Ever imagined a home that appears as if by magic, layer by precise layer, constructed by giant robots? Well, the future is here, and it’s built differently. We’re talking about 3d printed houses, a revolutionary concept that’s transforming the construction industry one extruded layer at a time. This isn’t just a quirky experiment; it’s a genuine movement gaining momentum, promising solutions to everything from housing shortages to environmental concerns. If you’ve ever wondered what it takes to print a house, or if these homes are just a fleeting fad, you’ve come to the right place. Let’s peel back the layers and unpack everything you need to know about these fascinating dwellings.
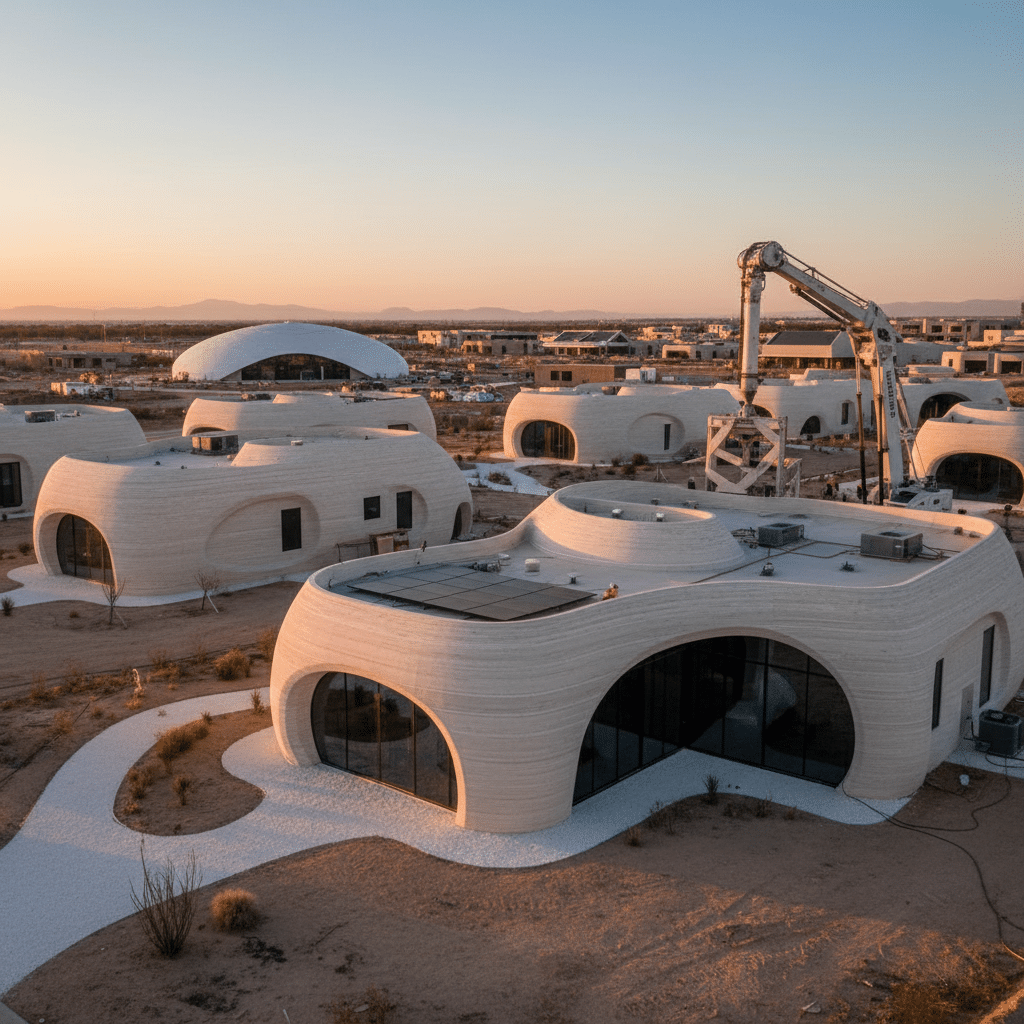


What Exactly Are 3D Printed Houses?
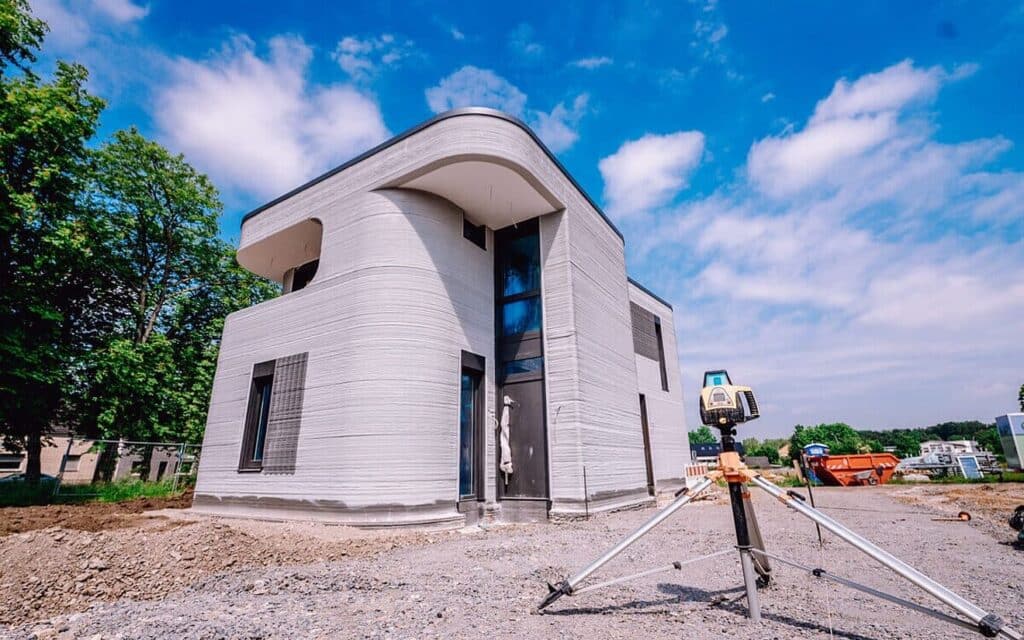
At its core, a 3D printed house is a structure built using additive manufacturing techniques. Instead of traditional methods involving bricks, mortar, and extensive manual labor, a massive robotic printer extrudes layers of material, typically a specialized concrete mix, to create the walls of a building. Think of it like a super-sized version of the desktop 3D printer many hobbyists use, but instead of plastic trinkets, it’s churning out habitable spaces.
The process starts with a digital design, much like a blueprint, which the printer then translates into a physical object. A gantry system or a large robotic arm moves the printhead, precisely depositing material layer by layer, building the walls from the ground up. This method allows for incredible precision and often much faster construction times than conventional building. It’s a complete game-changer, shifting construction from a labor-intensive craft to a technology-driven process.
