A car inverter makes it possible to power everyday devices from a vehicle’s battery, turning 12-volt DC into the same type of AC power found at home. To pick the best inverter, a person must match the wattage and features to the devices they plan to use. This simple step prevents overload, protects the battery, and keeps electronics working as intended.
Different inverters serve different needs. Small models handle phones and tablets, while larger ones can run laptops, small appliances, or even power tools. The type of wave output also matters, since sensitive electronics often need a pure sine wave inverter for safe and steady performance.
Safety features, installation choices, and outlet options also play a role in the decision. By understanding wattage, voltage, and design differences, anyone can choose an inverter that fits both their vehicle and their lifestyle.
Key Factors for Choosing the Best Car Inverter
A car inverter must match the devices it powers, the type of current those devices need, and the way it connects to the vehicle. The choice also depends on wattage, voltage, and whether the inverter produces a modified or pure sine wave output.

Types of Car Inverters: Modified vs Pure Sine Wave
There are two main types of inverters: modified sine wave and pure sine wave. Modified sine wave inverters are more affordable and work well with simple electronics like lights, phone chargers, or small tools. However, they may cause noise in audio systems or reduced efficiency in certain appliances.
Pure sine wave inverters produce a smoother and more consistent output. This type matches the power supplied by the electrical grid, which makes it safer for sensitive electronics such as computers, medical equipment, or high-end sound systems.
For drivers who need strong performance, a remote-controlled 5000W car inverter offers both high capacity and convenience. It supports larger appliances while allowing operation from a distance, which is useful in RVs or work vehicles.
Understanding Power Conversion: DC to AC
A car battery provides direct current (DC), but most household electronics rely on alternating current (AC). An inverter bridges this gap by converting DC into AC so devices like laptops, TVs, or small appliances can run off a vehicle’s power.
This conversion process is not 100% efficient. Some energy is lost as heat, which is why inverters often include cooling fans or vents. A higher quality inverter reduces these losses and keeps temperatures stable during use.
In addition, the smoothness of the AC signal affects how well equipment performs. Sensitive devices such as audio systems or medical tools often require a cleaner output. Therefore, understanding the conversion process helps explain why some inverters cost more and why certain models are better suited for demanding electronics.

Determining Your Power Requirements
Before choosing an inverter, it is important to calculate the total wattage of the devices that will run at the same time. A laptop may use 60 watts, a phone charger about 10 watts, and a small TV around 100 watts. Adding these numbers provides the minimum power level needed.
It is best to add a buffer of 20–30% above the total. This margin prevents overload and allows the inverter to handle power spikes that occur when devices start up. Without this headroom, the inverter may shut down or overheat.
Some equipment, such as refrigerators or power tools, can draw more power during startup than during normal operation. Accounting for this surge wattage avoids unexpected shutdowns and protects both the inverter and the devices.
Selecting the Right Wattage and Voltage
Inverters come in a wide range of wattage ratings, from small 150-watt units to large 5000-watt models. The right choice depends on the devices used most often. Small inverters that plug into a cigarette lighter handle phones and laptops, while higher wattage units connect directly to the battery for heavier loads.
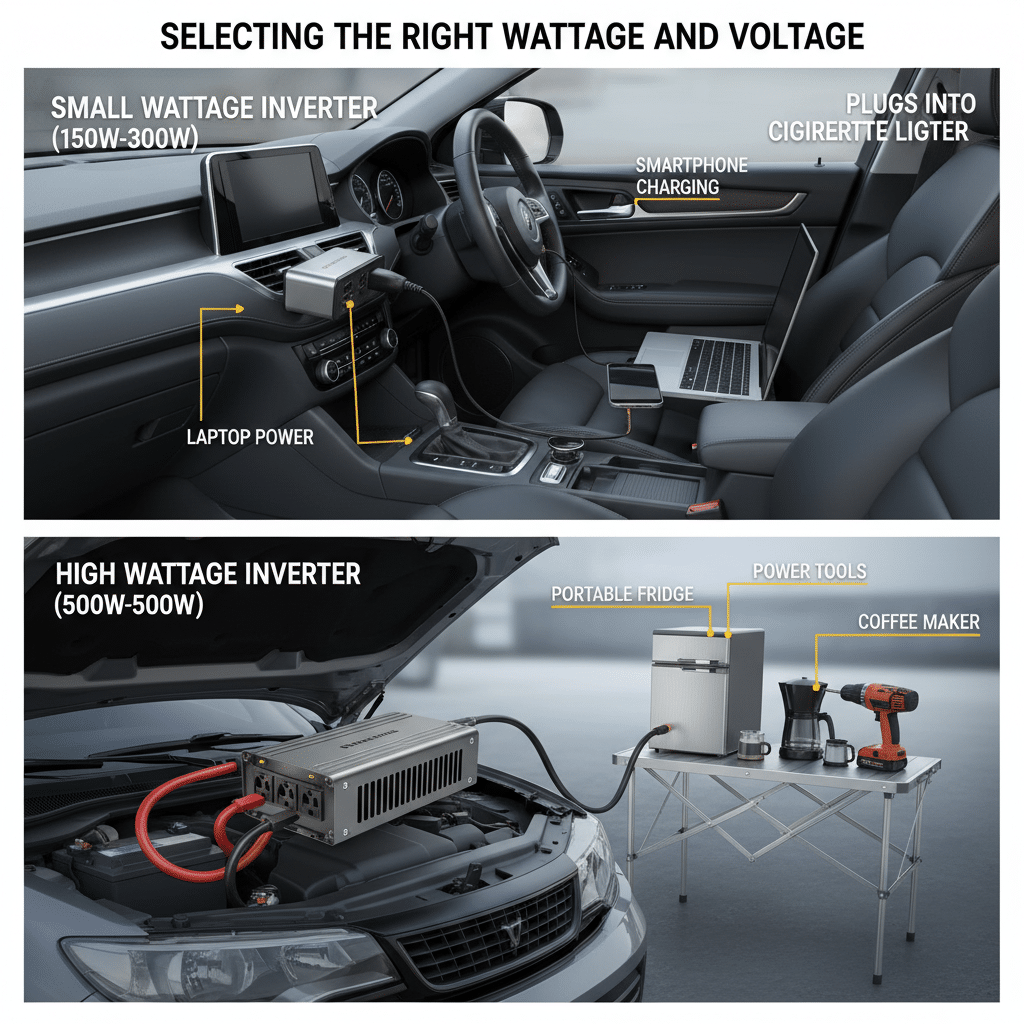

