Green architecture is changing the way homes are built by focusing on how buildings interact with their environment. This style of design creates homes that “breathe” with nature, meaning they use materials and systems that help regulate air and energy naturally. These homes stay comfortable while saving energy and reducing harm to the planet.
Many green homes use smart designs to bring in fresh air, manage moisture, and keep temperatures steady without relying heavily on machines. Instead of just adding a few eco-friendly features, these homes are planned from the ground up to work with the natural world. This approach helps improve air quality and makes living spaces healthier.
By blending nature into the design, green architecture encourages a better balance between people and the environment. People interested in greener living will find these homes offer practical ways to reduce energy use and live more sustainably.
Principles of Green Architecture
Green architecture focuses on building homes that work well with nature. It uses smart materials, clever energy-saving methods, and careful designs to protect the environment. These ideas help keep homes comfortable, healthy, and sustainable.
Sustainable Building Materials
Using the right materials is key in green architecture. Builders choose renewable, recycled, or low-impact materials that cause less harm to the planet. Examples include bamboo, reclaimed wood, and recycled metal.
Materials should also be non-toxic to improve indoor air quality. Natural insulation like sheep’s wool or cellulose is often preferred because it reduces energy loss.
Local sourcing is important too. It cuts down transportation emissions and supports nearby economies. Using durable materials means the building lasts longer and needs fewer repairs.
Energy Efficiency Strategies


Green homes work to use less energy without losing comfort. They often include high-quality insulation, energy-efficient windows, and smart ventilation systems.
Design features like passive solar heating help capture sunlight to warm the home naturally. Overhangs or shades prevent too much heat in summer.
Renewable energy sources such as solar panels or small wind turbines are added when possible. These methods lower energy bills and reduce carbon emissions.
Smart systems that control lighting and temperature make sure energy is only used when needed. They can adjust automatically based on time or occupancy.
Minimizing Environmental Impact


Green buildings are designed to fit well in their surroundings and limit waste. They often include rainwater harvesting systems and water-saving fixtures to reduce water use.
Using permeable materials for driveways and gardens helps rainwater soak into the ground rather than creating runoff. This protects nearby waterways.
Construction waste is minimized through careful planning and using recyclable materials. Landscaping choices favor native plants that need less water and care.
By focusing on these steps, green architecture helps protect the earth while making homes healthier and more efficient.
Designing Homes That Breathe
Homes that breathe use smart techniques to improve air flow, control temperature naturally, and bring nature inside. These methods help reduce energy use and create healthier living spaces.
Natural Ventilation Techniques

