Remember those sci-fi movies where characters just conjured up their outfits with a flick of a wrist? Well, we’re getting closer to that reality, and it’s all thanks to the magic of 3d printing fashion. What once felt like a futuristic pipe dream reserved for avant-garde runways is steadily making its way into our everyday wardrobes, promising a revolution in how we design, create, and wear our clothes. Forget flimsy fabrics and mass-produced pieces; we’re stepping into an era where your casual attire could be as unique as your fingerprint, crafted layer by intricate layer right before your eyes.
It’s an exciting time to be a fashion enthusiast, or even just someone who appreciates a good, comfy tee. The conversation around 3D printing used to be dominated by intricate, often stiff, structural pieces – more art installation than everyday wear. But that’s changing fast. Innovators are now pushing the boundaries, focusing on flexibility, comfort, and aesthetics that blend seamlessly into our casual lives. This isn’t just about looking cool; it’s about redefining customization, sustainability, and personal style in a way we’ve never imagined. Let’s dive into how 3D printing is stitching together the future of casual fashion, one layer at a time.
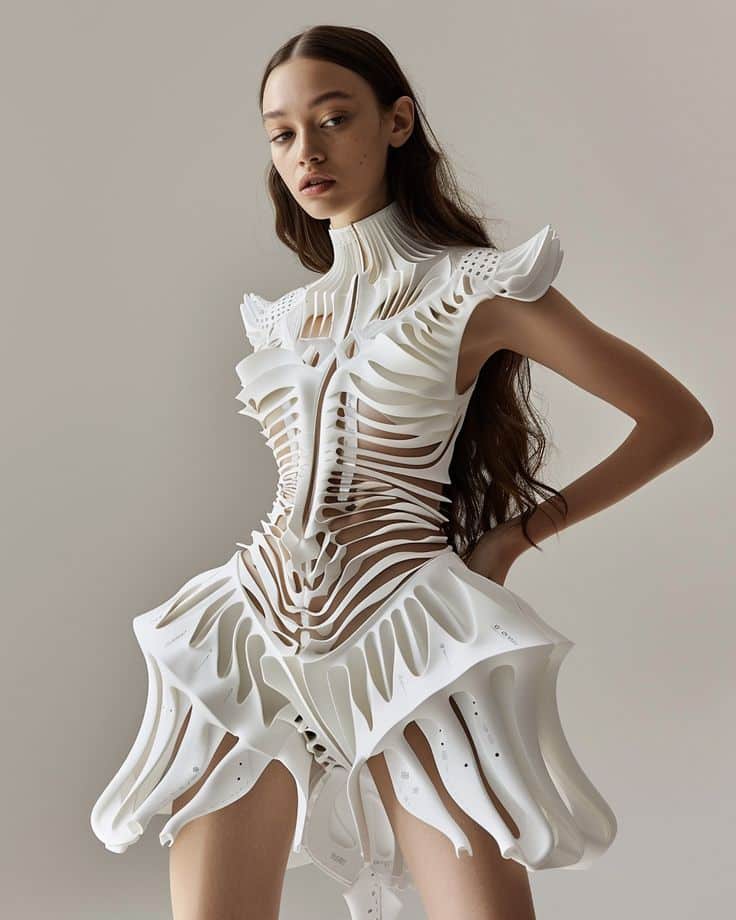


Beyond the Runway: The Rise of Everyday 3D Printed Wearables
For a long time, 3D printing in fashion felt like a spectacle, reserved for the high-end, experimental collections that walked only the most prestigious runways. Think Iris van Herpen’s breathtaking, gravity-defying gowns or intricate pieces that looked more like sculptures than clothing. While these creations certainly captivated the imagination, they rarely seemed destined for your weekend brunch or a casual stroll in the park. The perception was that 3D printed garments were rigid, perhaps uncomfortable, and definitely not “casual.”
However, this narrative is rapidly evolving. The fashion industry, known for its constant pursuit of innovation, has been pouring resources into making 3D printed items not just wearable, but genuinely comfortable and stylish for everyday life. We’re seeing a significant shift from purely conceptual designs to practical, accessible wearables. This means moving past the initial shock factor and into the realm of true integration. Designers are no longer just asking “Can we print this?” but “How can we make this something you’d actually want to wear every day?”
This transition is fueled by advancements in materials and printing techniques. Early iterations often relied on hard plastics, resulting in stiff, armor-like apparel. While visually striking, they lacked the drape, movement, and softness essential for casual wear. Now, researchers and designers are experimenting with flexible filaments, composite materials, and innovative structures that mimic the properties of traditional textiles. Imagine a pair of sneakers with a perfectly cushioned, breathable sole printed to your exact foot shape, or a lightweight bracelet with a geometric design that feels smooth and gentle against your skin. These are no longer futuristic fantasies but tangible products entering the market.
The move towards everyday 3D printed wearables also signifies a broader democratization of design. What was once the exclusive domain of haute couture is becoming a tool for independent designers and even consumers to create unique pieces. This empowers individuals to move beyond the limitations of mass production, offering bespoke solutions that cater to individual preferences and body types. The accessibility of desktop 3D printers and online design platforms means that the barriers to entry are lowering, fostering a new wave of creativity that blends technology with personal style.
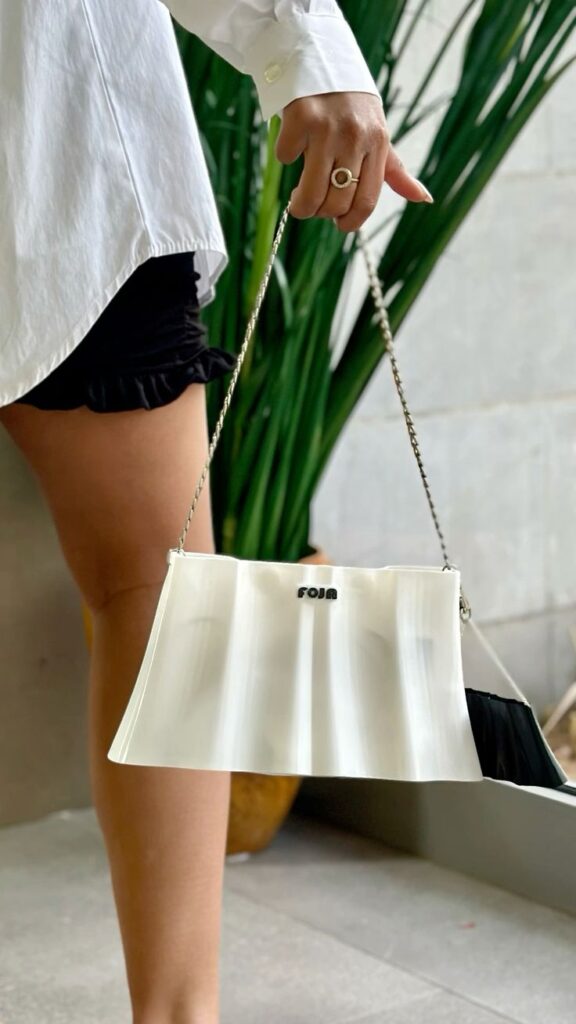


The Technology Behind the Trend: How 3D Printing Works for Fashion
At its core, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process of building a three-dimensional object layer by successive layer from a digital design. Instead of carving away material (subtractive manufacturing), you’re adding it precisely where needed. For fashion, this translates into incredible design freedom and the potential for unparalleled customization.