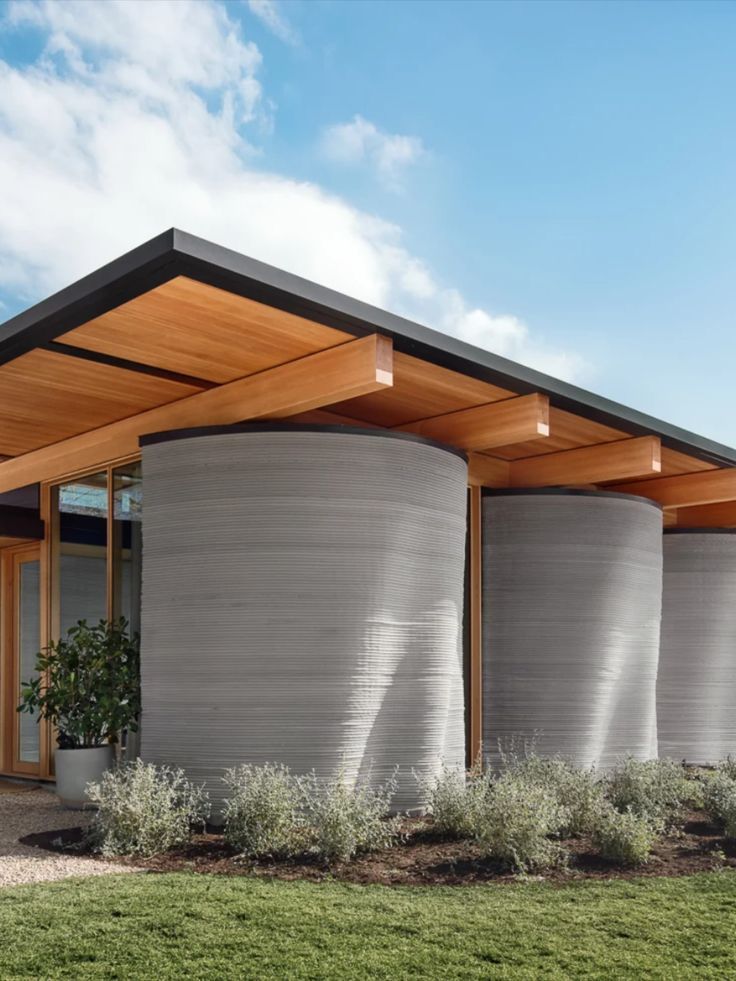
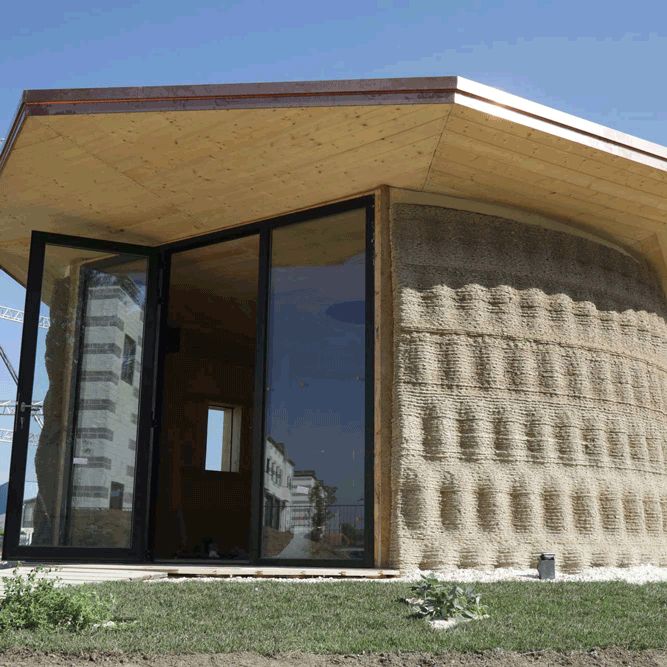


The Game-Changing Benefits of 3D Printing in Construction
So, why are so many people buzzing about 3D printed houses? The benefits are quite compelling, addressing some of the biggest challenges in modern construction and housing.
Remarkable Speed and Efficiency
One of the most eye-catching advantages is the sheer speed. While a traditional home might take months to frame and build, the structural walls of a 3D printed house can be completed in a matter of days, or even hours, depending on the design and printer. Companies like Icon have demonstrated printing entire homes in under 24 hours. This rapid deployment capability is incredibly valuable, especially in areas needing quick housing solutions or disaster relief. Less time on site means less overall project risk and faster occupancy.
Significant Cost Reduction
Who doesn’t love saving money? 3D printing slashes costs in several key areas.
- Labor: Since much of the heavy lifting is automated, the need for large construction crews is significantly reduced. This cuts down on labor costs, which are often a huge chunk of a building budget.
- Material Waste: Traditional construction often generates a lot of waste from cutting and fitting materials. 3D printing is an additive process, meaning it only uses the material needed, layer by layer, leading to minimal waste. This not only saves money but is also far better for the environment.
- Overall Project Cost: With reduced labor and material waste, the total cost of building can be dramatically lower, making housing more accessible and affordable.
Unprecedented Design Freedom
This is where things get really exciting for architects and homeowners alike. Conventional building methods are often limited by the practicalities of materials and human labor, making complex curves, unique textures, and intricate designs expensive and difficult. 3D printing laughs in the face of such limitations. It can create organic shapes, unusual wall patterns, and bespoke architectural elements with ease. If you’ve ever dreamt of a home that doesn’t look like every other box on the block, 3D printing offers the ultimate customization. It opens up possibilities for truly unique structures that are both functional and artistic.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
In an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, 3D printed houses offer a greener path forward.
- Reduced Waste: As mentioned, the additive nature of the process means less material waste ending up in landfills.
- Local Materials: Many 3D printing materials can be sourced locally, reducing transportation emissions. Some companies are even exploring using recycled content or earth-based materials.
- Energy Efficiency: The monolithic nature of 3D printed walls can lead to better insulation properties, meaning less energy is needed to heat or cool the home. This translates to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint over the home’s lifetime. If you’re looking to make your home more eco-friendly, exploring how solar panels can transform energy use in residential spaces is a fantastic complement to a 3D printed structure.
Addressing the Global Housing Crisis
The potential for 3D printed houses to tackle housing shortages worldwide is immense. Their speed, affordability, and ability to be deployed in remote or challenging environments make them an ideal solution for:
- Affordable Housing Initiatives: Providing safe, durable, and low-cost homes for underserved communities.
- Disaster Relief: Quickly erecting temporary or permanent shelters after natural disasters.
- Rapid Urbanization: Meeting the demand for new housing in quickly growing cities.

How Does the 3D Printing Process Work? (A Closer Look)
Let’s dive a bit deeper into the actual steps involved in bringing a 3D printed house to life. It’s a fascinating blend of digital design and on-site robotics.
The Design Phase: Digital Blueprints Come Alive
Every 3D printed house starts its journey as a digital file. Architects and engineers use sophisticated software like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) or BIM (Building Information Modeling) to create a detailed 3D model of the home. This model isn’t just a pretty picture; it contains all the precise instructions for the printer, including wall thickness, curves, openings for windows and doors, and even internal conduits for wiring or plumbing. This digital precision is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and design accuracy.