Voltage also matters. Most cars use a 12-volt battery system, but larger trucks or RVs may use 24 volts. Matching the inverter to the vehicle’s battery voltage prevents damage and improves efficiency.
For high-demand setups, such as powering multiple appliances or tools, a large pure sine wave inverter with direct battery connection provides steady performance. Features like digital displays, USB ports, or remote controls add convenience but should come after the main factors of wattage and voltage are addressed.
Basic Features and Installation Considerations
Choosing the right car inverter depends on how it connects to the vehicle, what safety protections it offers, the number and type of ports available, and how it affects the car battery over time. Each of these factors directly impacts performance, convenience, and long-term use.
Connection Methods: Cigarette Lighter vs Direct Battery
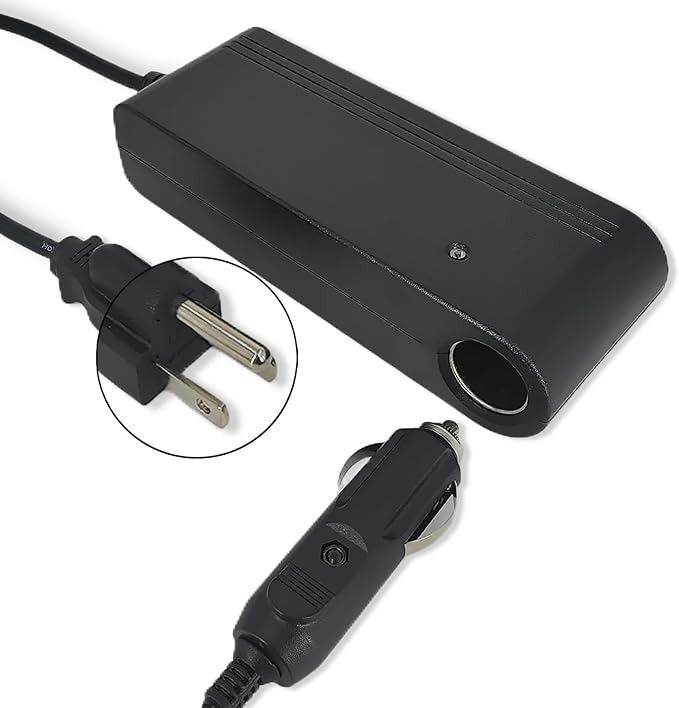

A cigarette lighter connection is the simplest setup. It works well for lower wattage inverters, usually up to about 200–300 watts. This method is best for small devices such as laptops, phone chargers, or cameras. It avoids direct wiring to the car battery, which makes it quick to use but limits power capacity.
A direct battery connection supports higher wattage inverters, often 500 watts or more. This setup uses heavy-duty cables connected straight to the car battery. It can power larger devices like compressors, power tools, or small appliances. However, it requires proper installation, including a fuse near the battery, to prevent damage or fire risk.
The choice depends on the devices a person wants to run. Small electronics work fine with a cigarette lighter plug, but high-demand equipment requires a direct battery connection for safe and steady power.
Safety Features and Overload Protection