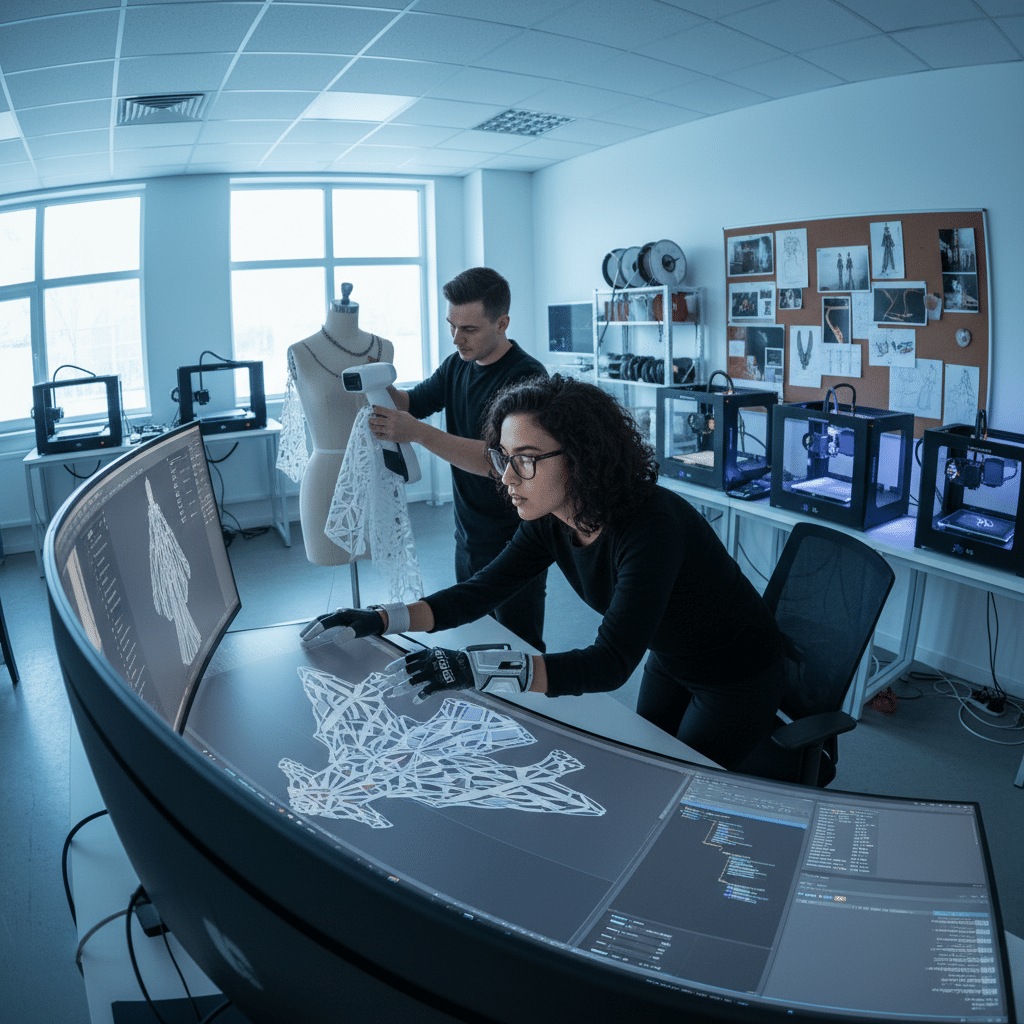
The journey from a concept in a designer’s mind to a physical 3D printed garment begins with digital design. This is where CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software comes into play. Designers use programs like SolidWorks, Rhino, Blender, or even specialized fashion design software to create a highly detailed, three-dimensional model of the item they wish to print. This digital blueprint isn’t just a static image; it contains all the intricate geometric information that the 3D printer needs to bring the design to life. Much like an artist sketching their vision, digital designers meticulously craft every curve, texture, and structural element. The precision offered by these tools allows for complex patterns and forms that would be impossible or incredibly labor-intensive to achieve with traditional methods. For aspiring designers, understanding the fundamentals of visualizing and drawing outfits is still crucial, even when working with digital tools, as it forms the basis of translating creative ideas into printable designs.
Once the digital model is complete, it’s typically “sliced” by specialized software. This slicing process breaks down the 3D model into hundreds, sometimes thousands, of individual 2D layers. Think of it like a stack of extremely thin cross-sections. This layered data is then sent to the 3D printer.
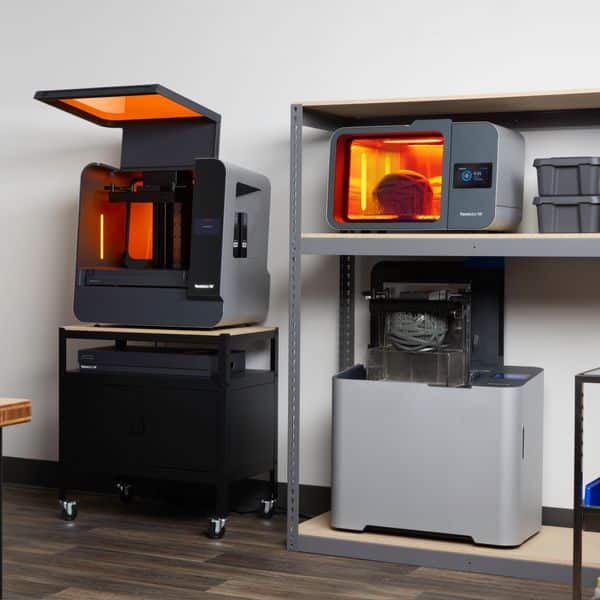


For fashion, several 3D printing technologies are particularly relevant:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is perhaps the most common and accessible type of 3D printing. An FDM printer works by heating a thermoplastic filament (a type of plastic material) and extruding it through a nozzle, depositing it layer by layer onto a build platform. Imagine a super-precise hot glue gun that builds upwards. FDM is great for creating prototypes and is increasingly being used for footwear, accessories, and structural elements within garments, especially with flexible filaments.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): This method uses a high-powered laser to selectively fuse small particles of powdered material (like nylon or even some composites) into a solid structure. After each layer is fused, the build platform lowers, and a new layer of powder is spread, allowing the process to repeat. SLS is fantastic because it doesn’t require support structures (the unfused powder acts as support), allowing for highly complex geometries and intricate, interlinking designs that can be flexible and durable. Many of the truly “fabric-like” 3D printed garments you might see are created with SLS.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers use a UV laser to cure liquid resin, solidifying it layer by layer. This technology is known for producing incredibly smooth surfaces and fine details, making it ideal for intricate jewelry or highly detailed embellishments. However, the materials tend to be more rigid, so its application in truly “casual” and flexible apparel is more limited to specific parts or accents.
