Imagine a world where your dinner isn’t just cooked, but printed. It sounds like something straight out of a sci-fi movie, doesn’t it? Yet, the incredible realm of 3d printing food is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it’s a delicious reality unfolding right before our eyes. This isn’t about replicating bland, nutrient paste (though it can do that!). We’re talking about intricate designs, personalized nutrition, and entirely new culinary experiences that push the boundaries of what we thought food could be.
For decades, 3D printing has been revolutionizing industries from aerospace to medicine, even making its way into areas like creating 3D printed drone parts. Now, it’s taking a bold leap into our kitchens and dining rooms. This technology promises to transform how we produce, prepare, and even perceive our meals, offering a blend of art, science, and gastronomy that’s truly captivating. Whether you’re a foodie, a tech enthusiast, or just curious about what’s next, prepare to have your taste buds and imagination awakened.
What Exactly is 3D Printing Food?
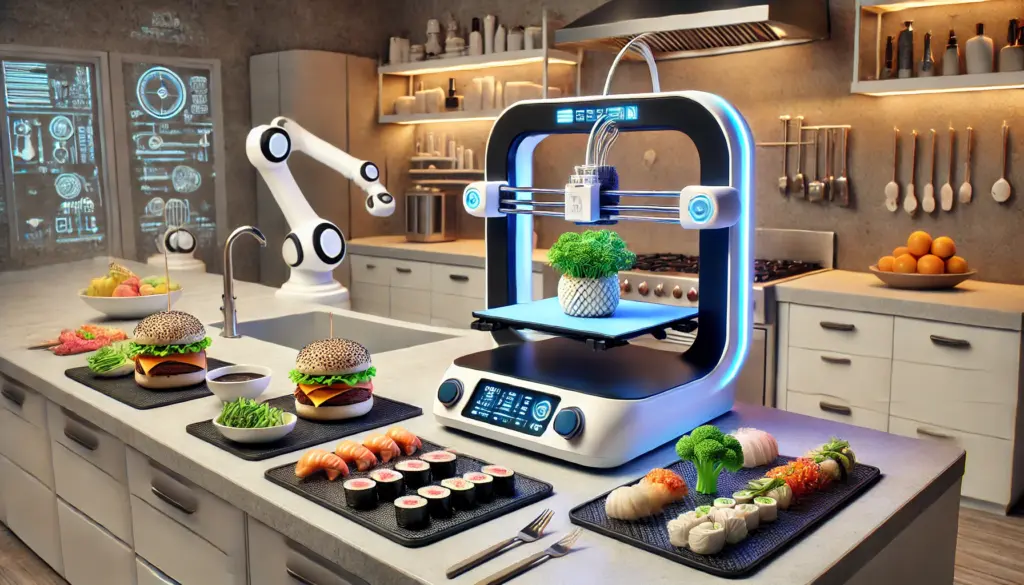

At its core, 3D printing food works on principles similar to other forms of additive manufacturing. Instead of plastic or metal, you’re using edible ingredients. Think of it as a fancy, high-tech pastry bag, but one that’s incredibly precise and automated. The process involves layering ingredients, one tiny drop or strand at a time, to build a three-dimensional object.
The Mechanics of Edible Creation
Most food 3D printers operate using an extrusion method. This means a paste-like ingredient – think chocolate ganache, cheese spread, or vegetable purees – is loaded into a syringe or cartridge. A robotic arm then precisely pushes this material through a nozzle, depositing it layer by layer onto a build plate. Each subsequent layer adheres to the one below it, gradually forming the desired shape.
Other methods exist too, like selective laser sintering for powdered ingredients (imagine printing with sugar or spices) or binder jetting, where a liquid binder is selectively applied to a powder bed. The choice of method largely depends on the type of food and the desired outcome. For example, a crisp cracker might use a different technique than a soft, intricate dessert.
What Can Be Printed? The Edible Inkwell