A quality inverter includes built-in safety features that protect both the inverter and connected electronics. Overload protection stops the unit from drawing more power than it can handle, which prevents overheating. Short-circuit protection shuts the system down if wiring faults occur, reducing the chance of sparks or fire.
Under-voltage protection keeps the car battery from draining too low. This feature helps preserve enough power to start the engine. Overheat protection uses sensors to shut the inverter off if internal parts reach unsafe temperatures.
These protections not only protect the inverter but also extend the life of devices plugged into it. Without them, sensitive electronics could fail, and the car battery could suffer permanent damage.
Port Options: AC Outlets and USB Ports
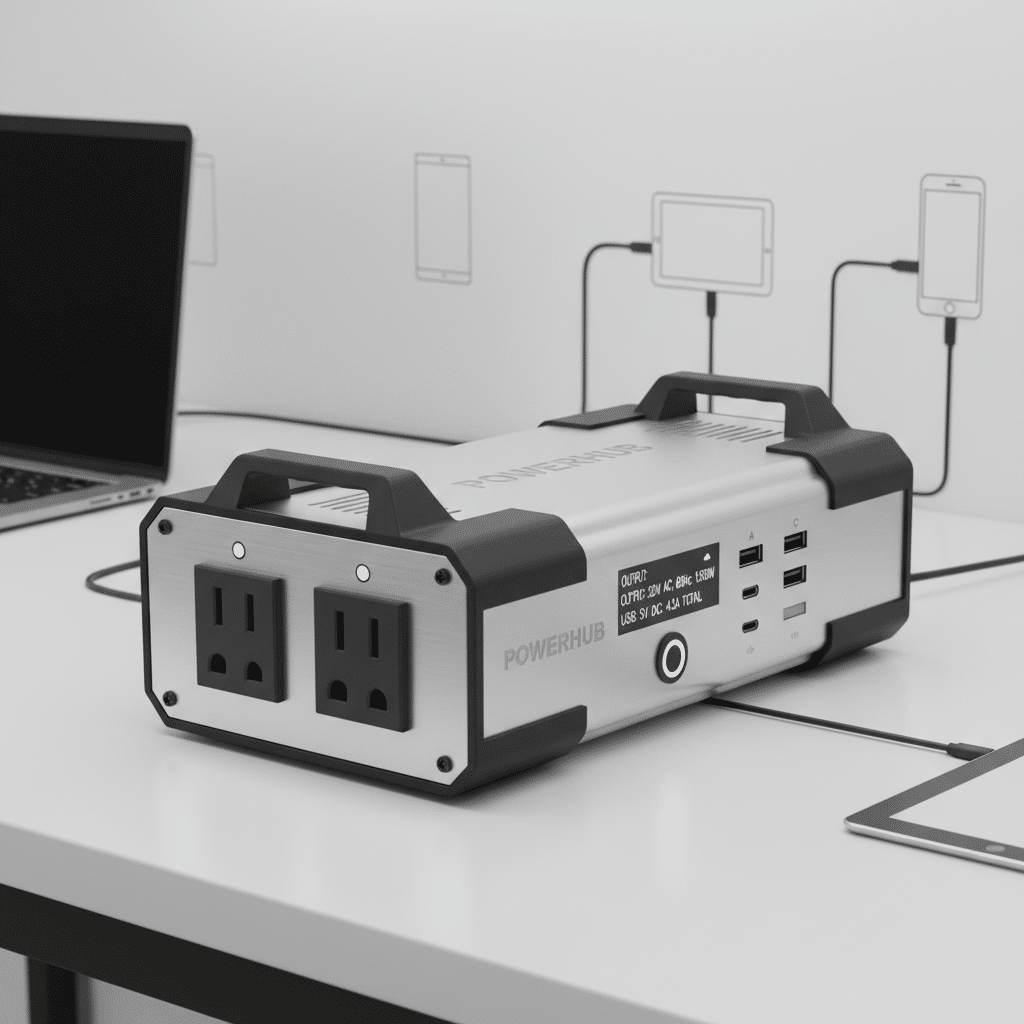
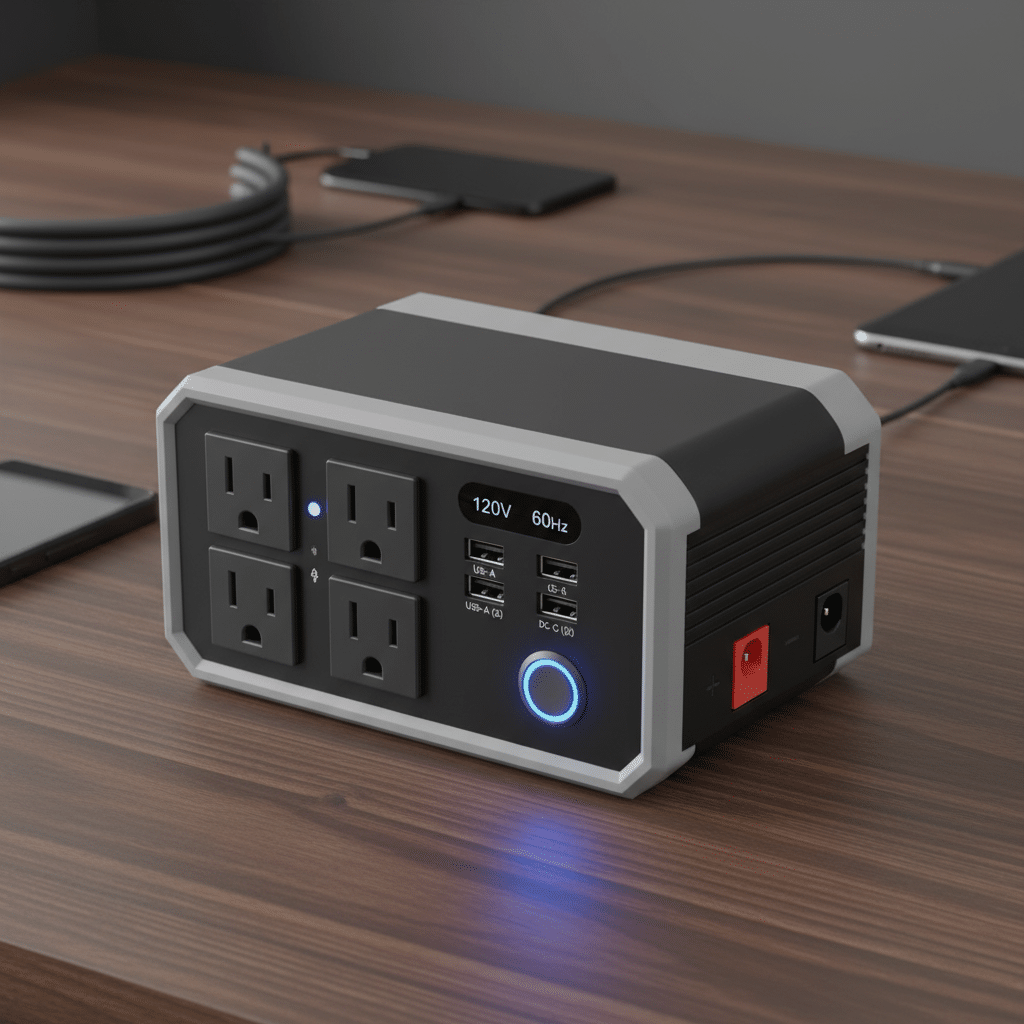