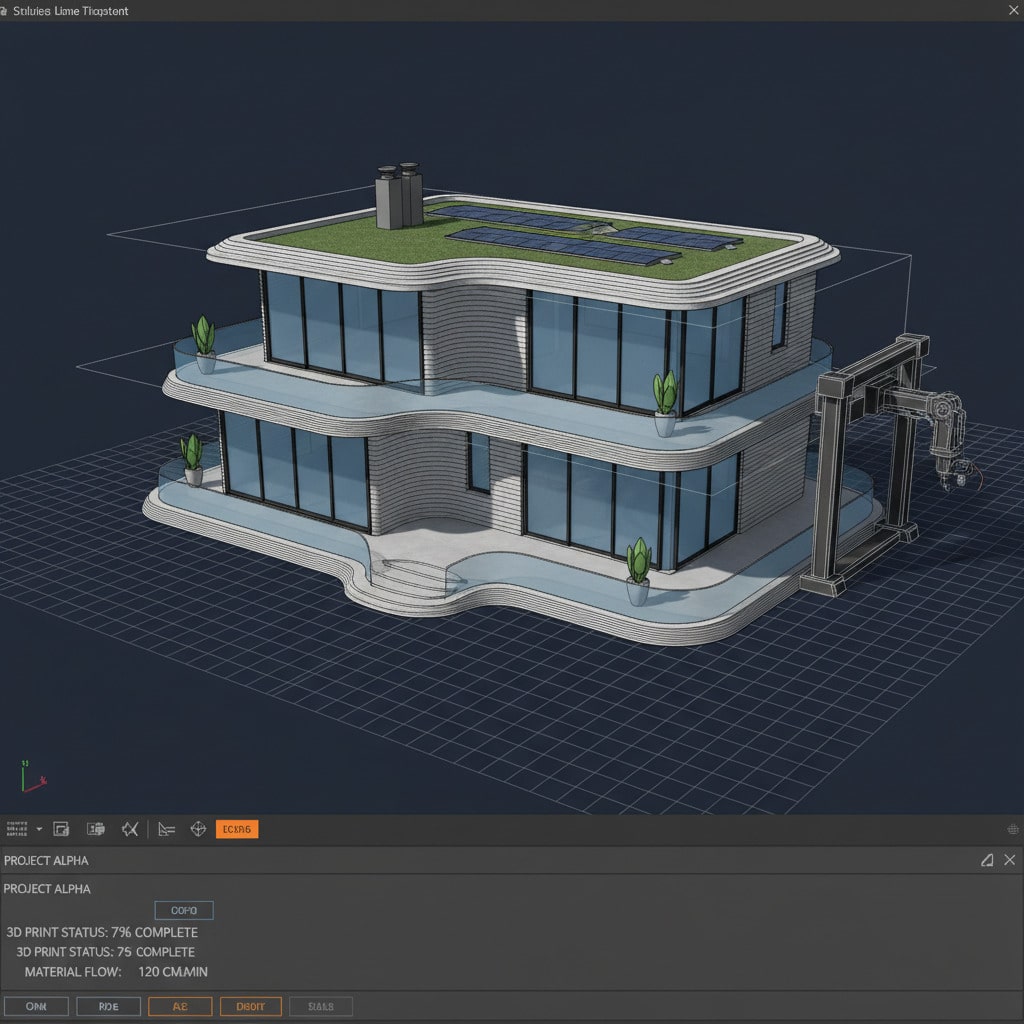
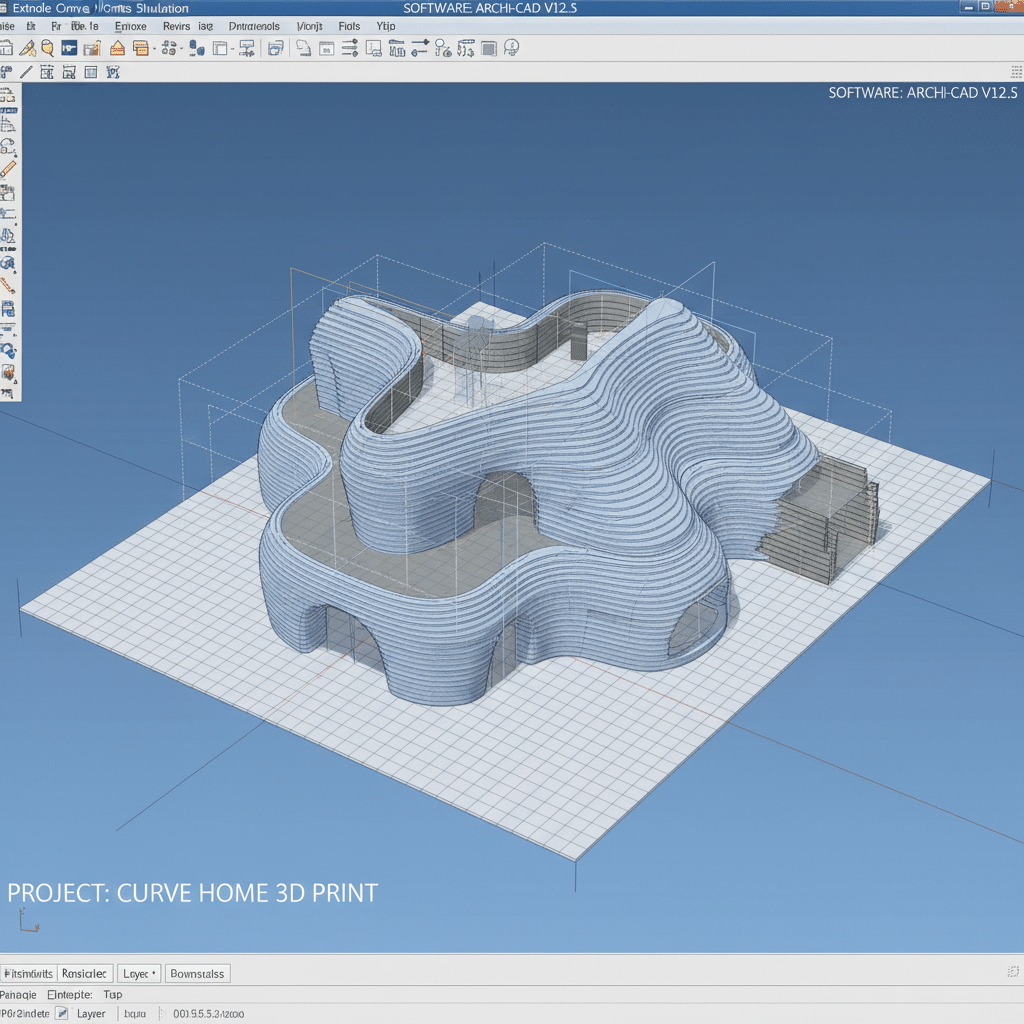
Material Preparation: The Right Mix for the Job
Once the design is ready, the next step involves preparing the “ink” for the giant printer. For most structural applications, this means a specialized concrete mix. However, it’s not your grandmother’s concrete. These mixes are engineered to be highly viscous (thick enough to hold their shape immediately after extrusion) yet flowable enough to pass through the printer’s nozzle smoothly. They often contain additives that control setting time, strength, and durability. This material is loaded into a hopper connected to the printer.