The choice of printing technology is deeply intertwined with the material used. Flexible filaments like Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) have been game-changers for casual fashion. TPU, for instance, offers rubber-like elasticity, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it perfect for shoe soles, flexible jewelry, or even intricate textile-like structures that need to move with the body. Other materials like specialized nylons or even bio-plastics are also being explored for their unique properties, pushing the boundaries of what 3D printed fashion can feel and look like.
The journey is still ongoing, but these technologies are rapidly evolving, bringing us closer to a future where 3D printed fashion is not just a novelty but a staple in our everyday wear.
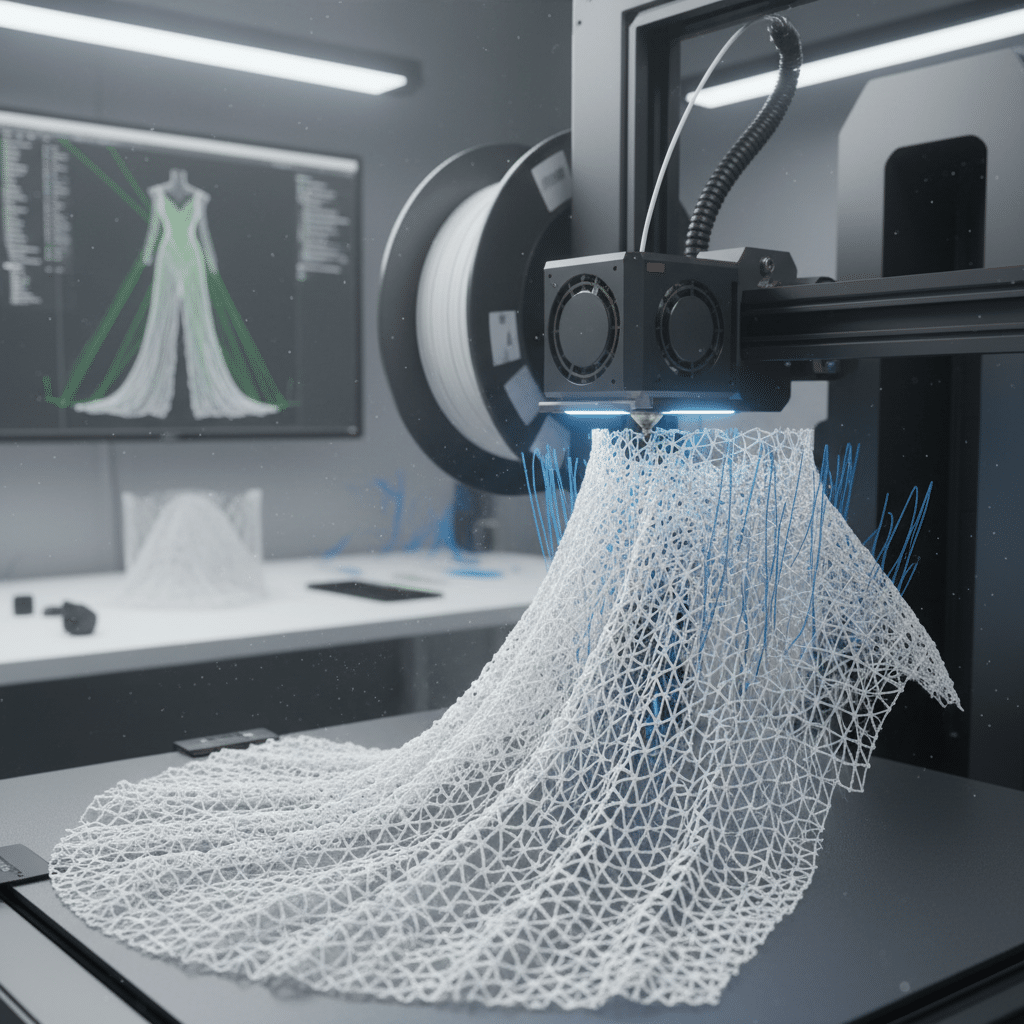

Materials Matter: From Rigid Plastics to Flexible Fabrics
When we think about 3D printed fashion from even a few years ago, images of stiff, geometric structures often come to mind. Early pioneers in the field, while creating visually stunning pieces, were largely limited by the rigidity of available materials like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene). These materials, while excellent for prototyping and many industrial applications, simply didn’t offer the comfort, drape, or flexibility required for everyday clothing. Imagine trying to wear a shirt made of hard plastic – not exactly a casual experience!
However, the world of 3D printing materials has exploded with innovation, directly addressing the needs of the fashion industry. The focus has shifted dramatically towards developing materials that can mimic the characteristics of traditional textiles – softness, elasticity, breathability, and drape.
One of the most significant breakthroughs has been the widespread adoption of flexible filaments, particularly Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU). TPU is a game-changer because it boasts rubber-like elasticity, high abrasion resistance, and excellent durability. This means designers can create items that bend, stretch, and move with the body, making them genuinely comfortable. Think of the flexible soles of modern sneakers or even intricate, web-like structures that conform to your shape without feeling restrictive.
Beyond TPU, other advanced polymers are also making waves:
- Flexible Nylons: These materials offer a good balance of strength and flexibility, and can be dyed post-printing for a wider range of colors. They’re often used in SLS printing to create interlocking structures that behave much like woven fabric.
- Composite Materials: Experimentation with combining different materials, like infusing flexible polymers with fibers or other additives, aims to achieve even greater textile-like qualities, such as a softer hand-feel or enhanced breathability.
- Bio-based and Recycled Materials: The drive for sustainability has led to the development of flexible filaments derived from renewable resources or made from recycled plastics. This aligns perfectly with the eco-conscious goals of many modern fashion brands.
The challenge isn’t just about finding flexible materials, but also about how these materials are structured during the printing process. Designers are leveraging the unique capabilities of 3D printing to create intricate lattice structures, mesh patterns, and interlocking scales that allow for greater airflow and movement than solid forms. These complex geometries, often inspired by natural forms like honeycomb or cellular structures, are what give 3D printed pieces their unique aesthetic and enhanced comfort.
For instance, a 3D printed shoe might feature a sole with an optimized lattice structure that provides cushioning and flexibility precisely where needed, while a garment might incorporate printed fabric panels with microscopic holes for ventilation. The goal is to move away from the “plastic-y” look and feel and towards textures that are tactile, appealing, and, most importantly, comfortable enough for all-day wear. The material revolution is undoubtedly one of the core pillars supporting the emergence of casual 3D printing fashion, transforming what was once rigid and futuristic into something pliable, wearable, and ready for your everyday life.