The variety of printable ingredients is constantly expanding. Currently, the most common “food inks” are those that can be easily extruded and hold their shape. This includes:
- Chocolates and Confectionery: Ideal for intricate designs, logos, and personalized sweets.
- Doughs and Pastries: Cookies, crackers, and even pasta can be printed with unique shapes.
- Cheeses and Spreads: Imagine an elaborate cheese sculpture or a perfectly portioned dip.
- Vegetable and Fruit Purees: These allow for customized textures and nutrient-rich creations, especially for those with specific dietary needs.
- Meat Alternatives: Some companies are exploring printing plant-based meat substitutes with specific textures.
- Sugars and Gels: Perfect for creating decorative elements and transparent structures.
The key is consistency. The ingredient needs to be viscous enough to be pushed through a nozzle but firm enough to maintain its structure once deposited. Scientists and chefs are continually experimenting with new formulations to broaden the palate of printable foods.
The Current Landscape: What’s Possible Right Now?
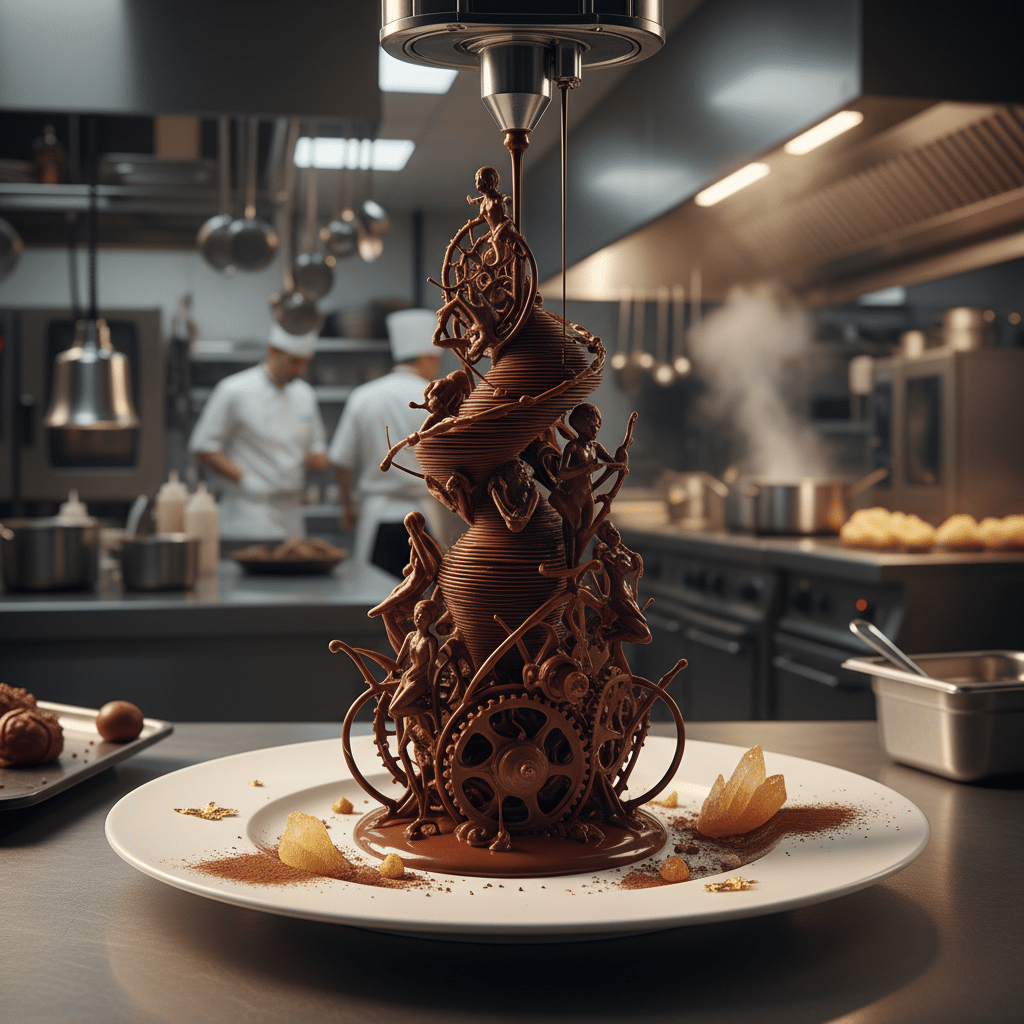