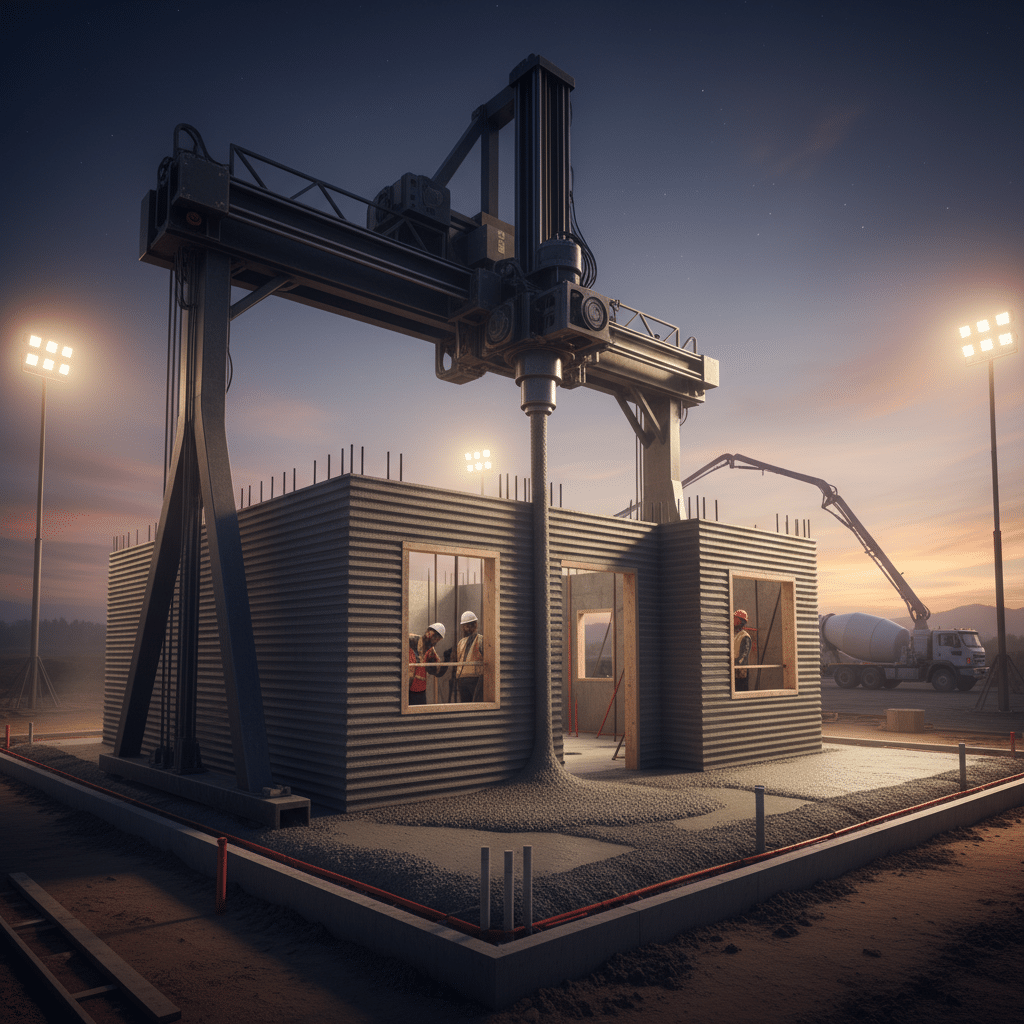
The Printing Process: Layer by Layer Construction
With the design loaded and material ready, the printer gets to work.
- Foundation: Just like traditional homes, 3D printed houses still need a proper foundation. This is usually poured concrete, prepared beforehand to provide a stable base for the printer.
- Extrusion: The robotic arm or gantry system begins to move according to the digital blueprint. The printhead extrudes the concrete mix, laying down continuous beads, one layer at a time. Each layer bonds to the one below it, gradually building up the walls.
- Hollow Walls: Many 3D printed designs feature hollow wall cavities. These can be filled with insulation later, or sometimes rebar (reinforcing steel bars) and concrete are inserted to enhance structural strength, especially in earthquake-prone areas.
- Openings: The printer is programmed to leave precise openings for windows, doors, and utility access points.
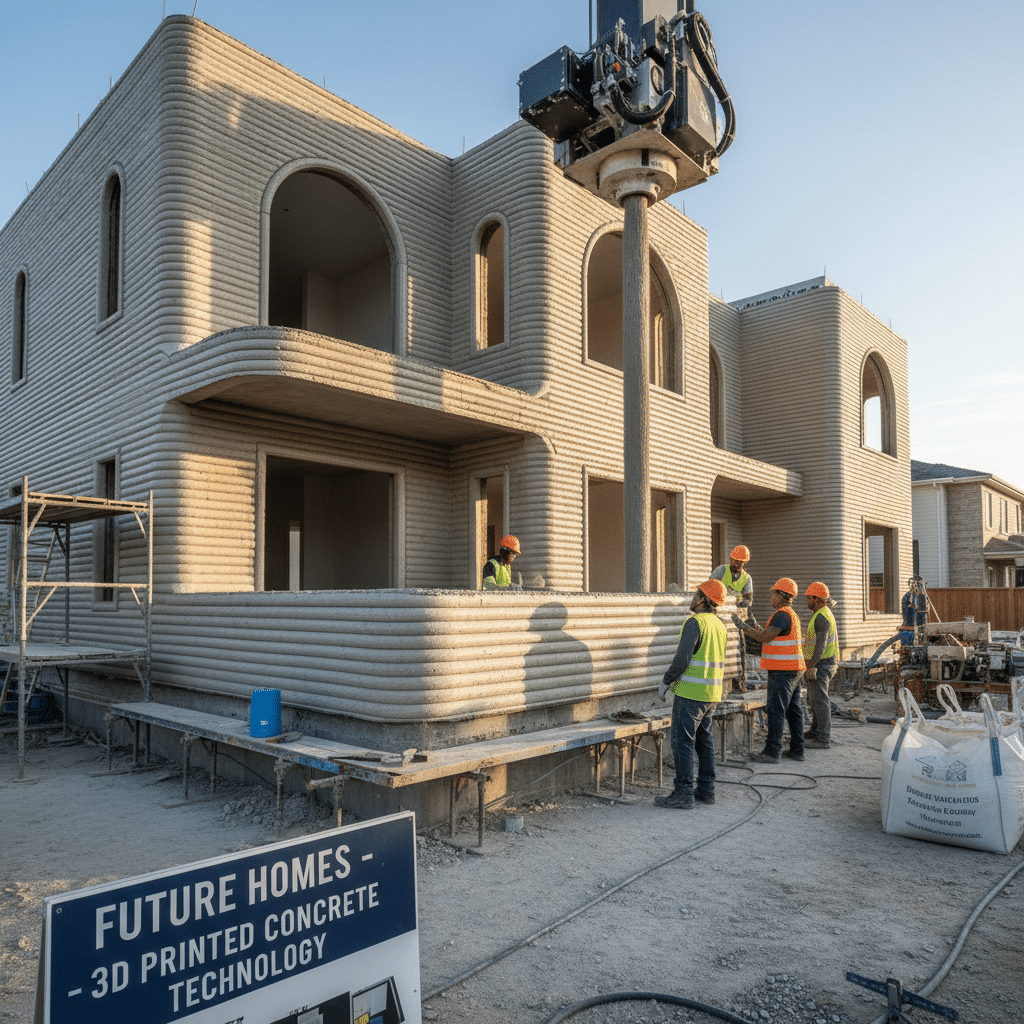
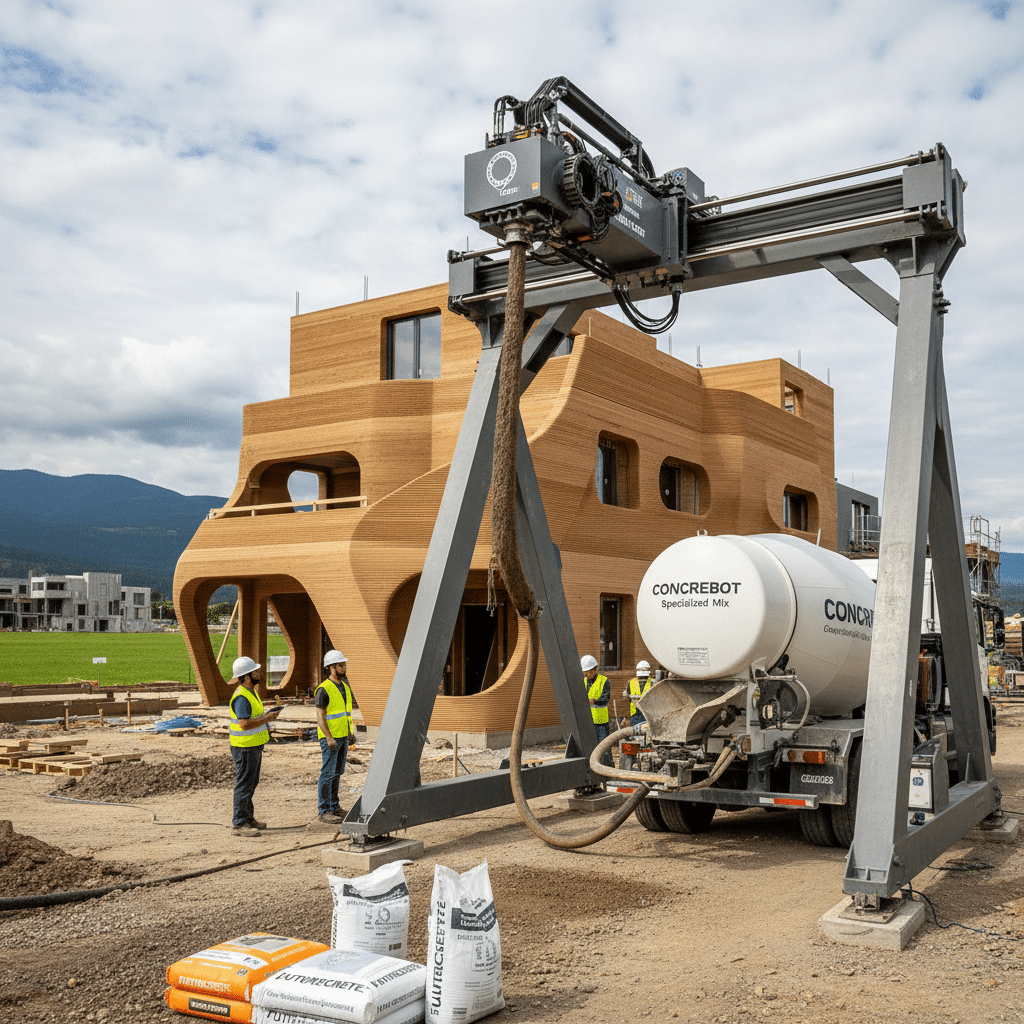
Finishing Touches: Bringing it to Life
While the printer handles the structural walls with impressive speed, a 3D printed house isn’t just “popped out” fully formed. Human craftspeople are still essential for the finishing stages.
- Roofing: Printers primarily build walls. The roof structure (trusses, shingles, etc.) is typically installed using conventional methods.
- Windows and Doors: These are fitted into the pre-printed openings.
- Utilities: Electrical wiring, plumbing, and HVAC systems are integrated into the structure, often routed through the hollow wall cavities. This is where skilled tradespeople really shine, ensuring everything is up to code and functional.
