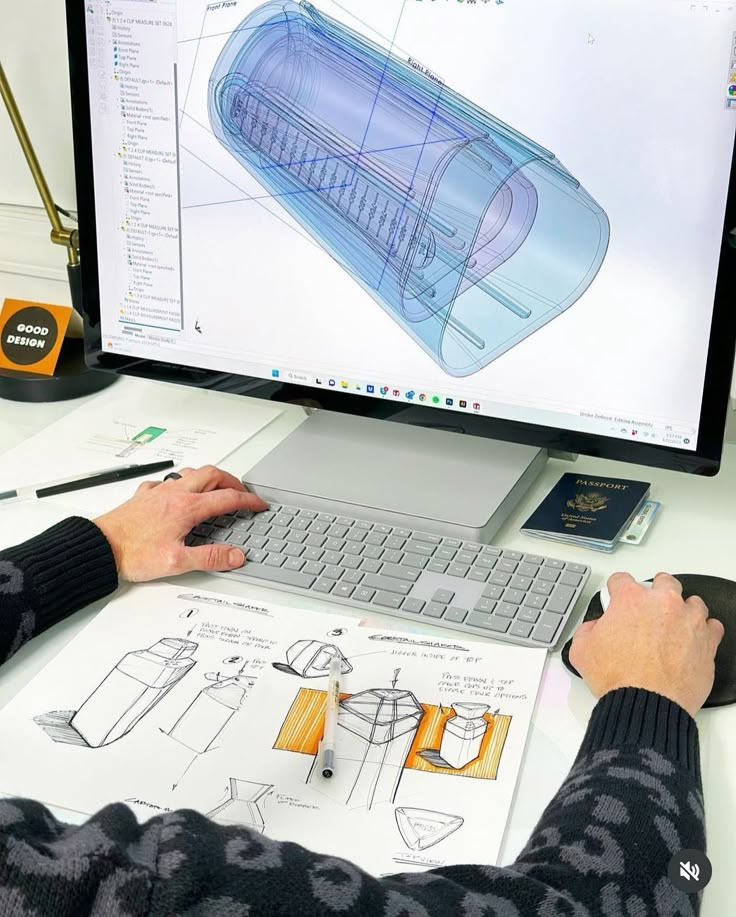
Industrial design transforms ordinary objects into extraordinary experiences, making even the most mundane items extraordinary through thoughtful, intentional design. Every product we interact with throughout our day – from morning coffee makers to evening reading lamps – represents a carefully crafted solution that balances form, function, and user experience.
According to the Industrial Designers Society of America (IDSA), industrial design fundamentally influences everyday products by focusing on their physical appearance, functionality, and manufacturability. This approach aims to improve user experiences through meticulously executed designs in items we encounter daily, such as household appliances and consumer electronics, turning routine interactions into moments of delight and efficiency.
The impact of industrial design extends far beyond aesthetic appeal. It’s about solving real-world problems through innovative solutions that make our daily lives smoother, more comfortable, and more intuitive. Consider how a well-designed kitchen appliance can transform meal preparation from a chore into an enjoyable experience, or how an ergonomically crafted smartphone can make communication more seamless and comfortable.
Examples of industrial design’s everyday impact include:
- Kitchen Appliances: Blending functionality with intuitive user interfaces
- Consumer Electronics: Creating devices that feel natural and responsive
- Furniture: Designing pieces that balance comfort, style, and practicality
- Transportation Tools: Developing user-friendly interfaces and ergonomic experiences
- Home Accessories: Solving everyday challenges with innovative design solutions
Learn about innovative lamp design trends that showcase industrial design principles, which demonstrate how even simple household items can become remarkable through thoughtful design. Industrial design ultimately bridges imagination and utility, turning everyday objects into experiences that enhance our quality of life.
Skills, Education, and Career Pathways

Industrial design offers an exciting career pathway that blends creativity, technical skills, and problem-solving abilities. Aspiring designers must cultivate a diverse skill set that goes beyond traditional artistic training, combining visual creativity with strategic thinking, technological proficiency, and deep understanding of human behavior.
According to the Segal Design Institute at Northwestern University, successful industrial design education emphasizes human-centered design principles and interdisciplinary approaches. These programs prepare students for complex design challenges by focusing on design thinking methodologies that integrate insights from psychology, engineering, and user experience research. Students learn to see design not just as an aesthetic exercise, but as a strategic problem-solving discipline.
Emerging technologies are dramatically reshaping the industrial design landscape. Research from ArXiv highlights how AI-based design tools are creating new challenges and opportunities for designers. Professionals must now develop skills to effectively collaborate with artificial intelligence systems, understanding how to communicate design goals and interpret AI-generated outputs. This requires a new type of technological literacy that goes beyond traditional design skills.
Key skills for industrial designers include:
- Visual Communication: Sketching, rendering, and graphic design
- Technical Proficiency: 3D modeling, CAD software, prototyping tools
- User Research: Understanding human behavior and interaction design
- Material Knowledge: Understanding properties of different materials
- Digital Literacy: Adapting to emerging design technologies
For those interested in exploring creative design career paths, check out our comprehensive guide to design career opportunities, which offers insights into the diverse and exciting world of industrial design. The field promises not just a career, but a chance to shape the way people interact with the world around them.
Discover How Industrial Design Can Transform Your Creative Vision
Struggling to bridge the gap between innovative ideas and real-world products is common for many aspiring designers and creative thinkers. This article explores key industrial design concepts like user-centered innovation, functional engineering, and systemic design that can inspire you to approach design challenges with confidence and clarity. Whether you want to refine your skills or gain fresh insights into product development, understanding these principles is essential to creating meaningful, impactful designs.
Unlock your full creative potential today by exploring the full range of industrial design insights on Industrial | Sky Rye Design. Find practical tutorials, inspiring case studies, and expert tips that demystify complex processes and bring your designs to life. Visit Sky Rye Design now and step into a world where creativity meets purposeful design. For broader creative inspiration, browse our Design category and discover how to turn your design challenges into rewarding successes.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is industrial design?
Industrial design is the professional practice of designing products, devices, objects, and services that enhance human interaction with the manufactured environment. It combines artistry and practicality to address user needs.
What are the main disciplines within industrial design?
Key disciplines include product design, transportation design, interaction design, biodesign, medical device design, and sustainable design. Each discipline focuses on different aspects of the design process and caters to specific industries.
How does the industrial design process work?
The industrial design process typically involves several stages: research and insight gathering, concept development, prototyping, refinement, and final production. This iterative approach enhances creativity and usability.
What skills are essential for a successful career in industrial design?
Key skills include visual communication, technical proficiency in 3D modeling and CAD software, user research capabilities, material knowledge, and digital literacy to adapt to emerging design technologies.
Recommended
- Evolution of Automotive Design: From Classic to Tech-Savvy |
- UI/UX Design Trends: What to Expect in 2024 | Sky Rye Design
- Convert Ideas into Reality Through Smart Design Sketches |
- Top 5 Automotive Design Schools to Check Out
- 17shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest14
- Twitter3
- Reddit0