While we’re not yet printing full, multi-course meals on demand in every home, 3D printing food has already found its niche in several exciting areas.
Confectionery and Garnish: Where Art Meets Edibles
This is perhaps the most visible application of food 3D printing today. Chefs and bakers are using these machines to create stunning, complex designs that would be impossible or incredibly time-consuming to achieve by hand. Think custom chocolate sculptures for a wedding cake, personalized sugar decorations for desserts, or intricate edible art pieces. Brands can also use this technology to print their logos onto food items, offering a unique branding opportunity.
Personalized Nutrition: Tailoring Meals to You
One of the most promising applications lies in personalized nutrition. Imagine a world where your breakfast cereal or energy bar is formulated precisely for your body’s needs, based on your dietary restrictions, allergies, activity level, and even genetic makeup. 3D printing can create food with specific nutrient profiles, ensuring you get exactly what you need without unwanted ingredients. This has huge implications for athletes, individuals with medical conditions (like diabetes or kidney disease), and the elderly who might struggle with chewing or swallowing certain textures.
Haute Cuisine and Experimental Dining
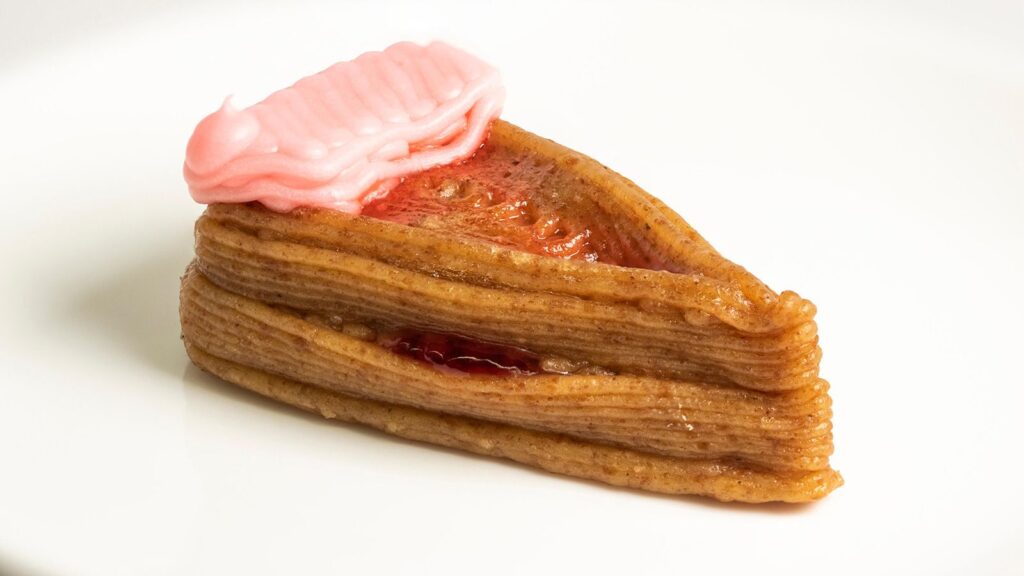

High-end restaurants are starting to embrace food 3D printing as a tool for culinary innovation. Chefs are using it to create visually stunning dishes with novel textures and shapes, pushing the boundaries of gastronomy. It allows for an unparalleled level of precision and reproducibility in complex plating. Diners are treated to an experience that combines artistic presentation with cutting-edge technology, turning a meal into a performance.
Space Food and Military Applications: Beyond Earth’s Kitchens
In environments where resources are limited and shelf-life is critical, 3D printing offers intriguing solutions. NASA has already explored the concept of 3D printing food for long-duration space missions. Astronauts could print customized meals from nutrient-dense cartridges, reducing waste and providing variety. Similarly, military forces could utilize this technology in remote areas to create on-demand, nutritionally complete rations tailored to the energy requirements of troops.
Beyond the Plate: The Benefits and Advantages
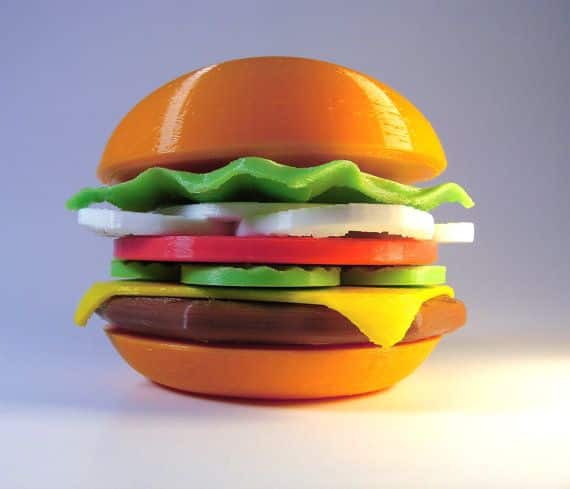