- Interior and Exterior Finishes: Drywall, flooring, paint, cabinets, and exterior cladding are added to personalize the home. Just like any other house, you’ll still need to consider how to improve your wardrobe room or choose the right thermostat for your home.
Key Technologies and Materials Driving Innovation
The world of 3D printed construction is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in both hardware and materials.
The Printers: Giants of the Construction Site
There are two main types of large-scale 3D printers used for buildings:
- Gantry Systems: These printers operate on a fixed frame that spans the entire building footprint. The printhead moves along this gantry, covering the entire area. They are very precise and ideal for single-story or smaller multi-story buildings within their frame.
- Robotic Arm Systems: These are essentially giant industrial robots, similar to those found in automotive factories, but adapted for construction. They have a wider range of motion and can be mounted on tracks to cover larger areas or even print multiple structures. They offer more flexibility in terms of site setup.
Both systems are often equipped with sensors and AI-driven control systems to ensure accuracy, monitor material flow, and even adapt to changing site conditions.
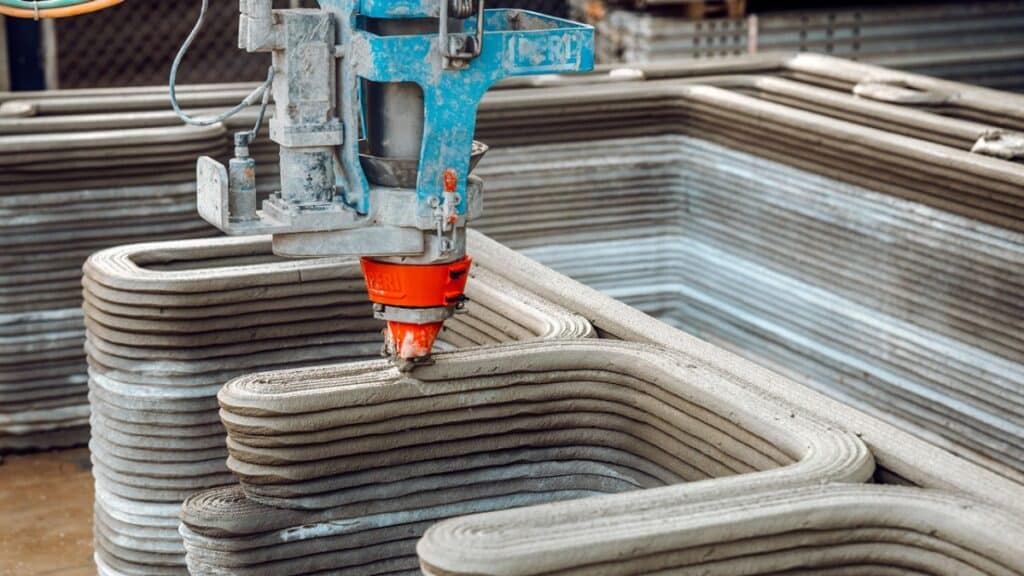

Printable Materials: Beyond Basic Concrete
While specialized concrete mixes are the most common, research and development are constantly pushing the boundaries of what can be printed.
