Choosing the right motorcycle helmet is one of the most important steps you can take for your safety on the road. A good helmet should fit snugly, hold valid safety certifications like DOT, ECE, or SNELL, and offer comfort for your riding needs. Factors like weight, ventilation, and the specific style of helmet also play a key role in your overall riding experience.
Whether you ride daily or just on weekends, understanding what to look for in a helmet can make a significant difference in both safety and comfort. The right helmet isn’t just about looks—it’s about protecting your head in the event of an accident, fitting properly, and including features that suit your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Always check for real safety certifications and a secure, comfortable fit.
- Consider helmet features like ventilation and weight for added comfort.
- Choose a helmet style that meets your safety and riding requirements.


Understanding Motorcycle Helmet Types
Each motorcycle helmet type offers a distinct combination of protection, comfort, and ride experience. The differences in design, coverage, and ventilation directly impact safety and usability for various riding styles.
Full-Face Helmets
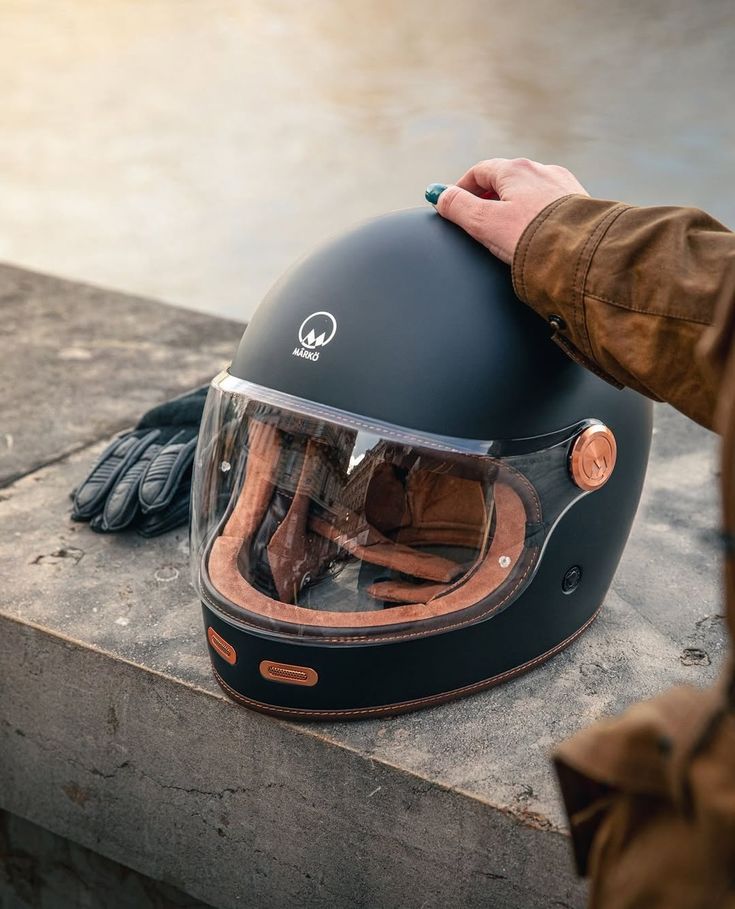
Full-face helmets provide the most complete coverage for your head, including the chin and jaw, which are particularly vulnerable during accidents. The outer shell extends around your entire skull, while a solid chin bar offers extra impact protection.
Many riders choose this helmet type for high-speed or highway use because of its robust safety features. Full-face helmets usually include a face shield that protects your eyes and face from debris, wind, and bugs. Ventilation systems are common, helping to reduce fogging and keep you comfortable in different weather conditions.
A full-face helmet’s snug fit can also reduce wind noise and distractions. Look for models meeting recognized safety standards such as DOT, ECE, or Snell for reliable impact protection. Some options provide removable liners, making them easier to clean after long rides.
Modular Helmets
Modular helmets, sometimes called flip-up helmets, blend features of full-face and open-face designs. The chin bar and visor can be lifted with a hinge, allowing you to speak, eat, or get air without removing the helmet.
This design offers improved versatility, especially for touring and adventure riders who frequently stop or communicate on the road. While modular helmets provide better jaw protection than open-face helmets, their moving parts may create slightly more wind noise and less impact resistance than full-face models.
Most modular motorcycle helmets come with integrated sun visors and multiple vents for airflow. Be sure the helmet is properly locked in the closed position while riding, as an unlatched chin bar can compromise safety. Check for DOT or ECE certification before purchasing.
Open-Face Helmets
Open-face helmets, or 3/4 helmets, leave your face exposed but cover the top, sides, and back of your head. They feature a sturdy outer shell and padded liner but offer less protection around the chin and jaw compared to full-face or modular helmets.
This type of helmet is often favored for city commuting and lower-speed riding due to its increased field of vision and lighter weight. Many open-face models include a face shield or sun visor to help block wind and debris. For extra protection, you can pair them with goggles or sunglasses.
If you value a sense of openness and communication with your surroundings, an open-face helmet may suit your needs. However, keep in mind the trade-off with reduced facial protection in crashes.
Half Helmets
Half helmets provide minimal coverage, protecting just the top and part of the sides of your head. They do not shield your face, chin, or lower sides, which increases vulnerability during an accident compared to other helmet types.
These are commonly used by cruiser or scooter riders who prefer maximum airflow and the lightest possible gear. Many half helmets lack advanced features such as face shields, integrated vents, or sun visors, though you can often add your own eye protection with glasses or goggles.
DOT certification is especially important for half helmets since coverage is limited. Comfort padding and adjustable straps help improve the fit, but always balance comfort with essential safety components when considering this style.