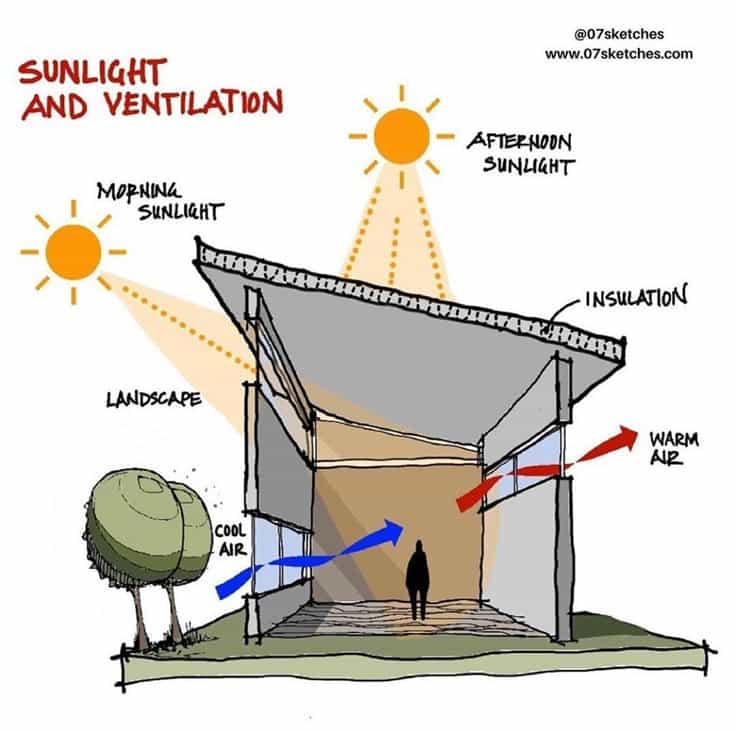
Natural ventilation means using openings like windows, vents, and doors to let fresh air move through the home. This improves air quality and keeps the indoor environment comfortable without relying on machines.
Cross-ventilation is a common method. It happens when air enters through one side of the house and exits through the opposite side. This moves air fast and cools the home. Stack ventilation uses the fact that warm air rises, letting hot indoor air escape through high vents or chimneys, while cooler air comes in below.
Designing windows and vents in the right spots is key. Home orientation and local wind direction also affect how well natural ventilation works.
Passive Cooling and Heating
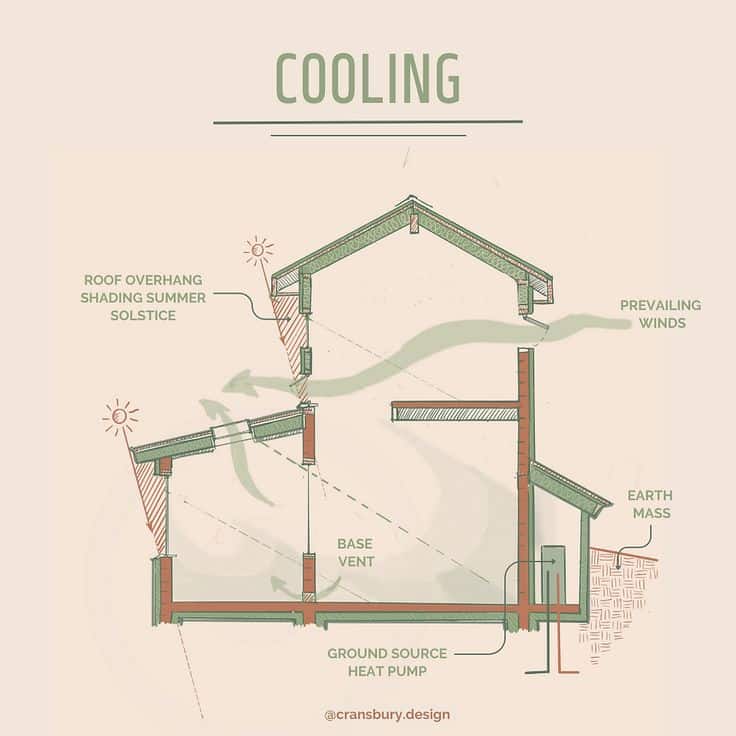
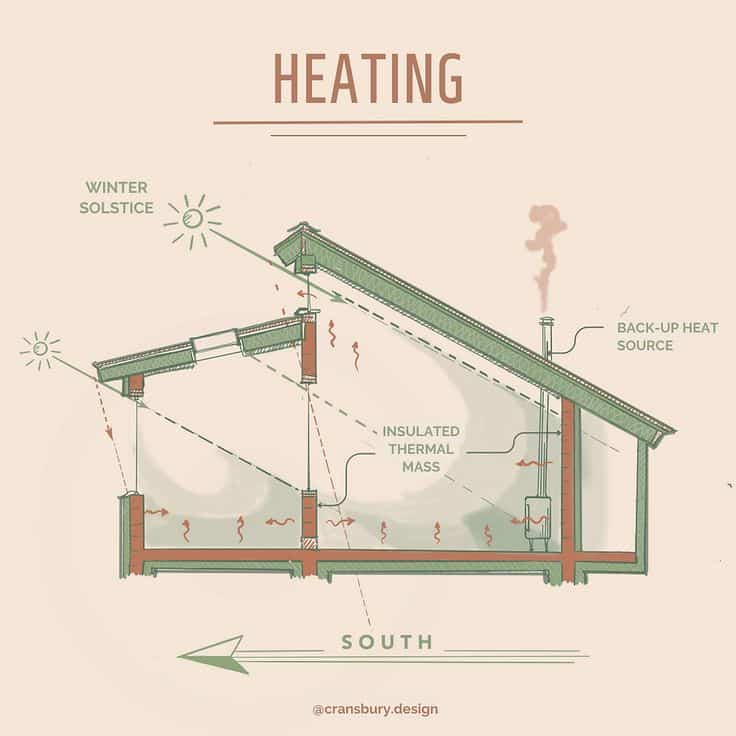
Passive cooling and heating use building design to control temperature without energy-consuming devices. This lowers heating and cooling bills.
Thick walls, insulation, and shaded windows keep heat out in summer and trap warmth in winter. Materials like stone, brick, and concrete store heat during the day and release it at night.
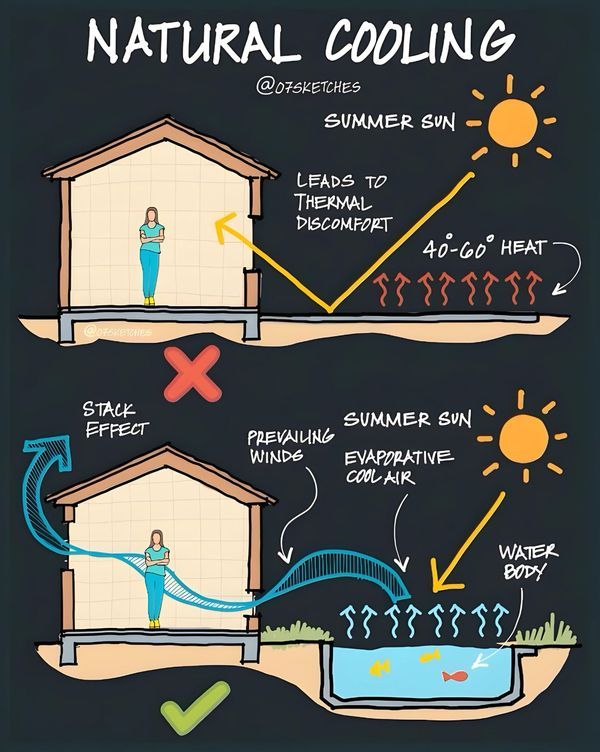