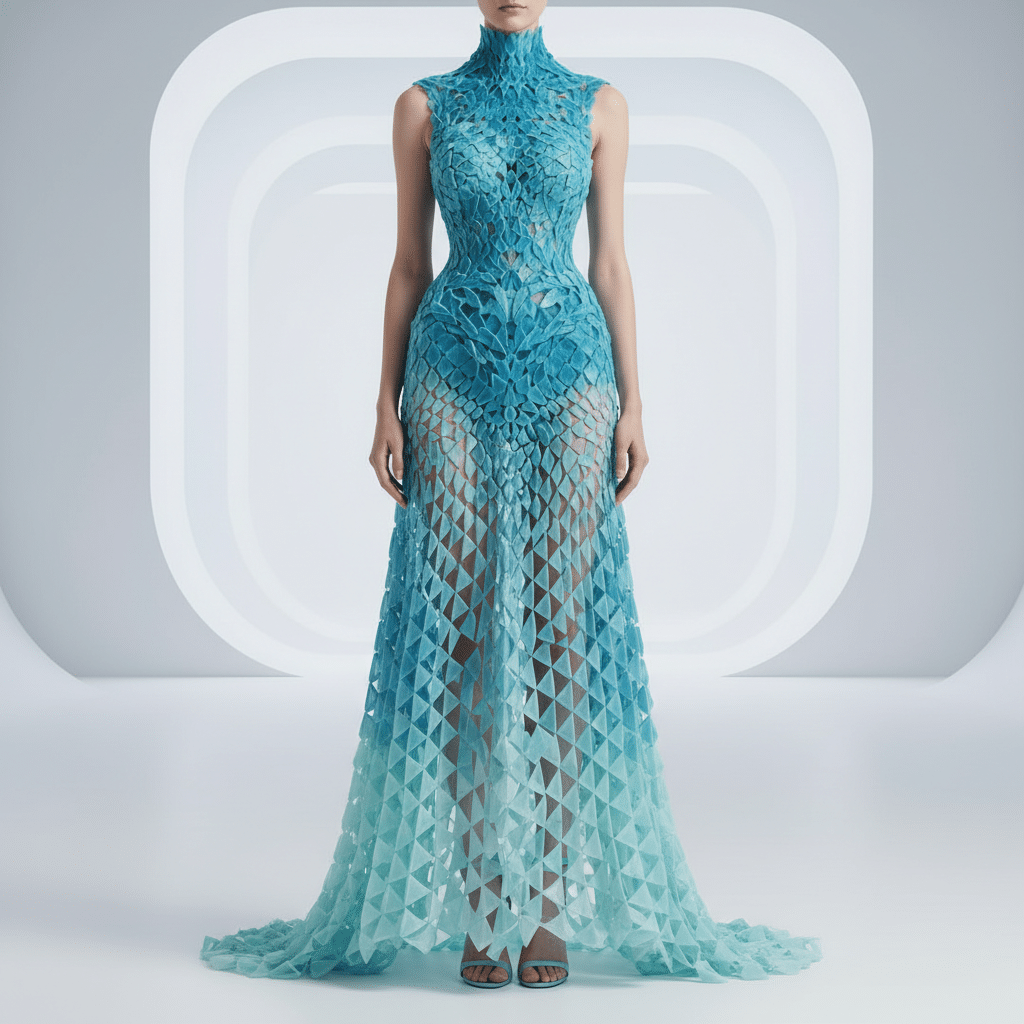

Customization is King: Personalizing Your Wardrobe
In a world increasingly driven by individuality and unique expression, the mass-produced nature of traditional fashion often leaves something to be desired. How many times have you wished a garment fit just a little better, or came in a slightly different pattern, or was entirely unique to you? This is where 3D printing fashion truly shines, putting customization at the very heart of the design and consumption process. It’s moving us from “off-the-rack” to “made-to-order” on an entirely new level.
One of the most compelling aspects of 3D printing is its ability to create truly bespoke items. Imagine shoes perfectly molded to the contours of your feet, offering unparalleled comfort and support. Or a dress that’s not just your size, but precisely tailored to your specific body measurements, curves, and proportions. This level of personalization goes far beyond standard sizing, addressing the nuances of individual anatomy that traditional manufacturing struggles to accommodate. For items like 3D printed cosplay props, this custom fit and design capability is already invaluable, and it’s quickly translating to everyday wear.
The process of achieving this customization can be incredibly straightforward. With advancements in 3D scanning technology, your body can be accurately mapped, and that data can then be fed into design software. This allows designers to generate a digital model of an item that is an exact, personalized fit for you. This means no more ill-fitting sleeves, gaping waistbands, or uncomfortable pressure points. The garment or accessory becomes an extension of your body, tailored for maximum comfort and aesthetic appeal.


Beyond fit, 3D printing unlocks limitless design customization. Want a unique pattern that reflects your favorite hobby? A texture that mimics a natural element? Or perhaps integrate your personal brand or logo into a casual accessory? All of this becomes not just possible, but relatively easy to execute. This capability transforms the consumer from a passive buyer into an active co-creator, engaging directly in the design process. Whether it’s choosing a specific color gradient, altering a geometric pattern, or adding a personal emblem, 3D printing provides the tools to make it happen. This level of personalized production aligns perfectly with the trend of designing a merch for individuals or small businesses, offering unique items that truly stand out.
This bespoke approach also minimizes waste. Instead of producing large quantities of standardized sizes that may or may not sell, 3D printing enables on-demand manufacturing. Items are created only when they are ordered, reducing overproduction and the environmental footprint associated with unsold inventory. It’s a powerful shift towards a more sustainable and consumer-centric fashion model, where your wardrobe isn’t just fashionable, but also perfectly, uniquely yours. The future of casual wear is deeply personal, and 3D printing is the key to unlocking that potential.
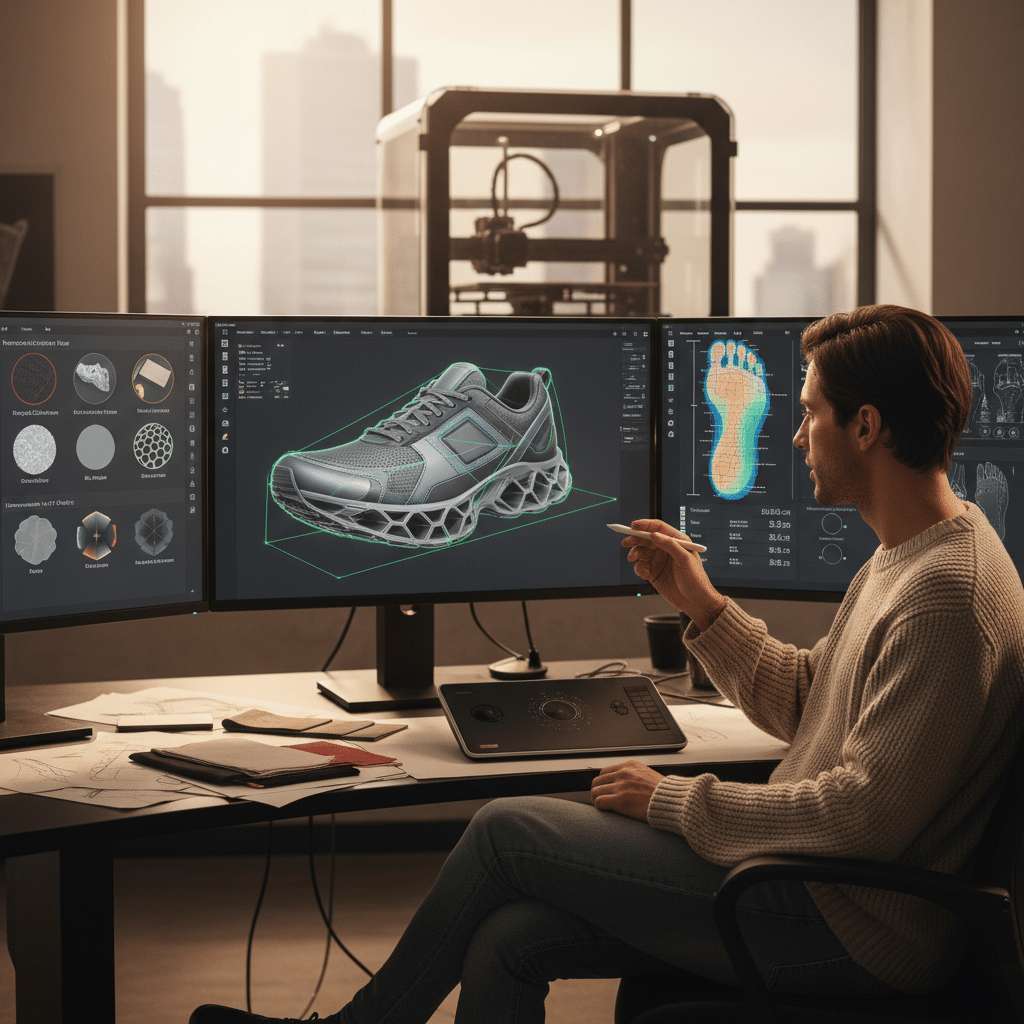
Casual Applications: Where 3D Printing Shines in Everyday Style
While the initial forays of 3D printing into fashion were often about grand statements, its true impact might just be found in the subtle, practical, and undeniably cool items we wear every single day. The technology is rapidly finding its niche in enhancing our casual style, offering unique advantages that traditional manufacturing simply can’t match.