The hype around 3D printing food isn’t just about cool gadgets; it’s driven by a host of practical and transformative benefits.
Unparalleled Customization and Personalization
This is arguably the biggest game-changer. Imagine designing your own pasta shape, selecting its ingredients, and even infusing it with specific vitamins. With 3D printing, the possibilities are endless. This level of customization extends to:
- Dietary Restrictions: Easily create gluten-free, dairy-free, or allergen-specific meals without cross-contamination.
- Aesthetics: Design food that’s not just delicious but also a feast for the eyes. Think architectural desserts or savory sculptures. It can even inspire new ways of thinking about how we make room for comfort without sacrificing our home’s personality by making our dining experiences uniquely ours.
- Portion Control: Precisely control calorie intake and portion sizes, which is excellent for weight management or specific health goals.
Novelty and Aesthetics: The Art of Eating
Food is an experience, and 3D printing elevates this experience to an art form. It allows for the creation of intricate patterns, geometric shapes, and even edible portraits that are simply impossible with traditional cooking methods. This visual appeal can enhance dining experiences, spark conversation, and make special occasions even more memorable. It’s about turning food into a canvas.
Nutritional Control and Dietary Needs: Food as Medicine


For individuals with specific health needs, 3D printed food can be life-changing. It offers the ability to:
- Modify Texture: Create soft, easily chewable, or pureed foods for the elderly or those with dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), ensuring they receive adequate nutrition.
- Targeted Fortification: Embed specific vitamins, minerals, or supplements directly into food items.
- Reduce Sodium/Sugar: Precisely control the amount of “unhealthy” ingredients while maintaining flavor and appeal.
Waste Reduction: A Sustainable Future?
In traditional food production, a significant amount of waste occurs at various stages. 3D printing can help by:
- Using Exact Quantities: Only the required amount of “food ink” is used, minimizing leftover ingredients.
- Repurposing By-products: Potentially turning food waste into printable pastes, creating a more circular food economy.
- On-Demand Production: Reducing the need for mass production and storage of perishable goods, cutting down on spoilage.
New Culinary Experiences: An Uncharted Frontier
3D printing opens doors to flavor and texture combinations that were previously unimaginable. Imagine a dessert that combines the crispness of a cracker with the melt-in-your-mouth quality of a mousse, all in one bite. It encourages culinary experimentation and challenges chefs to think beyond conventional cooking techniques. It’s a whole new palette for gastronomic innovation.
Challenges on the Menu: What’s Holding it Back?
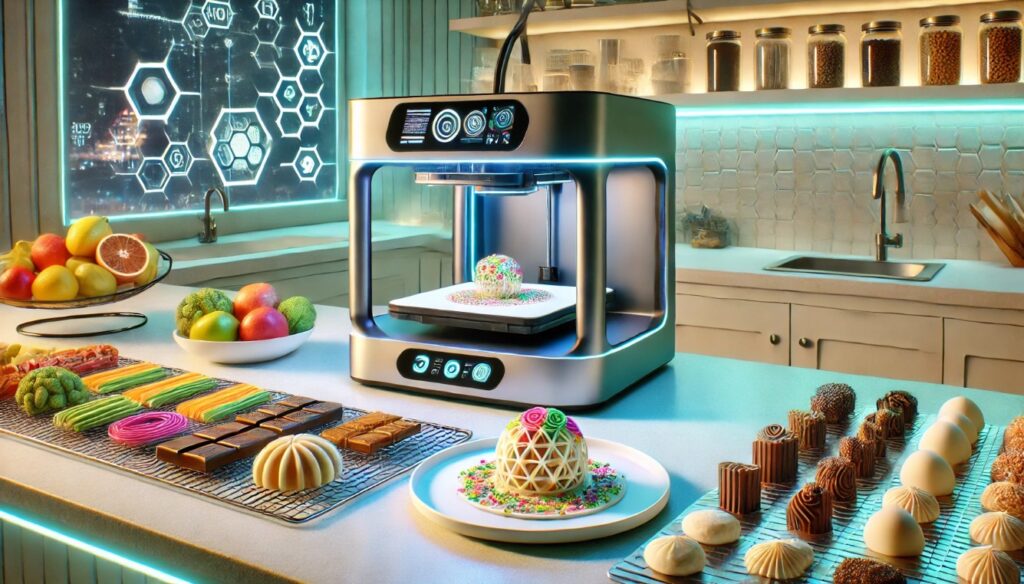