Roof overhangs and trees block direct sun in hot months but let sunlight warm the home during colder months. Proper window placement catches sunlight in winter and avoids it in summer.
Ventilation works with these features to keep air moving, preventing heat buildup.
Biophilic Design Elements


Biophilic design connects people with nature inside their homes. It uses natural materials, plants, and light to create a calming environment.


Wood, stone, and natural fibers add texture and warmth. Large windows and skylights bring in natural light and views of green spaces, improving mood and well-being.
Indoor plants help clean the air and add life to rooms. Gardens, water features, and natural colors further strengthen the link to nature.
This design approach supports health by making spaces feel fresh and inviting.
Energy and Resource Management
Green homes focus on using energy and resources wisely. They rely on clean power, save water, and use technology to keep systems working efficiently. These features help lower bills and reduce environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Integration


Green homes often include solar panels or small wind turbines to create their own power. These systems reduce reliance on the grid and cut energy costs. Solar panels can be placed on rooftops, making use of sunlight throughout the day.
Battery storage is also important. It stores extra energy for use at night or on cloudy days. Some homes connect to the grid in a way that lets them send surplus energy back, earning credits or reducing bills.
Using renewable energy supports cleaner air by lowering fossil fuel use. It also makes homes more resilient during power outages.
Water Conservation Systems


Water-saving features are key in green homes. These can include low-flow faucets and toilets that reduce water use without sacrificing comfort. Rainwater harvesting systems collect rain to use in irrigation or flushing toilets, cutting water waste.
Greywater recycling treats water from sinks and showers so it can be reused for landscaping. This reduces the demand on freshwater supplies.
Green homes often use drought-resistant plants in landscaping to minimize irrigation needs. Together, these approaches help lower water bills and protect local water sources.
Smart Home Technologies
Smart home tech helps manage energy and water use automatically. Sensors can turn lights and appliances off when rooms are empty. Thermostats learn residents’ schedules to adjust heating and cooling efficiently.
Smart meters track energy use in real-time. This data helps homeowners spot waste and make smarter choices. Automated irrigation systems water plants only when needed, based on soil moisture sensors.
These systems make green living easier and keep resource use low without constant effort from residents.
Health and Comfort in Eco-Friendly Homes
Eco-friendly homes focus on creating living spaces that feel fresh, quiet, and safe. They achieve this by improving air quality, using safe building materials, and carefully controlling sound and temperature. These features work together to make homes healthier and more comfortable for everyday life.
Improved Indoor Air Quality