Footwear: The Perfect Stride
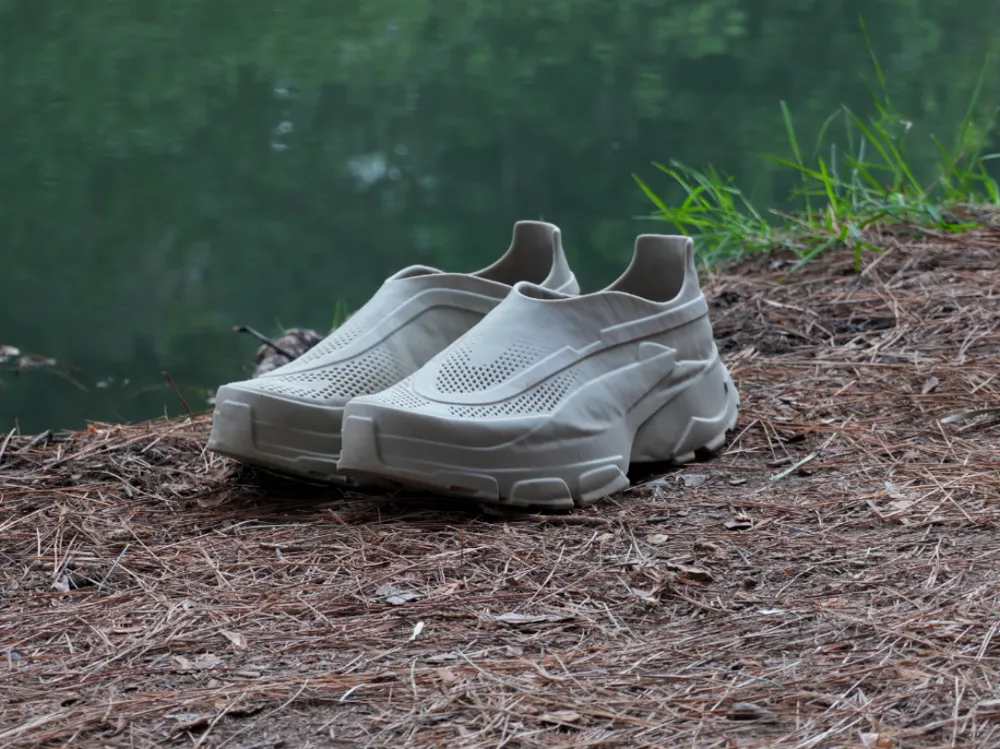
Perhaps one of the most visible and successful casual applications of 3D printing is in footwear. Sneakers are an ideal canvas due to their complex structures and the demand for both performance and aesthetics.
- Custom Soles and Midsoles: Brands like Adidas have already launched commercially available sneakers featuring 3D printed midsoles. These can be engineered with lattice structures that provide cushioning, responsiveness, and stability precisely where the foot needs it most, tailored to an individual’s gait and weight. This offers an unparalleled level of performance customization, enhancing comfort for everything from a leisurely walk to a serious run.
- Personalized Fit: Imagine a pair of casual shoes where the entire upper is 3D printed to perfectly cradle your foot, eliminating common issues like rubbing or pressure points. The precision allows for bespoke sizing and shaping, leading to truly comfortable and long-lasting footwear.
- Unique Aesthetics: Beyond function, 3D printing allows for incredibly intricate and innovative sole patterns, textures, and designs that would be impossible to mass-produce with traditional methods. This pushes the boundaries of sneaker design, creating eye-catching casual kicks that truly stand out.