The number and type of ports affect how many devices can be used at once. Most inverters include AC outlets for household-style plugs. Some models offer dual AC outlets, which allow two larger devices to run at the same time.
Many inverters also feature one or more USB ports, which are useful for charging phones, tablets, or other small electronics without adapters. Dual USB ports provide added convenience for families or multiple users.
Choosing the right mix of outlets depends on the intended use. For example, a driver who needs to run a laptop and charge two phones should look for an inverter with at least one AC outlet and dual USB ports.
Battery Power, Drain, and Maintenance

A car inverter draws power directly from the vehicle’s battery. Higher wattage devices require more amps, which increases battery drain. For example, a 500-watt inverter can pull over 40 amps from a 12-volt battery. Using such power for long periods without the engine running may leave the battery too weak to start the car.
To reduce risk, users should monitor battery voltage and avoid leaving heavy loads connected while the vehicle is off. Installing an inline fuse near the battery adds extra protection against sudden surges.
Regular checks of cable connections and inverter ventilation also help maintain safe operation. Proper use keeps the battery healthy and guarantees that the inverter delivers steady power without unnecessary strain.
Conclusion
Choosing the right car inverter depends on matching power needs, device types, and usage habits. A clear look at wattage, surge demands, and battery limits helps avoid problems on the road.
Pure sine wave inverters suit sensitive electronics, while modified sine wave models work for simpler tools and chargers. Each type has benefits, so the choice depends on what devices the user plans to run.
Safety features such as overload shutoff, low voltage protection, and cooling systems add an extra layer of confidence. Build quality and proper installation also make a clear difference in long-term use.
By weighing power capacity, inverter type, and safety design, drivers can select a model that fits both daily convenience and occasional emergencies. This approach keeps devices powered while protecting the vehicle’s electrical system.
- 3shares
- Facebook0
- Pinterest0
- Twitter3
- Reddit0