Good air quality is a top priority in green homes. They use ventilation systems that bring in fresh outside air while removing stale indoor air. This helps lower dust, allergens, and harmful chemicals inside the home.
Plants and natural materials also contribute by reducing indoor toxins. Filters in HVAC systems catch tiny particles that can irritate lungs. Some homes include air-purifying technologies that continuously clean the air.
In addition, sustainable homes avoid materials that release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This lowers the chances of headaches, allergies, or breathing problems linked to indoor pollution.
Use of Non-Toxic Materials
Choosing non-toxic materials is key to health in eco-friendly homes. Paints, sealants, and finishes without harsh chemicals reduce exposure to harmful substances.
Materials like natural wood, clay, and stone replace plastics and synthetic products that often contain toxins. These safe materials also age better and create a warmer, more natural feeling indoors.
Non-toxic insulation and adhesives contribute to a healthier environment by limiting chemical off-gassing. This choice protects the health of everyone living in the home, especially children and those with sensitivities.
Acoustic and Thermal Comfort
Comfort in green homes extends beyond air quality. Acoustic features help reduce noise from outside and between rooms, making the home quieter and more peaceful.
Thermal comfort is balanced by smart design. High-quality insulation, windows, and shading keep indoor temperatures steady. This cuts down on heating and cooling needs while keeping the home cozy year-round.
Together, soundproofing and temperature control create a calm, relaxing space ideal for rest and work. These elements help reduce stress and improve overall well-being inside the home.
Modern Trends and Innovations
Many new ideas are changing how green homes are built and lived in. These ideas focus on saving energy, using nature to help buildings breathe, and cutting pollution. They make homes healthier and better for the planet.
Green Roofs and Living Walls
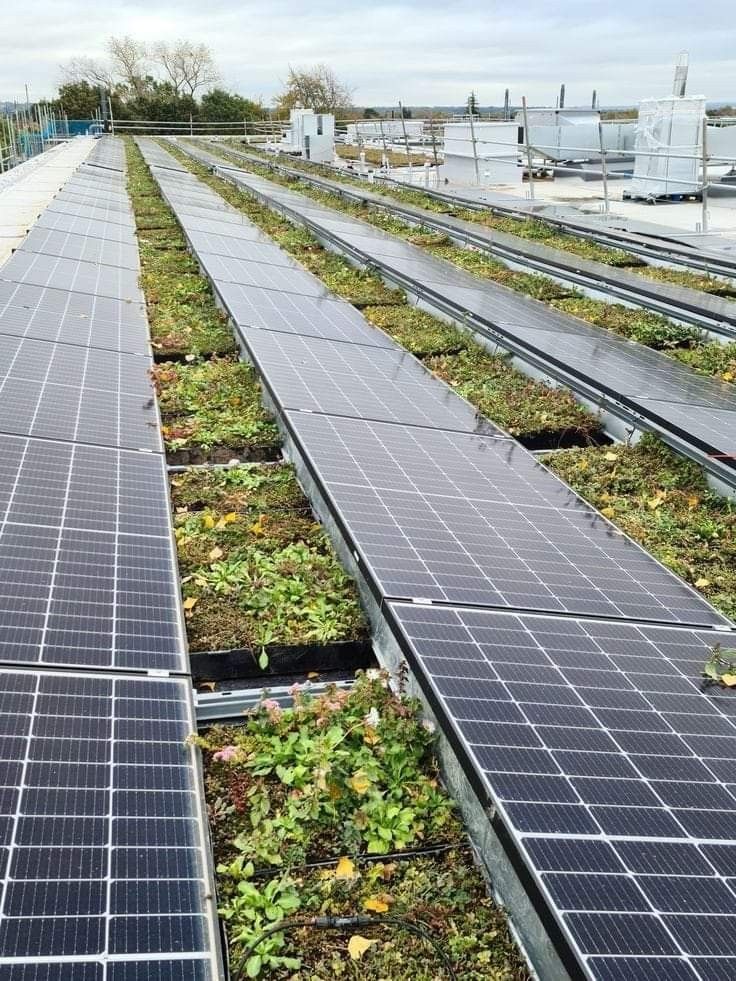