- Geopolymers: These are sustainable alternatives to Portland cement, often made from industrial byproducts like fly ash. They have a lower carbon footprint and can offer excellent strength and durability.
- Mud/Clay Mixes: For ultra-sustainable or off-grid projects, some innovators are experimenting with printing with earth-based materials, returning to ancient building practices with modern technology.
- Polymers and Composites: For non-structural elements or specific applications, advanced polymers and fiber-reinforced composites are being explored for their lightweight properties and strength.
- Insulating Materials: Efforts are underway to develop printable materials that also have inherent insulating properties, simplifying the construction process even further. This fits well with the broader trend of 3D print ideas that are revolutionizing various industries.
Software and Automation: The Brains Behind the Build
The digital backbone is just as important as the physical machinery. Advanced software not only translates designs but also manages the printing process in real-time.
- Algorithmic Design: Designers can use algorithms to generate complex, optimized structures that would be impossible to create manually.
- Process Optimization: Software monitors material consumption, print speed, and environmental factors (like temperature) to ensure optimal results.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze printer performance data to predict potential issues before they cause delays, ensuring smooth operation.
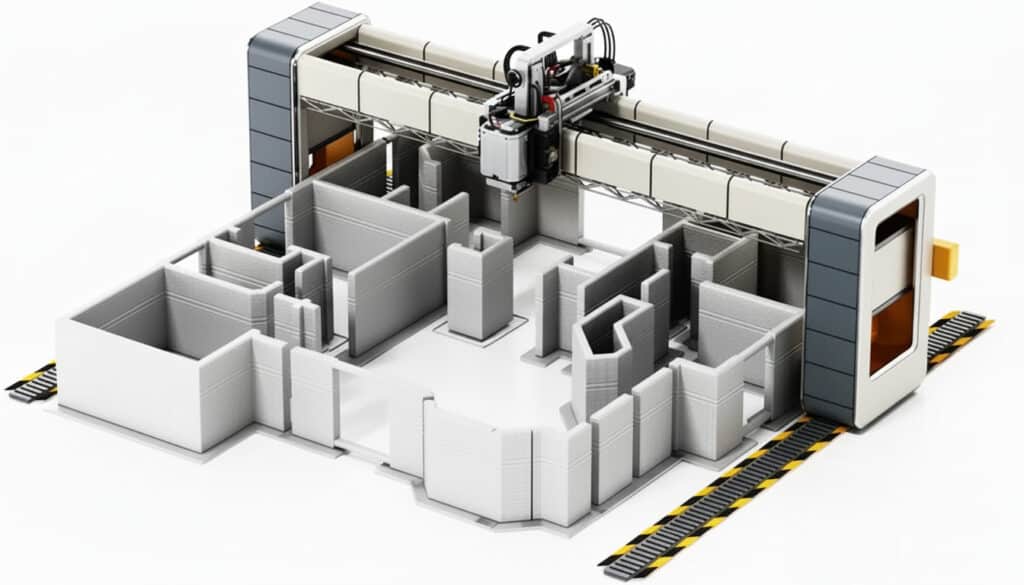
Real-World Examples and Success Stories
The concept of 3D printed houses isn’t just theoretical; it’s happening right now across the globe, with impressive projects demonstrating its viability and potential.
Icon and the Future of Housing
Perhaps one of the most recognized names in the 3D printing construction space is Icon, a Texas-based company. They’ve made headlines for their work on affordable housing initiatives, particularly in partnership with Habitat for Humanity. Icon has printed entire communities of homes, showcasing their ability to scale production. Their homes are known for their durability and speed of construction, offering a robust solution to housing needs. They even collaborated with the military on structures designed for rapid deployment.
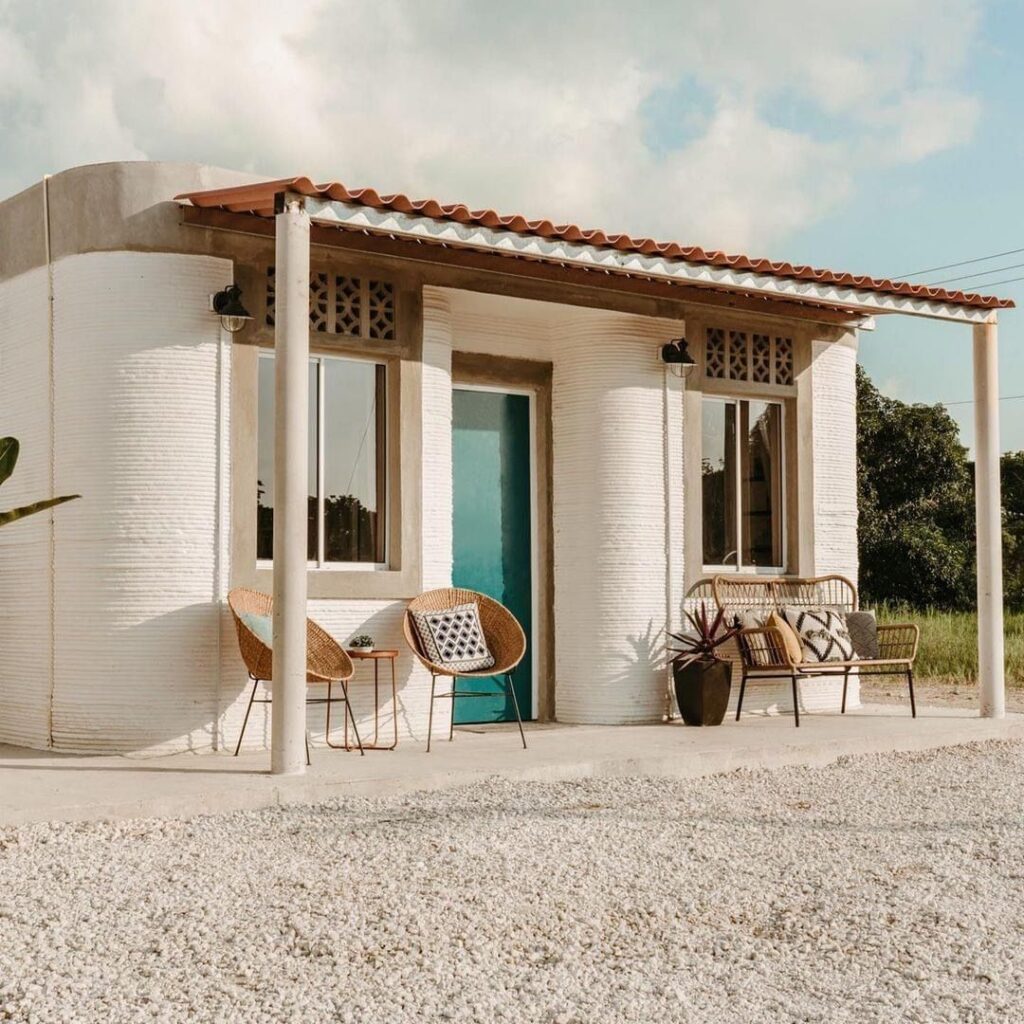
Communities for the Unhoused
In Mexico, Icon partnered with New Story to build a community of 3D printed homes for families living in extreme poverty. These colorful, resilient homes provided a significant upgrade in living conditions, demonstrating the technology’s humanitarian impact. This project highlighted how 3D printing can not only build quickly but also address critical social issues.
