Recovery may take longer than expected, and that’s why experiencing an injury can have profound effects on victims. Prolonged recovery from physical injuries can lead to significant mental health challenges. The psychological consequences may remain unaddressed, yet they are just as important as the physical aspects of healing.
Mental health must be viewed in conjunction with physical health to achieve a well-rounded recovery. Keep reading to address mental health concerns coming from an accident and know what to do to fully recover.
Role of a Lawyer in Recovery


Following an injury, victims will be faced with increased stress and emotional burden. A lawyer specializing in personal injury cases can provide significant support by guiding clients through the legal complexities. For those injured in a motorcycle crash, a specialized lawyer can help victims manage their legal claims effectively. Legal representation allows individuals to focus on their physical and mental recovery instead of dealing with negotiations and court procedures.
With a skilled lawyer, victims can receive fair compensation for their suffering, enabling them to access various resources, including therapy. The sense of security that comes from having professional legal support can reduce anxiety and improve mental well-being throughout the recovery process.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)

Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) arises after experiencing severe trauma, even a significant injury or accident. Individuals may relive traumatic events through vivid flashbacks or nightmares, resulting in increased anxiety and emotional distress. PTSD can manifest in hyperarousal, avoidance behaviors, and emotional numbing.
Individuals recovering from serious injuries like those sustained in accidents find themselves triggered by reminders of the incident, causing them to struggle even more during their recovery process. Treatment for PTSD encompasses Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR). Psychotherapy can help individuals process their trauma and develop coping strategies. Untreated symptoms of PTSD may exacerbate the recovery journey, prolong physical healing, and hinder an individual’s return to daily life.
Anxiety Disorders


Anxiety disorders are another common mental health concern during injury recovery. The unpredictability associated with prolonged rehabilitation can heighten feelings of worry and unease. Individuals may experience generalized anxiety, panic attacks, or specific phobias related to their injury or recovery process. The uncertainty about the future and ongoing physical limitations can fuel anxiety.
Many times, these feelings make it difficult for individuals to progress effectively in their rehabilitation. Coping strategies for managing anxiety can include mindfulness exercises, support groups, and regular communication with healthcare providers.
However, sometimes it may require advanced interventions, such as TMS Therapy, to regulate brain activity and reduce symptoms for those with severe anxiety, making it easier to continue their recovery journey. Understanding their concerns, staying informed about the recovery process, and actively participating in their rehabilitation can alleviate anxiety. Creating a strong support system helps bring comfort during this challenging time.
Understanding their concerns, staying informed about the recovery process, and actively participating in their rehabilitation can alleviate anxiety. Creating a strong support system helps bring comfort during this challenging time.
Low Self-Esteem

Experiencing a serious injury disrupts self-image and identity, resulting in a drop in self-esteem for many individuals. The inability to perform daily tasks or engage in past activities can cause feelings of inadequacy or failure. As patients grapple with altered abilities and physical features, they may internalize negative beliefs about themselves that contribute to poor mental health.
To combat these feelings, mental health professionals can assist individuals in reshaping their self-perception and cultivating self-acceptance. Strategies might include focusing on achievements and setting realistic goals to help recover a sense of agency and worth. Through cognitive reframing and strength-based approaches, individuals can regain confidence as they move through their recovery journeys.
Depression and Mood Disorders
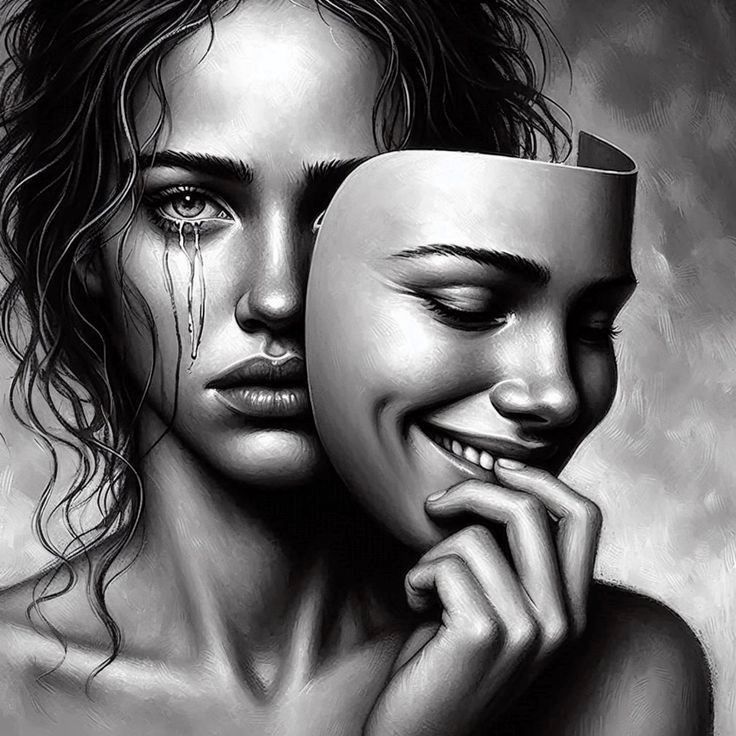