Evaluating Safety Certifications and Ratings
Helmet safety certifications directly impact your protection against head injuries in the event of a crash. Understanding the differences between each certification standard can help you assess helmet safety ratings and ensure you are using a helmet that meets recognized requirements.
DOT Certification
In the United States, the Department of Transportation (DOT) certification is the most widely recognized safety standard for motorcycle helmets. A DOT-approved helmet must meet the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) No. 218. This includes tests that evaluate a helmet’s ability to absorb impact, resist penetration, and maintain a secure retention system.
You can identify a DOT-certified helmet by the DOT symbol, typically located on the outside back of the helmet. This label means that the helmet meets minimum government standards for motorcycle safety.
While all helmets sold in the US must at least meet DOT requirements, some experts advise that DOT-only helmets may not always offer the highest level of protection. Independent testing is not always required for certification—manufacturers often self-certify their products.
ECE Certification
The ECE (Economic Commission for Europe) certification is widely used across more than 50 countries. Helmets that meet the ECE 22.05 or updated ECE 22.06 standards have passed rigorous tests for shock absorption, strap strength, and field of vision. Unlike DOT, ECE testing involves government supervised independent laboratories, adding another layer of oversight.
ECE standards are generally recognized for providing strong protection. They require each helmet model to be tested and periodically re-tested, which can increase consistency in helmet safety ratings.
ECE-certified helmets will display an ECE label or sticker, typically inside or on the chin strap. If you plan to ride internationally, especially in Europe, ECE approval is usually mandatory for legal road use.
Snell Certification
The Snell Memorial Foundation is a non-profit organization that maintains high standards for helmet safety. Snell certification is optional but seen as a mark of rigorous independent testing and enhanced safety features.
Snell certified helmets, such as those with the Snell M2020D or M2020R rating, undergo extensive impact and penetration testing. The foundation updates its certification cycles regularly to reflect advances in helmet technology.
Snell testing procedures often exceed DOT or ECE requirements, making these helmets popular among racers and performance-oriented riders. Look for a Snell sticker or label inside the helmet liner to confirm certification.
When comparing helmet safety ratings, Snell approval provides assurance that the helmet meets stricter performance benchmarks, especially regarding repeated impacts and real-world accident scenarios.


Ensuring Proper Helmet Fit and Comfort
A motorcycle helmet must fit your head securely for both safety and comfort. Key factors include measuring your head accurately, understanding size and shape, checking padding quality, and identifying any pressure points while trying on the helmet.
Measuring Your Head
Begin by measuring your head to find the right helmet size. Use a flexible tape measure and wrap it around your head about one inch (2.5 cm) above your eyebrows and just above your ears, ensuring the tape stays level throughout.
Record the measurement in centimeters or inches and refer to helmet manufacturer sizing charts, as sizes can vary between brands. Trying to guess your head size often leads to helmets that are too loose or too tight, reducing both protection and comfort.
It’s recommended to measure your head more than once to ensure accuracy. If your measurement falls between sizes, most experts advise choosing the smaller size for a snug, secure fit, as padding tends to compress slightly over time.
Helmet Size and Shape
Selecting the right helmet size and shape is crucial for overall fit. Helmets are typically offered in different shell shapes: round, intermediate oval, and long oval. Matching the helmet’s shape to your head prevents discomfort and pressure hotspots.
Try on several helmets within your size to compare the fit. The helmet should feel snug but not painfully tight. Your head should not move freely inside the shell, and the helmet should rest comfortably on your crown.
Helmet fit tables and size charts provided by manufacturers are a helpful resource. Always cross-reference your measurements before making a decision. Different brands may have subtle variations even for the same labeled size.
Padding and Cheek Pads
Padding and cheek pads play a major role in both comfort and helmet fit. Quality helmets feature removable and washable interior liners, allowing you to maintain freshness and adjust fit as needed.
When you put the helmet on, the cheek pads should press gently but firmly on your cheeks. There should be some resistance when you move the helmet side to side or up and down. Loose cheek pads indicate an overly large helmet or worn-out padding.
Check for additional comfort features such as moisture-wicking or hypoallergenic linings. Some helmets offer interchangeable cheek pads of varying thickness, letting you fine-tune the fit to match your preferences and face shape.
Identifying Pressure Points
Identifying and avoiding pressure points is key to long-term comfort, especially on extended rides. After wearing a new helmet for several minutes, pay attention to any areas of discomfort or pressure, commonly found around the forehead, temples, or jaw.
Even minor pressure points can cause headaches and irritation if ignored. It’s important to spend adequate time wearing the helmet in-store or at home before removing tags so you can assess for hidden fit issues. Look for even pressure around your entire head.
If you experience persistent discomfort in a certain area, try adjusting the internal padding or consider a helmet with a different head shape. Comfort should never be compromised, as this not only affects your experience but may also reduce your focus and safety on the road.