Green roofs are layers of plants grown on rooftops. They help keep homes cool by blocking sunlight and reduce rainwater runoff. This lowers energy costs and keeps cities cooler during hot days.
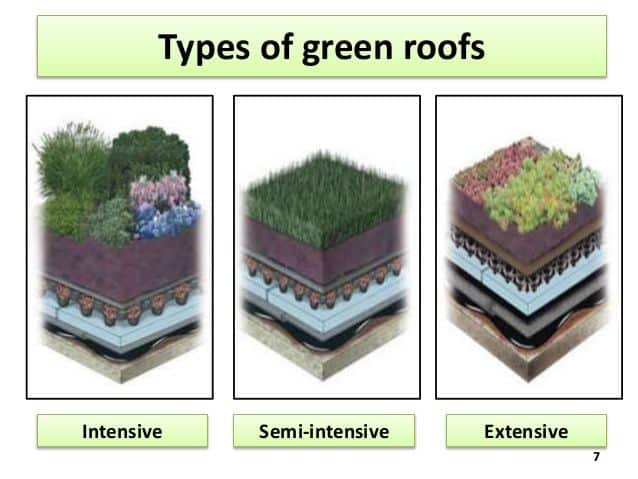
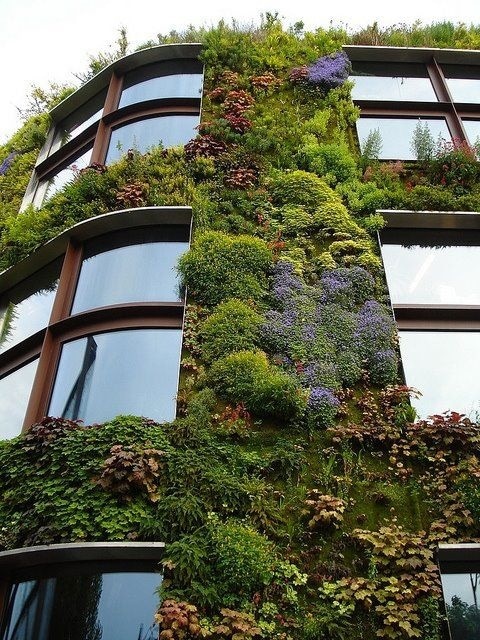
Living walls, also called vertical gardens, are walls covered with plants. They improve air quality by absorbing pollutants and producing oxygen. Both green roofs and living walls provide homes with natural insulation and create spaces for wildlife like birds and bees.
Together, these plant-based features support cleaner air and reduce heating or cooling needs, making homes more comfortable and eco-friendly.
Modular and Prefabricated Eco-Homes
Modular homes are made from pieces built in factories and put together on-site. This method cuts waste and speeds up construction.
Prefabricated eco-homes use sustainable materials like recycled wood, bamboo, and non-toxic finishes. They are designed to be energy-efficient, often including solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and natural ventilation.
Builders focus on precision and less material waste in factories. This approach lowers costs and reduces the carbon footprint of new homes while maintaining high standards for comfort and health.
Net-Zero Emission Housing
Net-zero houses produce as much energy as they use over a year. They rely on solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable sources to create power.
These homes use energy-saving technologies such as LED lighting, high-performance insulation, and smart thermostats to reduce consumption.
Water-saving fixtures and efficient appliances help lower resource use. Achieving net-zero means a house has nearly no impact on the environment, which helps fight climate change and keeps utility bills low.
- 0shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest0
- Twitter0
- Reddit0