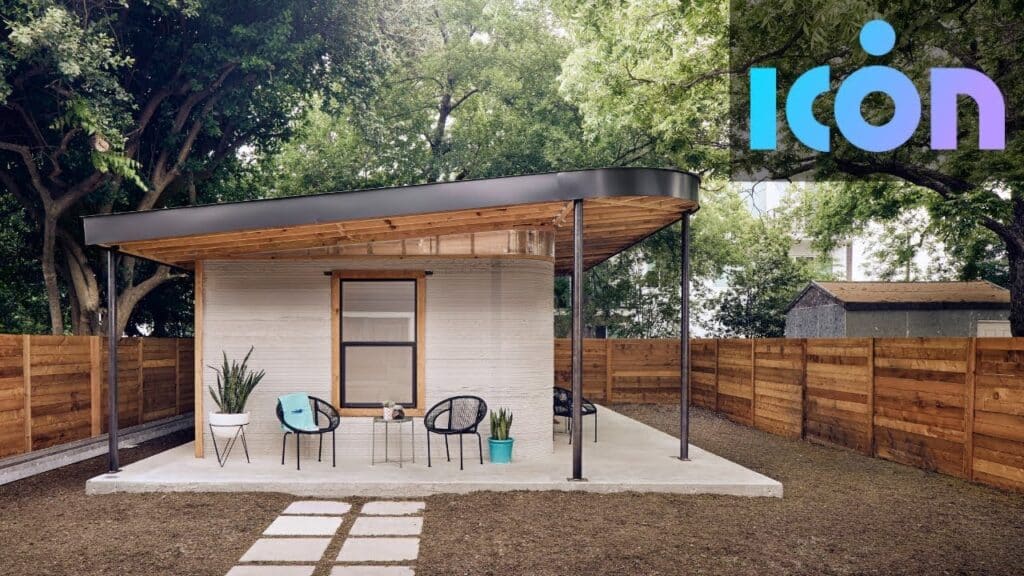

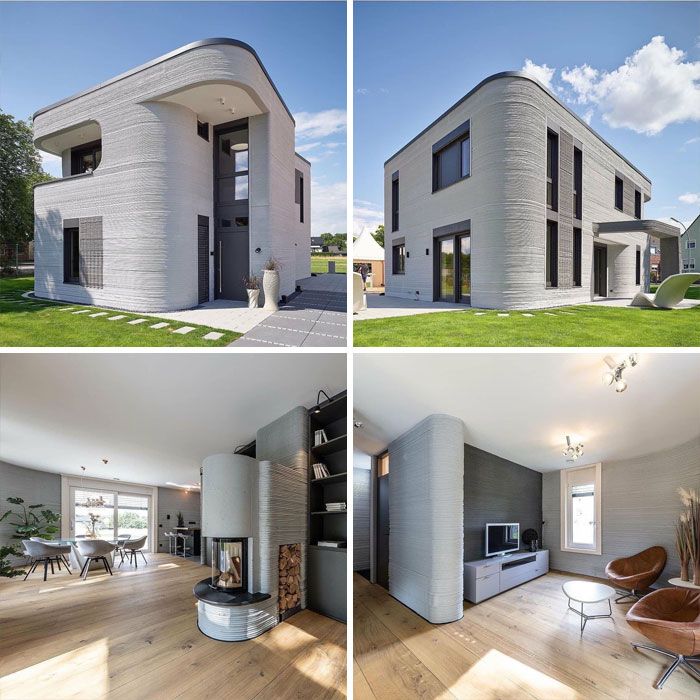
Europe’s Innovative Approaches
Europe is also a hotbed of 3D printed construction. In the Netherlands, Project Milestone saw the development of the world’s first commercially rented 3D printed homes. In Germany, PERI 3D Construction has been involved in printing multi-story residential buildings, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in terms of scale and complexity. These projects often focus on integrating smart home features and sustainable design principles, proving that innovation isn’t limited to a single region.

The Space Frontier
Beyond Earth, 3D printing is being seriously considered for extraterrestrial construction. NASA and other space agencies are exploring how autonomous 3D printers could build habitats on the Moon or Mars using local regolith (soil) as a primary building material. This visionary application highlights the technology’s potential for self-sufficiency and extreme environment construction, far removed from Earth’s traditional supply chains.
Challenges and Considerations
While the future of 3D printed houses looks incredibly bright, it’s not without its hurdles. Like any disruptive technology, there are challenges to overcome before it becomes mainstream.
Regulatory Hurdles and Building Codes
One of the biggest obstacles is navigating existing building codes and regulations. These codes are often designed around traditional construction methods and materials, making it difficult for novel techniques like 3D printing to gain approval. Local authorities and regulatory bodies need to catch up, develop new standards, and create pathways for certification. This often involves rigorous testing and demonstration of structural integrity, safety, and durability. Securing permits and ensuring compliance can be a lengthy process, which means finding the right professional to bring your ideas to life is crucial.
Skilled Labor Integration
While 3D printing reduces the need for some types of manual labor, it doesn’t eliminate human involvement. Instead, it shifts the demand to different skill sets. There’s a growing need for:
- CAD/BIM Specialists: To design and optimize the digital models for printing.
- Printer Operators: To set up, calibrate, and monitor the large-scale printers.
- Robotics Technicians: To maintain and troubleshoot the complex machinery.
- Finishing Trades: Electricians, plumbers, roofers, and interior finishers are still essential for completing the homes and integrating all the necessary systems. The challenge lies in training and upskilling the existing workforce to adapt to these new demands.
Public Perception and Acceptance
For many, the idea of living in a “printed” house might conjure images of flimsy, temporary structures. Overcoming this skepticism and building public trust is vital. Showcasing the durability, aesthetic appeal, and long-term value of 3D printed homes through successful projects and clear communication is key. People need to feel confident that these homes are safe, comfortable, and a sound investment. The novelty factor can be exciting, but long-term acceptance requires reassurance.
Infrastructure and Scaling Up
To truly revolutionize housing, 3D printing needs to move beyond individual projects and scale up to mass production. This requires:
- Standardization: Developing industry-wide standards for materials, printing processes, and quality control.
- Supply Chains: Establishing robust supply chains for specialized printing materials and equipment.
- Investment: Significant investment in research, development, and manufacturing capacity for the printers themselves.
- On-site Logistics: Efficiently managing the deployment of large printers and material delivery to multiple sites.