Depression frequently emerges as an emotional response to prolonged injury recovery. Patients might experience feelings of hopelessness, sadness, and disinterest in daily activities once enjoyed. The inability to resume physical capabilities can result in a sense of lost identity and increased emotional dysregulation. Individuals recovering from injuries are at a higher risk of developing mood disorders compared to the general population. Decreased mobility, isolation from social networks, and ongoing pain can worsen depressive symptoms.
Therapeutic interventions, including medication and psychotherapy, can help manage depressive symptoms. Engaging in social activities and developing healthy routines can support mood improvement. Re-establishing a connection with social circles during recovery can provide emotional support and build resilience against depressive symptoms.
Social Isolation
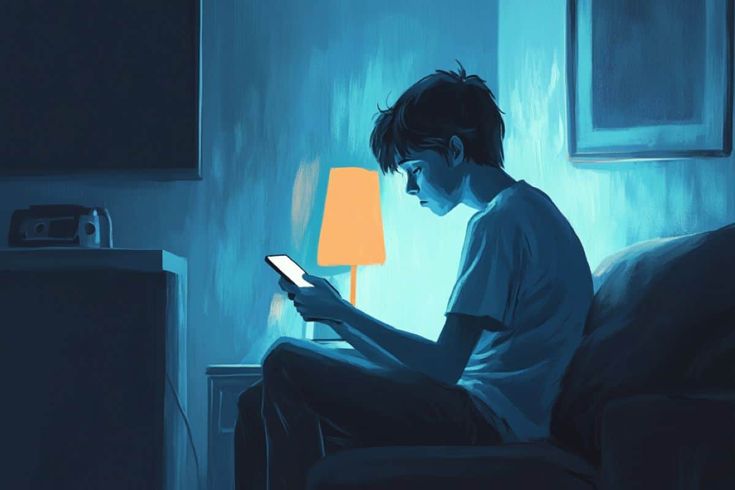

Social isolation accompanies prolonged injury recovery. Many individuals find it challenging to engage socially due to their physical limitations, which may be the leading cause of feelings of loneliness and sadness. Isolation can result in a cycle where decreased social interactions result in increased emotional struggles, making recovery more complicated.
This issue is most prevalent for those who have lost physical mobility or independence due to their injuries. Enforcing regular contact with friends and family can help mitigate the impact of isolation. Reconnecting with social supports, whether through virtual means or limited physical interactions, can reinforce emotional well-being. Engaging with the community through support groups or rehabilitation classes can be a motivational boost. Finding ways to remain socially active during recovery will help accident victims maintain their mental health.
Coping Mechanisms
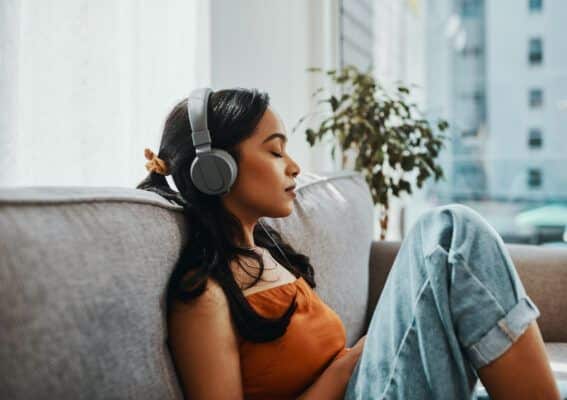

Finding effective coping mechanisms is a necessary step for those experiencing mental health symptoms during injury recovery. Some effective strategies may include physical activities adapted to individual capabilities, such as gentle yoga or walking. These activities promote physical health and release endorphins that improve mood.
Mindfulness practices have recently gained popularity for their efficacy in reducing anxiety and stress. Keeping a journal can serve as an outlet for emotions, allowing individuals to reflect on their recovery journey and process thoughts. Seek professional help when coping alone proves insufficient. Employers, friends, and family members should be made aware of these mechanisms to provide appropriate support. Building a routine around these coping strategies can create a sense of normalcy and offer a structure that benefits emotional well-being during challenging times.
Seeking Professional Help
Most individuals may mistakenly believe they can manage their mental health symptoms without support, leading to long-term complications. Recognizing persistent sadness, overwhelming anxiety, or thoughts of self-harm will help them take corrective action. Mental health professionals can provide tailored interventions based on individual needs.
Therapy can be a safe space for individuals to process their emotions and develop coping strategies. Joining support groups allows individuals to connect with others experiencing similar challenges and reduce feelings of isolation. Awareness and education about mental health can empower individuals throughout the recovery process, promoting better outcomes in mental and physical realms. Seeking help should be encouraged as a proactive step, not a last resort.

Mental health concerns linked to prolonged injury recovery should not be overlooked. Addressing issues like PTSD, anxiety, depression, and social isolation is necessary for achieving a full recovery. By effectively managing mental health, individuals can improve their physical rehabilitation and return to their daily activities with renewed vigor.
- 3shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest0
- Twitter3
- Reddit0