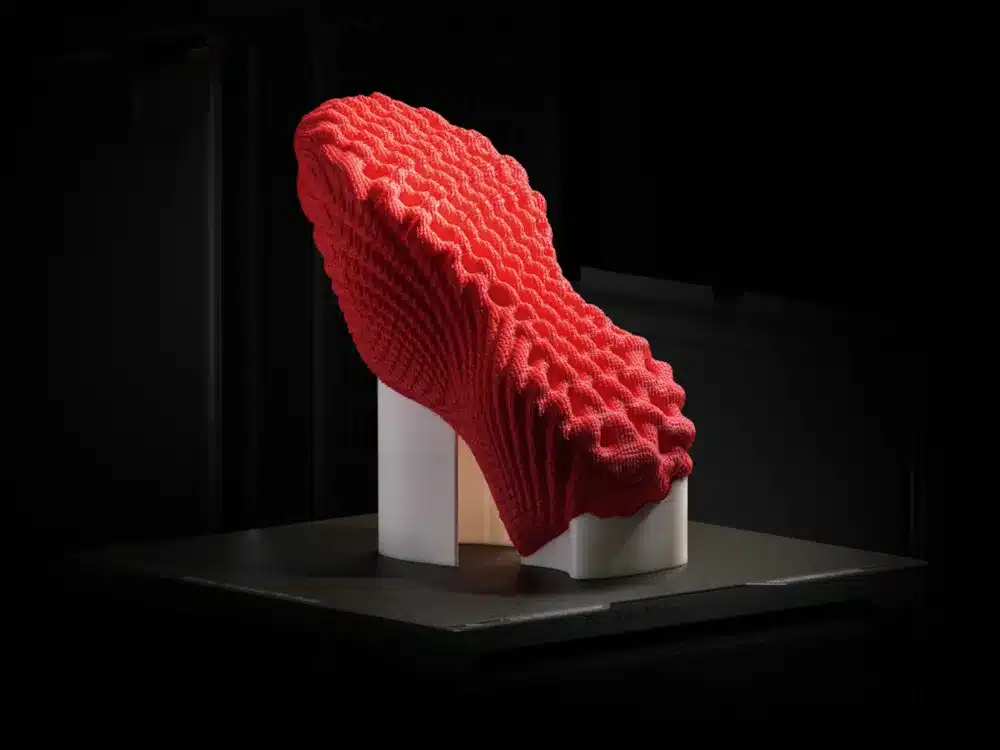


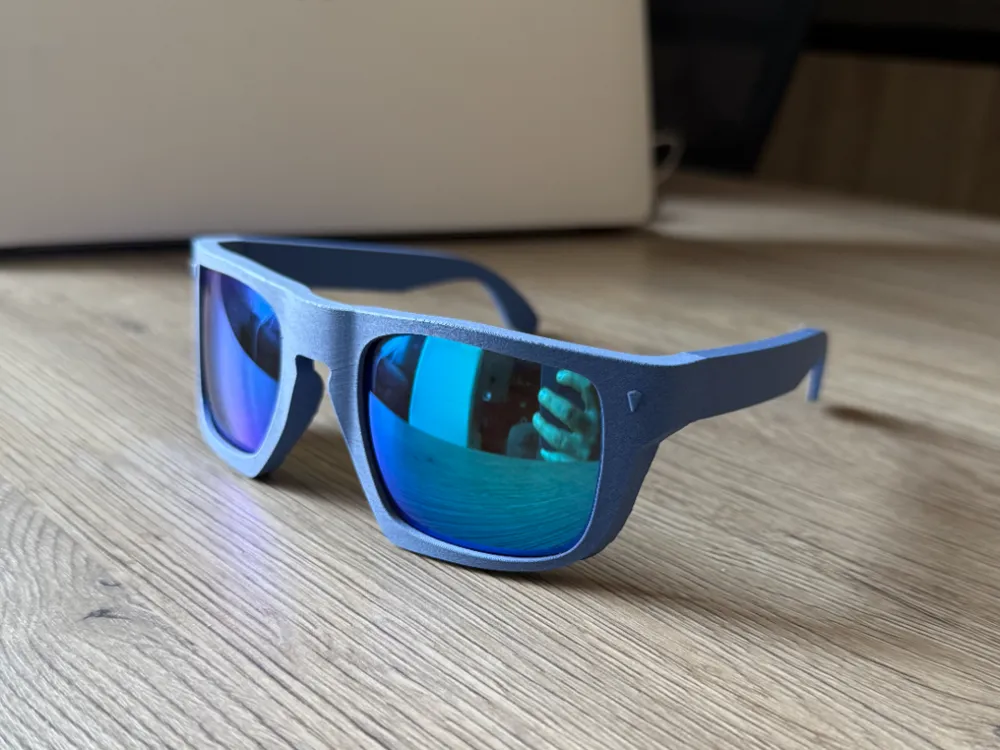
Accessories: The Finishing Touch
Accessories are often the easiest entry point for new technologies in fashion, and 3D printing is no exception. They offer a low-risk way to experiment with unique designs and materials.
- Jewelry: From delicate earrings to chunky statement necklaces, 3D printing allows for intricate geometric patterns, lightweight hollow structures, and unique textures that can be printed in various materials, including flexible polymers or even metals. This means you can get a truly one-of-a-kind piece that reflects your personal style.
- Bags and Belts: While full bags might be complex, 3D printed elements can add a touch of futuristic flair. Think of a uniquely textured buckle, a custom handle, or decorative panels integrated into a casual tote or backpack. Belts can be printed with interlocking segments for flexibility and a distinctive look.
- Eyewear: Custom-fit glasses frames are another excellent application. 3D printing allows for frames that perfectly match the wearer’s face shape and measurements, offering superior comfort and preventing slipping. Designers can also create avant-garde shapes and intricate detailing that isn’t feasible with injection molding.
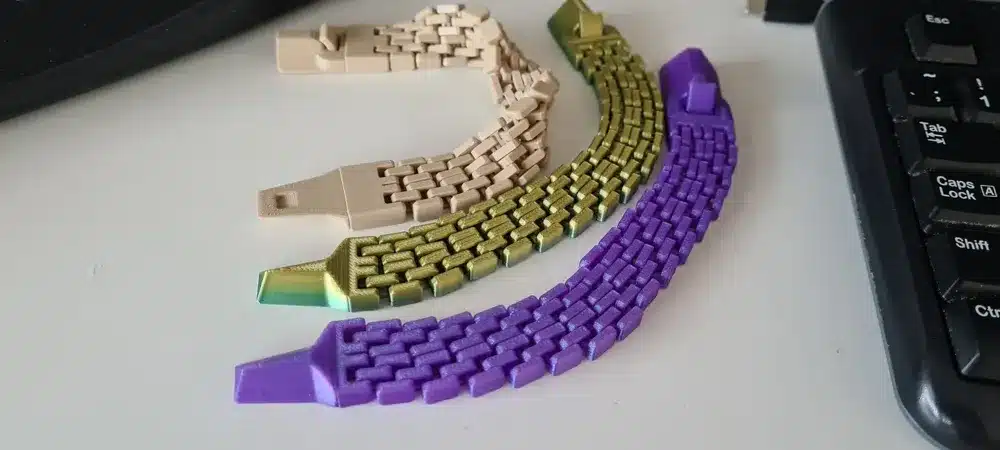
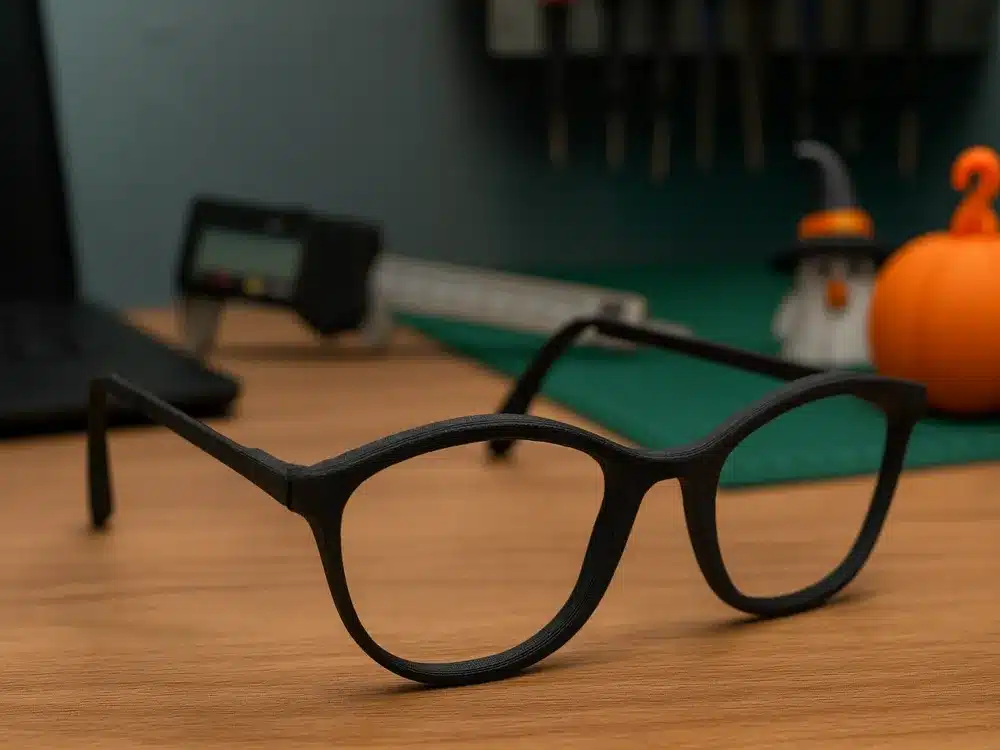


Embellishments and Details: Elevating Basics
Even if a full 3D printed garment isn’t your speed, incorporating printed elements can elevate everyday basics.