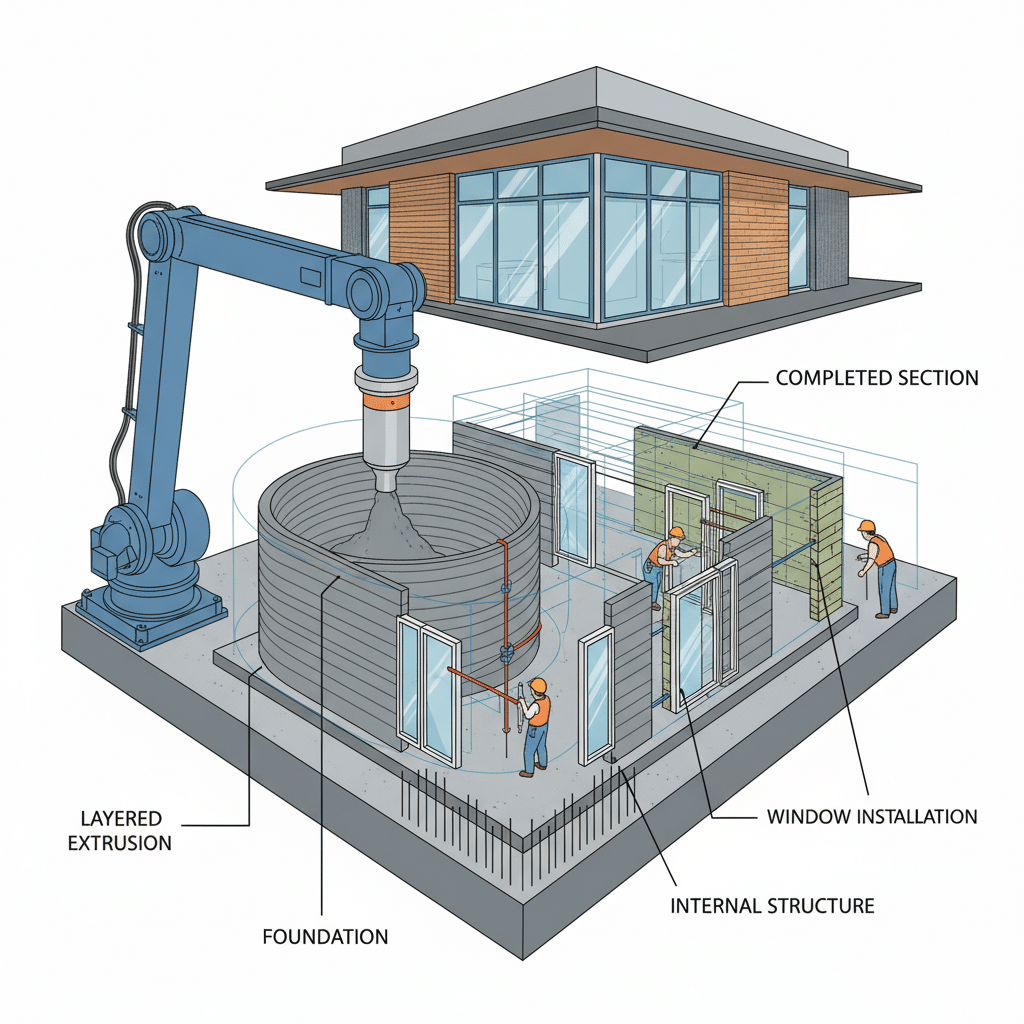
The Future Landscape: What’s Next for 3D Printed Homes?
The trajectory of 3D printed houses is pointing towards an incredibly exciting future, promising even more innovation and integration into our daily lives.
Mass Adoption and Further Cost Reduction
As the technology matures and becomes more widespread, we can expect to see further reductions in construction costs, making 3D printed homes even more accessible. This means not just more communities but also individual homeowners considering these options. Standardized designs and processes will streamline production, bringing the benefits to a broader market.
Off-World Construction
As hinted earlier, the potential for building habitats on the Moon and Mars using 3D printing is a serious area of research. Imagine autonomous robots landing on another planet, collecting local resources, and building a base before humans even arrive. This isn’t science fiction anymore; it’s a legitimate long-term goal for space exploration.
Integration with Smart Home Technology
Future 3D printed homes will likely be smart homes by design. The precision of 3D printing allows for the seamless integration of sensors, wiring, and conduits directly into the walls during the printing process. This means features like smart lighting, climate control, security systems, and even health monitoring could be built-in from day one, rather than added as afterthoughts. Choosing the right thermostat for your home, for instance, might become part of the initial design brief.
Hybrid Construction Models
It’s unlikely that 3D printing will completely replace all traditional construction methods overnight. More probably, we’ll see hybrid models where 3D printing is used for specific components (like complex wall structures) while other elements (such as roofing, plumbing, or intricate interior finishes) are completed using conventional or prefabricated methods. This blend could offer the best of both worlds: speed and design freedom for structural elements, combined with the proven expertise for finishing.
Extreme Personalization
Imagine designing your home on an app, choosing every curve, texture, and built-in furniture piece, then watching it come to life. 3D printing could enable a level of personalization previously unimaginable for mass housing. Each home could be uniquely tailored to the occupant’s needs and aesthetic preferences, without significant additional cost.


Investing in a 3D Printed Home: What to Know
Thinking about getting a 3D printed house for yourself? Here are a few things to keep in mind.
Finding Builders and Developers
The market for 3D printed homes is growing, but it’s still relatively niche. You’ll need to research companies specializing in this technology in your area or region of interest. Look for builders with a proven track record, clear explanations of their materials, and a portfolio of completed projects. Ask about their compliance with local building codes and their warranty offerings.
Financing Options
Traditional mortgage lenders might still be unfamiliar with 3D printed homes. While this is changing rapidly as more projects are completed, you might encounter some initial hurdles. It’s wise to speak with lenders early in the process and provide them with detailed information about the construction method, materials, and any certifications the builder holds. As the market matures, financing will become more straightforward.
Long-Term Value and Maintenance
Currently, 3D printed homes are generally considered highly durable due to the robust nature of the materials used. The monolithic wall structures can be incredibly strong and resistant to environmental factors. Maintenance should be comparable to or even less than traditional homes, particularly regarding the exterior walls. However, as with any home, regular upkeep of the roof, windows, and internal systems will be necessary.
Conclusion
The advent of 3D printed houses isn’t just an interesting technological quirk; it’s a profound shift that promises to reshape the way we think about construction, housing, and even urban development. From its remarkable speed and significant cost reductions to its unprecedented design freedom and potential for environmental sustainability, the benefits are clear and compelling. While challenges like regulatory hurdles and the integration of new labor skills remain, the industry is rapidly innovating to overcome them.
As we look to the future, we can anticipate a world where personalized, affordable, and sustainably built homes are the norm, not the exception. 3D printing is paving the way for solutions to global housing crises and even enabling humanity’s reach to distant planets. So, next time you think about building your dream home, remember that the future might just involve a giant printer bringing your vision to life, layer by precise layer. The foundation for tomorrow’s homes is being laid today, and it’s built with imagination, innovation, and a whole lot of concrete.
- 0shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest0
- Twitter0
- Reddit0