Despite its exciting potential, 3D printing food faces several hurdles before it becomes a commonplace kitchen appliance.
Cost and Accessibility: The Price Tag of Innovation
Current food 3D printers, especially those capable of intricate designs, can be quite expensive. This limits their adoption to high-end restaurants, research labs, and industrial settings. For the average consumer, the investment is simply too high for a novelty item. While prices are expected to drop as the technology matures, it’s still a significant barrier.
Speed and Scale: Slow Food in a Fast World
One of the biggest limitations is the printing speed. Layer-by-layer deposition is inherently slower than mass production methods. Printing a single, complex item can take minutes or even hours, which isn’t practical for feeding large numbers of people quickly. Scaling up production to meet commercial demand remains a significant challenge, though continuous improvements are being made.
Texture and Taste: The Full Sensory Experience


While 3D printers excel at visual presentation, replicating the nuanced textures and complex flavors of traditionally prepared food is harder. A printed steak might look amazing, but if it lacks the fibrous chewiness and juicy mouthfeel of a grilled cut, it won’t satisfy. Developing food inks that can genuinely mimic traditional ingredients’ sensory properties is an ongoing area of research. Think about the comforting aesthetics of a cozy hygge home; the appeal of food extends beyond mere appearance to encompass warmth and familiarity.
Regulatory Hurdles: Who’s Watching the Printer?
As a new technology, food 3D printing faces questions about food safety regulations. What standards apply to “food inks”? How are ingredients sourced and stored? Who ensures the printers themselves are food-safe and hygienic? Clear guidelines and certifications are needed to build consumer trust and allow for widespread adoption.
Public Perception: Bridging the “Unnatural” Gap
For many, the idea of “printed food” conjures images of highly processed, artificial meals. Overcoming this perception requires education and demonstration of the technology’s benefits, emphasizing that it’s a new method of preparation, not necessarily a new type of ingredient. The goal is to show that 3D printed food can be just as, if not more, natural, healthy, and delicious than its traditional counterparts.
The Future is Flavorful: Where Are We Heading?

Despite the challenges, the trajectory for 3D printing food is undeniably upwards. The future promises even more exciting developments.
Towards Mass Production and Customization
Imagine industrial-scale 3D food printers capable of rapidly producing custom meals for hospitals, schools, or even airline catering. These machines could integrate with dietary databases, printing thousands of unique meals tailored to individual needs every day. This efficiency could revolutionize institutional food service.
Sustainable Food Systems: A Green Revolution
3D printing could play a vital role in addressing global food security and sustainability. By enabling the use of alternative proteins (like insects or algae), utilizing food by-products, and reducing waste, it offers a path towards more efficient and environmentally friendly food production. We could see localized food production hubs where ingredients are grown and printed on demand, minimizing transportation and its carbon footprint.
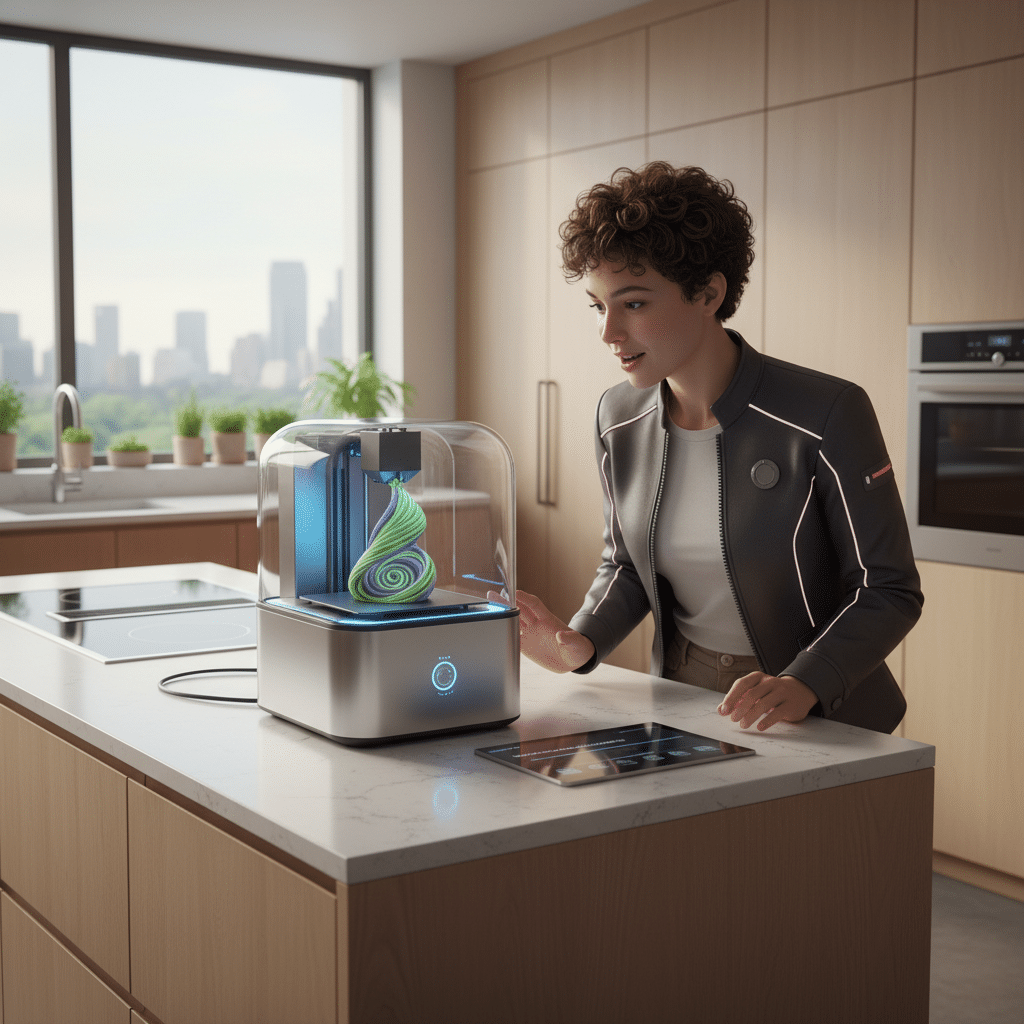
At-Home Food Printing: The Smart Kitchen of Tomorrow