- Appliques and Patches: Add unique, raised textures or intricate designs to a denim jacket, a t-shirt, or a canvas bag. These can be printed in flexible materials and then attached, offering a distinct, personalized touch.
- Collars and Cuffs: Imagine a regular shirt adorned with a subtly textured, 3D printed collar or cuff detailing. These elements can add structural interest and a futuristic edge to an otherwise simple garment.
- Buttons and Fasteners: Custom 3D printed buttons can be a fantastic way to personalize a piece of clothing, offering unique shapes, sizes, and designs that truly reflect your style.
Sportswear: Performance Meets Personalization
For active individuals, 3D printing offers tangible performance benefits in casual sportswear. Lightweight, breathable, and supportive structures can be integrated into athletic wear. Think of compression sleeves with targeted support zones, or activewear with integrated ventilation patterns designed for optimal airflow. This blend of functionality and customization makes 3D printing a perfect fit for the demands of modern athletics and active lifestyles.
Whether it’s the comfort of a perfectly fitted shoe, the statement of a unique accessory, or the subtle detail that transforms a basic, 3D printing is paving the way for a truly personalized and innovative approach to casual fashion. It’s no longer about just streetwear meets sparkle: why rhinestone hoodies are the new power piece, but about entirely new ways to integrate unique elements into our everyday fashion narratives.
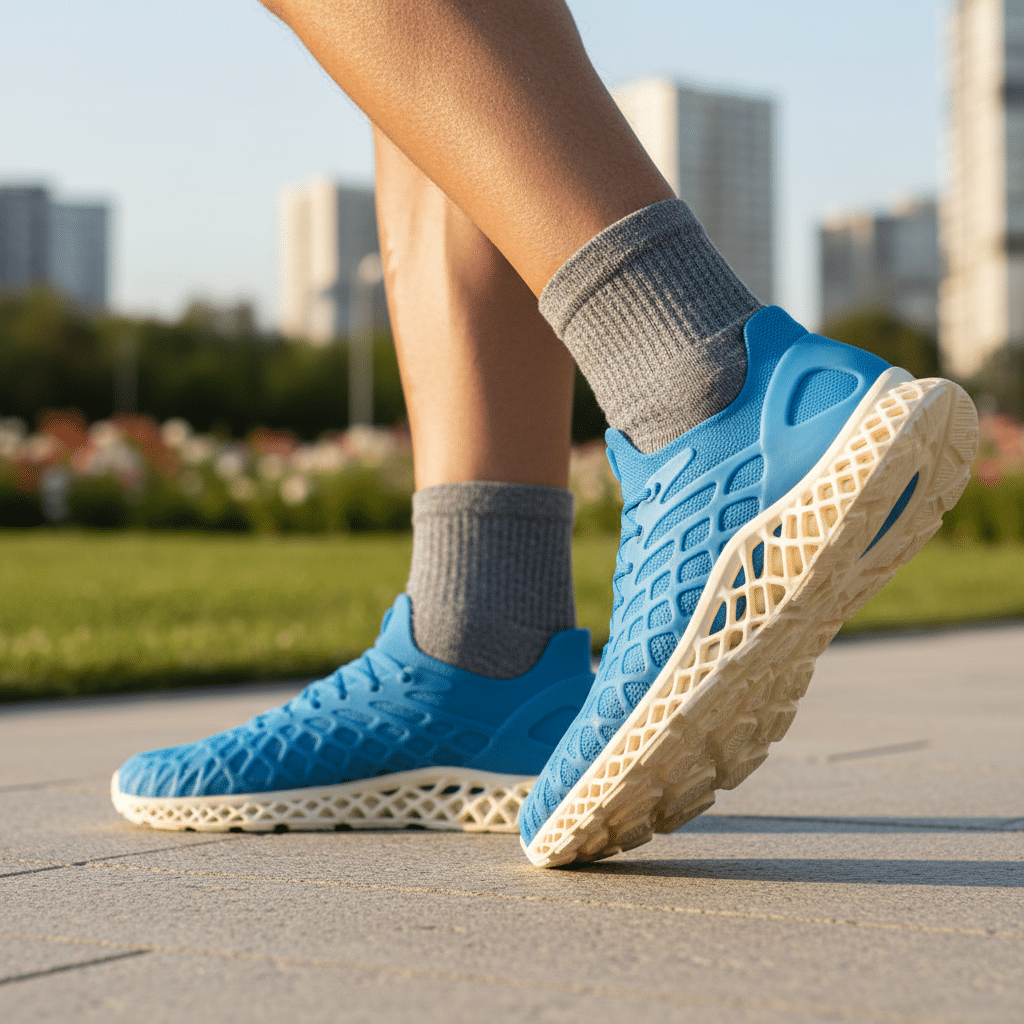

The Environmental Edge: Sustainability and Circular Fashion
Beyond the allure of cutting-edge design and hyper-personalization, 3D printing fashion carries a significant promise for addressing one of the industry’s most pressing issues: sustainability. The traditional fashion model, often characterized by “fast fashion,” is notoriously resource-intensive and environmentally damaging, contributing to vast amounts of waste and pollution. 3D printing offers a compelling alternative, paving the way for a more responsible and circular approach to clothing production.
One of the most immediate benefits is reduced waste. Traditional garment manufacturing often involves cutting patterns from large sheets of fabric, leading to significant material scraps – sometimes as much as 15-20% of the material is wasted. 3D printing, being an additive process, builds objects layer by layer only where material is needed. This “zero-waste” or “minimal-waste” manufacturing approach dramatically cuts down on textile waste. For instance, creating a 3D printed accessory only uses the exact amount of filament required for that specific item, leaving virtually no offcuts.
This technology also facilitates on-demand production. Instead of forecasting trends and mass-producing collections months in advance, often leading to overstock and unsold garments that end up in landfills, 3D printing allows for items to be made only when an order is placed. This eliminates the need for large inventories and significantly reduces waste from unsold goods. Imagine a future where your favorite shirt design is printed for you only after you click ‘buy’, ensuring that every piece created has a home.
Local manufacturing is another key advantage. With 3D printers becoming more accessible and capable, production can shift from distant factories to local hubs, or even to a consumer’s home. This drastically reduces the carbon footprint associated with global shipping and logistics. It shortens supply chains, makes production more transparent, and can stimulate local economies. The ability to produce items closer to the point of consumption is a powerful step towards a greener future.