Key Safety Features to Consider
Selecting a motorcycle helmet means focusing on components that directly affect your safety. The materials, inner liner technology, and retention systems all work together to provide crucial impact protection in the event of a crash.
Impact-Resistant Materials
Modern helmets use advanced materials to absorb and distribute impact energy. The most common outer shells are polycarbonate, fiberglass, and carbon fiber. Each material offers distinct benefits:
- Polycarbonate: Lightweight and affordable, polycarbonate shells are known for flexibility that helps dissipate force.
- Fiberglass helmets: Fiberglass combines multiple layers for enhanced strength and flexibility while maintaining manageable weight.
- Carbon fiber helmets: Carbon fiber helmets are lighter and stronger compared to other materials, though typically more expensive. They are favored by riders seeking premium protection without extra weight.
Look for shells that are labeled as impact-resistant. The material choice can influence helmet durability, comfort, and price, so balance your needs carefully.
EPS Liner Technology
Beneath the shell, the EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) liner is the main layer responsible for managing impact. The EPS liner compresses on impact to absorb kinetic energy, minimizing the force transmitted to your head.
Some helmets use multi-density EPS liners for tailored protection in different impact scenarios. High-quality helmets layer the EPS liner to give added protection in specific zones, such as the sides and crown.
Proper liner thickness and density affect both your safety and comfort. It is important that the liner fits well and contains no significant gaps or pressure points. Removable liners and padding can help you adjust the fit without diminishing safety.
Chin Straps and Retention Systems
A secure helmet requires a reliable chin strap system. The strap keeps your helmet firmly in place during an impact, reducing the risk of it coming off in a crash.
Most helmets use a D-ring or quick-release buckle design. D-ring closures are widely regarded for their dependability, as they rarely loosen unintentionally. Quick-release buckles offer convenience and are easier to use with gloves but must be checked for durability and security.
Ensure the chin strap fits snugly but comfortably under your chin. Replace worn straps immediately and never modify the retention system, as altering it may compromise helmet safety and void warranties.


Additional Features and Final Considerations
When selecting a motorcycle helmet, attention to features like airflow, visibility, and helmet compatibility with your riding habits can make a substantial difference. Each of these aspects contributes to your comfort and safety on the road.
Ventilation and Sun Visors
Effective ventilation improves comfort by reducing heat and humidity inside the helmet. Look for helmets with adjustable intake and exhaust vents that allow you to control airflow based on riding conditions. Adequate ventilation helps prevent sweat buildup and fogging during long rides or in hot climates.
A sun visor can be a valuable addition, offering quick relief from glare and harmful UV rays. Many helmets now include integrated drop-down sun visors that can be operated with one hand. This feature helps when you transition between bright sunlight and shaded areas frequently.
Table: Ventilation and Sun Visor Features
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Adjustable Vents | Customizable airflow |
| Integrated Sun Visor | Reduces glare and eye strain |
| Removable Liners | Easier to clean, improves hygiene |
Anti-Fog Visor Options
A clear field of vision is essential, especially in cool or damp weather. Anti-fog visors or shields help prevent the visor from steaming up, maintaining visibility and safety. Some helmets offer a specially coated anti-fog shield, while others are compatible with Pinlock® inserts—a popular accessory that creates a double-glazed effect.
If you often ride in varied weather, prioritize helmets with anti-fog solutions. Keep in mind that good ventilation also contributes to managing visor fogging, so the combination of vent design and anti-fog technology is important. Not all helmets include these features, so check compatibility before purchasing aftermarket inserts.
Riding Style and Helmet Choice
Your riding style should strongly influence your helmet selection. For highway touring, you may want a full-face helmet with enhanced wind noise reduction and comfort features. Commuters might prioritize a modular helmet for easy removal and integrated communication systems.
If you frequently ride off-road, focus on helmets with increased ventilation and an extended peak for sun protection and debris deflection. Cruiser and urban riders might value lighter, more compact designs. Matching your helmet to your primary riding environment ensures both comfort and optimal protection.
- 155shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest155
- Twitter0
- Reddit0