While not yet a reality for the masses, the dream of a personal food 3D printer in every home is potent. Imagine downloading recipes, loading pre-made ingredient cartridges, and having a gourmet meal or a perfectly portioned snack printed for you with minimal effort. This could transform meal prep, making healthy eating more accessible and exciting. The advancements in general 3D printing are already remarkable, as seen in how 3D printing has changed our lives across many sectors, and food is next.
Medical and Elderly Care Applications: Enhancing Quality of Life
Beyond personalized nutrition, 3D printing food has immense potential in medical settings. It could create precise dosages of medication embedded in palatable food for children or those with swallowing difficulties. For the elderly, it could ensure appealing, texture-modified meals that are easy to consume, combating malnutrition and improving overall quality of life.
New Ingredients and Food Types: Culinary Exploration
Researchers are constantly experimenting with new ingredients, including plant-based alternatives, cultured meat cells, and even entirely synthetic components. 3D printing provides the perfect platform to explore these novel food sources, allowing for controlled experimentation with texture, flavor, and nutritional content. This could lead to entirely new categories of food we can’t even imagine today.
How to Experience 3D Printed Food Today (or Soon!)

If you’re eager to get a taste of this culinary revolution, here’s how you can do it:
Visit Specialized Restaurants or Pop-ups
Some avant-garde restaurants and culinary tech events are already showcasing 3D printed dishes. Keep an eye out for news from major cities or food festivals that might feature this cutting-edge technology. It’s often presented as part of a tasting menu or a unique dining experience.
Follow Culinary Tech Trends and Startups
The field is constantly evolving, with new startups and research initiatives emerging regularly. Follow food tech blogs, industry publications, and innovation platforms to stay informed about the latest developments, product launches, or commercial availability of printed food items.
Explore DIY Kits (When Available)
As the technology becomes more accessible, we might start seeing more consumer-friendly DIY kits or desktop food printers for home use. These could allow enthusiasts to experiment with simple designs and personalized recipes in their own kitchens. For now, commercial 3D printers are usually the domain of professionals, but understanding the 6 best commercial 3D printers can give you an idea of the current capabilities.
The Delicious Tomorrow
The journey of 3d printing food is still in its early stages, but its potential is undeniably vast. From crafting exquisite edible art to tackling global challenges like food waste and malnutrition, this technology is set to redefine our relationship with what we eat. It’s a testament to human ingenuity, blending the precision of engineering with the creativity of culinary arts. As we move forward, expect to see more personalized, aesthetically stunning, and nutritionally optimized meals gracing our tables, all thanks to the magic of 3D printing.
So, next time you sit down for a meal, imagine a world where your food isn’t just cooked, but intelligently designed, precisely created, and perfectly tailored just for you. The future of food is printing, and it tastes pretty amazing. Are you ready to take a bite?
- 1share
- Facebook0
- Pinterest1
- Twitter0
- Reddit0