Furthermore, the materials used in 3D printing offer immense potential for circularity. Many thermoplastic filaments, like TPU or nylon, are recyclable. This means that at the end of a garment’s life, the material could theoretically be shredded, re-pelletized, and used to print new items. Some companies are even exploring closed-loop systems where their own 3D printed products can be returned for recycling and repurposing into new designs. This vision of “cradle-to-cradle” fashion, where materials are continuously reused rather than discarded, is a significant departure from the linear “take-make-dispose” model. The precise nature of 3D printing can even influence general design principles, where concepts like the importance of white space in design: less is more can be applied to material usage, optimizing every millimeter of the print.
While challenges remain in scaling up material recycling and establishing widespread infrastructure, the inherent capabilities of 3D printing position it as a powerful tool for driving a more sustainable, eco-friendly, and circular future for casual fashion. It’s not just about what we wear, but how it impacts the world around us.
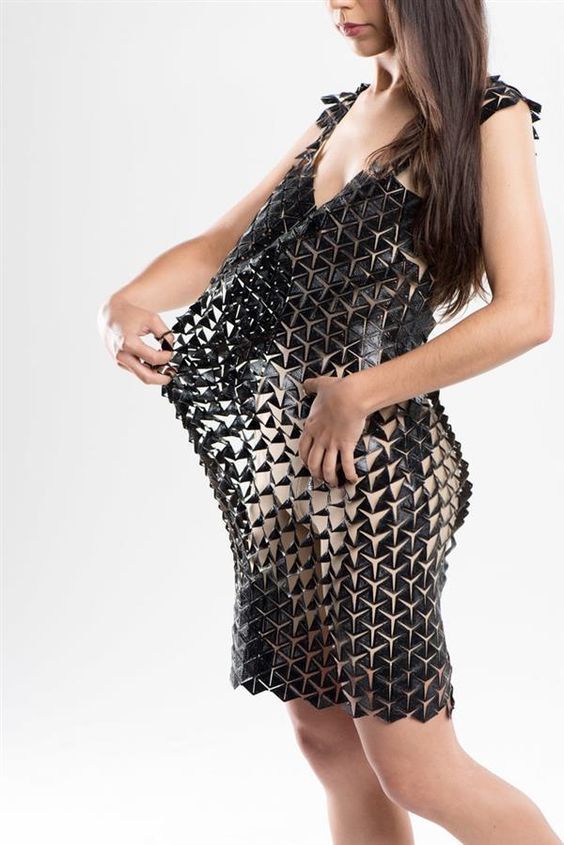
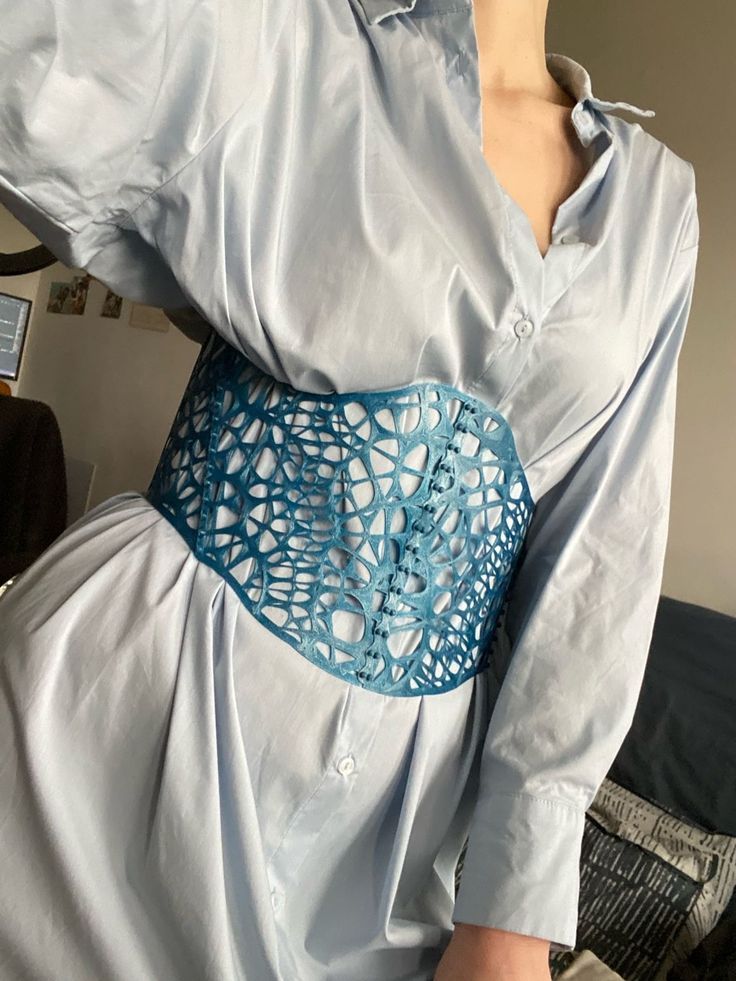


Conclusion
The journey into the world of 3D printing fashion for casual wear is a thrilling exploration of innovation, sustainability, and personal style. What began as an experimental frontier for haute couture is rapidly evolving into a practical, accessible, and exciting new dimension for our everyday wardrobes. We’ve seen how breakthroughs in flexible materials and advanced printing technologies are moving us beyond rigid plastics, allowing for comfortable, wearable designs that can bend, stretch, and breathe.
The power of 3D printing lies in its unparalleled ability to offer true customization, allowing for garments and accessories that are perfectly fitted, uniquely designed, and deeply personal. From bespoke footwear that cradles your feet to intricate accessories that reflect your individual flair, the casual applications are only just beginning to unfold. Moreover, this technological revolution brings with it a significant promise for a more sustainable future, offering solutions to reduce waste, enable on-demand production, and foster a truly circular economy in fashion.
While challenges like cost, speed, and material refinement still exist, the relentless pace of innovation suggests that these obstacles are merely temporary. The vision of a personalized, digitally crafted wardrobe, perhaps even printed at home, is no longer a distant dream but a tangible reality within reach.
So, as you look at your everyday clothing, imagine a future where every stitch, every seam, and every detail could be precisely engineered for you. The world of 3D printing fashion isn’t just about stepping into tomorrow; it’s about shaping it, one stylish, sustainable, and uniquely YOU piece at a time. The revolution is here, and it’s inviting you to wear the future.
What is 3D printing fashion and how is it transforming everyday clothing?
3D printing fashion involves creating clothing and accessories layer by layer using digital designs, allowing for customization, sustainability, and new design possibilities that are making casual wear more unique and adaptable.
How does 3D printing technology work in creating clothing and accessories?
3D printing builds objects by adding material layer by layer from a digital model created with CAD software, using techniques like FDM, SLS, or SLA, which enable the production of complex and customized fashion items.
What are some practical everyday applications of 3D printing in casual fashion?
3D printing is used in footwear for custom soles and fits, in accessories like jewelry, bags, and eyewear with unique designs, as well as in decorative elements like patches, buttons, or structural details that elevate basic garments with a futuristic touch.
- 24shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest24
- Twitter0
- Reddit0



